在上一篇文章《大模型开发之langchain0.3(一):入门篇》 中已经介绍了langchain开发框架的搭建,最后使用langchain实现了HelloWorld的代码案例,本篇文章将从0到1搭建带有记忆功能的聊天机器人。
一、gradio
我们可以使用gradio“画”出类似于chatgpt官网的聊天界面,gradio的特点就是“快”,不用考虑html怎么写,css样式怎么写,该怎样处理按钮的响应。。这一切都被gradio处理完了,我们只需要使用即可。
gradio官网:https://www.gradio.app/
官网首页上列举了几种典型的gradio使用场景,其中一种正是我们想要的chatbot的使用场景:
找到左下方对应的源码链接,复制到我们的项目:- import time
- import gradio as gr
- # 生成器函数,用于模拟流式输出
- def slow_echo(message, history):
- for i in range(len(message)):
- time.sleep(0.05)
- yield "You typed: " + message[: i + 1]
- demo = gr.ChatInterface(
- slow_echo,
- type="messages",
- flagging_mode="manual",
- flagging_options=["Like", "Spam", "Inappropriate", "Other"],
- save_history=True,
- )
- if __name__ == "__main__":
- demo.launch()
- pip install gradio==5.23.1
根据上一节内容,将大模型的输出给到gradio即可,完整实现代码如下:- import gradio as gr
- from langchain.chat_models import init_chat_model
- model = init_chat_model("gpt-4o", model_provider="openai")
- def do_response(message, history):
- resp = model.invoke(message)
- return resp.content
- demo = gr.ChatInterface(
- do_response,
- type="messages",
- flagging_mode="manual",
- flagging_options=["Like", "Spam", "Inappropriate", "Other"],
- save_history=True,
- )
- if __name__ == "__main__":
- demo.launch()
可以看到,响应时间比较长,足足有十秒钟,在这期间看不到中间的过程,只在最后一次性输出了最终内容,对于用户来说很不友好。
接下来将它改造成流式输出。
优化一:流式输出
想要改造流式输出,首先得大模型支持流式输出,再者改造gradio,让它支持流式输出显示。
关于模型的流式输出文档:https://python.langchain.com/docs/how_to/streaming_llm/
关于gradio的流式输出显示文档:https://www.gradio.app/guides/creating-a-chatbot-fast#streaming-chatbots
简单来说,gradio的流式输出很简单,将do_response方法改造成生成器函数即可- import time
- import gradio as gr
- def slow_echo(message, history):
- for i in range(len(message)):
- time.sleep(0.3)
- yield "You typed: " + message[: i+1]
- gr.ChatInterface(
- fn=slow_echo,
- type="messages"
- ).launch()
- from langchain_openai import OpenAI
- llm = OpenAI(model="gpt-3.5-turbo-instruct", temperature=0, max_tokens=512)
- for chunk in llm.stream("Write me a 1 verse song about sparkling water."):
- print(chunk, end="|", flush=True)
- import gradio as gr
- from langchain.chat_models import init_chat_model
- model = init_chat_model("gpt-4o", model_provider="openai")
- def response(message, history):
- resp = ""
- for chunk in model.stream(message):
- resp = resp + chunk.content
- yield resp
- demo = gr.ChatInterface(
- fn=response,
- type="messages",
- flagging_mode="manual",
- flagging_options=["Like", "Spam", "Inappropriate", "Other"],
- save_history=True,
- )
- if __name__ == '__main__':
- demo.launch()
这样就实现了流式输出。
但是这个程序还有问题:它没有记忆功能,如下所示
接下来对它继续优化,加上记忆功能
优化二:上下文记忆功能
在改造之前,需要先了解几个概念:Chat history、Messages
大模型之所以有记忆功能,是因为每次和大模型对话,都会将历史记录一起送给大模型。
和大模型的交互的过程中,最常见的有三种消息类型:System Message、Human Message、AI Message。
消息类型释义System Message就是开始对话之前对大模型的引导信息,比如“你是一个智能助手,回答用户信息请使用中文”,这样让大模型“扮演”某种角色。Human Message我们提出的问题AI Message大模型响应的问题。这三种消息被langchain封装成了不同的类以方便使用:SystemMessage、HumanMessage、AIMessage
那如何将对话历史记录告诉大模型呢?
答案在于model.stream方法,stream默认我们只传输了一个字符串,也就是用户的提问消息,实际上它的类型是LanguageModelInput
LanguageModelInput的定义如下
Union的意思就是“选择其中之一”的意思,也就是说LanguageModelInput可以是PromptValue、字符串,或者Sequence[MessageLikeRepresentation]任意之一,关键点就在于Sequence[MessageLikeRepresentation],从字面意思上来看它是一个列表类的对象,MessageLikeRepresentation的定义如下,它支持BaseMessage类型
也就是说,可以传递一个BaseMessage类型的List给stream方法,而SystemMessage、HumanMessage、AIMessage 均是BaseMessage的子类。。。一切清晰明了了,可以用一行代码实现gradio历史记录到BaseMessage列表的转换:- h = [HumanMessage(i["content"]) if i["role"] == 'user' else AIMessage(i["content"]) for i in history]
- import gradio as gr
- from langchain.chat_models import init_chat_model
- from langchain_core.messages import HumanMessage, AIMessage
- model = init_chat_model("gpt-4o", model_provider="openai")
- def response(message, history):
- h = [HumanMessage(i["content"]) if i["role"] == 'user' else AIMessage(i["content"]) for i in history]
- h.append(HumanMessage(message))
- resp = ""
- for chunk in model.stream(h):
- resp = resp + chunk.content
- yield resp
- demo = gr.ChatInterface(
- fn=response,
- type="messages",
- flagging_mode="manual",
- flagging_options=["Like", "Spam", "Inappropriate", "Other"],
- save_history=True,
- )
- if __name__ == '__main__':
- demo.launch()
好了,到此,我们用了不到30行代码实现了一个基本的智能聊天机器人,这个程序还有什么问题需要注意的吗?我们思考一下,每次和大模型交互,都要将所有历史记录传递给大模型,这行的通吗?实际上每种大模型都有输入长度的限制,如果不加以限制的话,会很容易超出大模型能够输入字符的上限,接下来改造下这段代码,限制输入的字符数量。
优化三:限制输入长度
关于输入长度过长的优化,实际上是一个比较复杂的问题,可以参考以下官方文档:
Context Window的概念:https://python.langchain.com/docs/concepts/chat_models/#context-window
Memory的概念:https://langchain-ai.github.io/langgraph/concepts/memory/
trim_message的详细用法:https://python.langchain.com/docs/how_to/trim_messages/
trim_message在chatbot中的应用案例:https://python.langchain.com/docs/tutorials/chatbot/#managing-conversation-history
总结一下,用户能输入的字符长度实际上是大模型能“记住”的文本长度,如果过长,就会达到"Context Window"的极限,大模型要么删除一部分文本继续处理,要么直接抛出异常,前者会导致处理数据结果不准确,后者则会导致应用程序直接报错。
可以使用trim_message方法解决该问题,它有各种策略截取过长的输入文本,甚至可以自定义策略。比如以下使用方式:- from langchain_core.messages import trim_messages
- trimmer = trim_messages(
- max_tokens=300,
- strategy="last",
- token_counter=model,
- include_system=True,
- allow_partial=False,
- start_on="human",
- )
完整代码如下所示:- from langchain.chat_models import init_chat_model
- import gradio as gr
- from langchain_core.messages import HumanMessage, AIMessage, trim_messages
- model = init_chat_model("gpt-4o", model_provider="openai")
- trimmer = trim_messages(
- max_tokens=300,
- strategy="last",
- token_counter=model,
- include_system=True,
- allow_partial=False,
- start_on="human",
- )
- def response(message, history):
- h = [HumanMessage(i["content"]) if i["role"] == 'user' else AIMessage(i["content"]) for i in history]
- h.append(HumanMessage(message))
- result = trimmer.invoke(h)
- //查看trim结果
- print(result)
- resp = ""
- for chunk in model.stream(result):
- resp = resp + chunk.content
- yield resp
- demo = gr.ChatInterface(
- fn=response,
- type="messages",
- flagging_mode="manual",
- flagging_options=["Like", "Spam", "Inappropriate", "Other"],
- save_history=True,
- )
- if __name__ == '__main__':
- demo.launch()
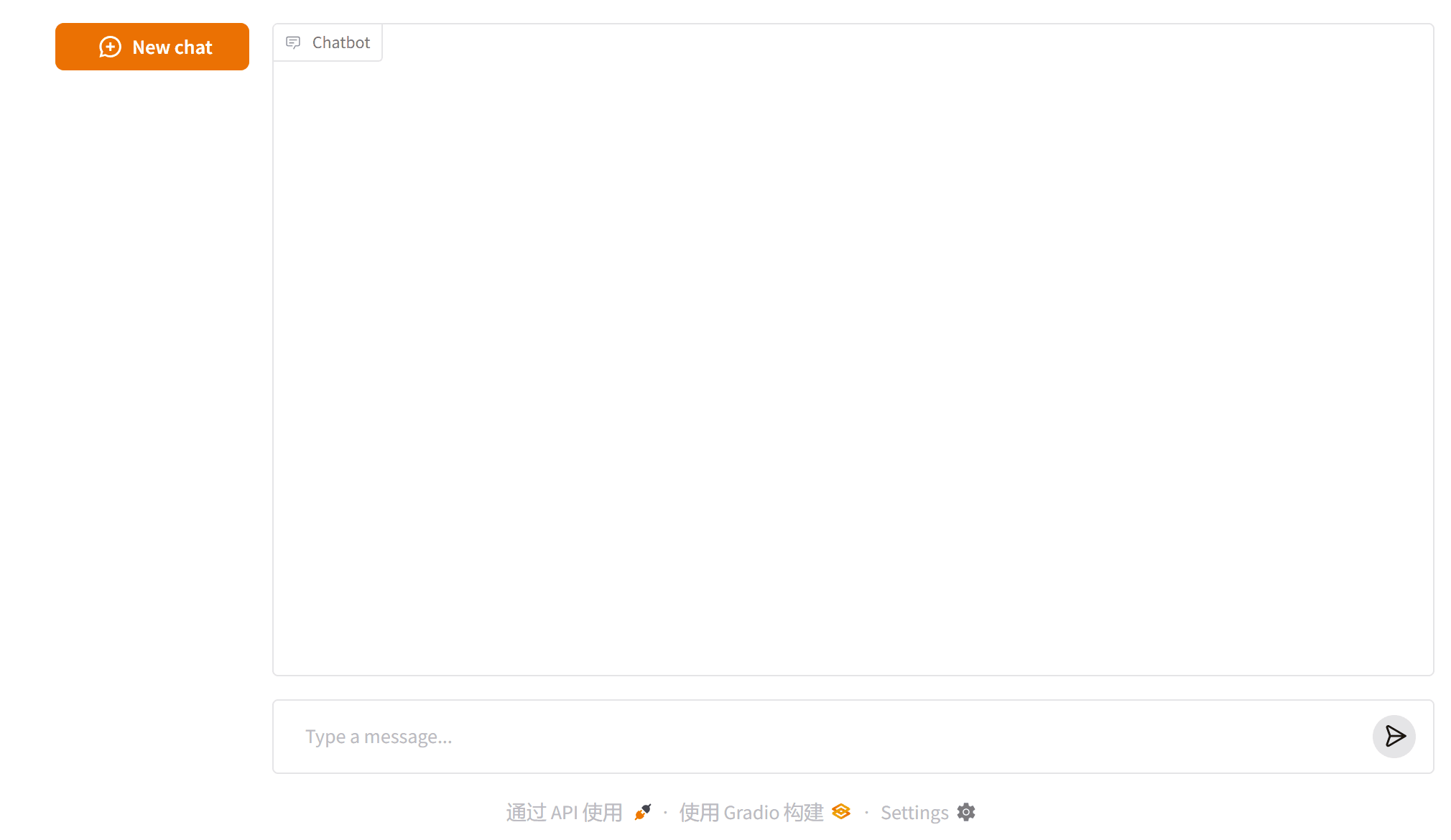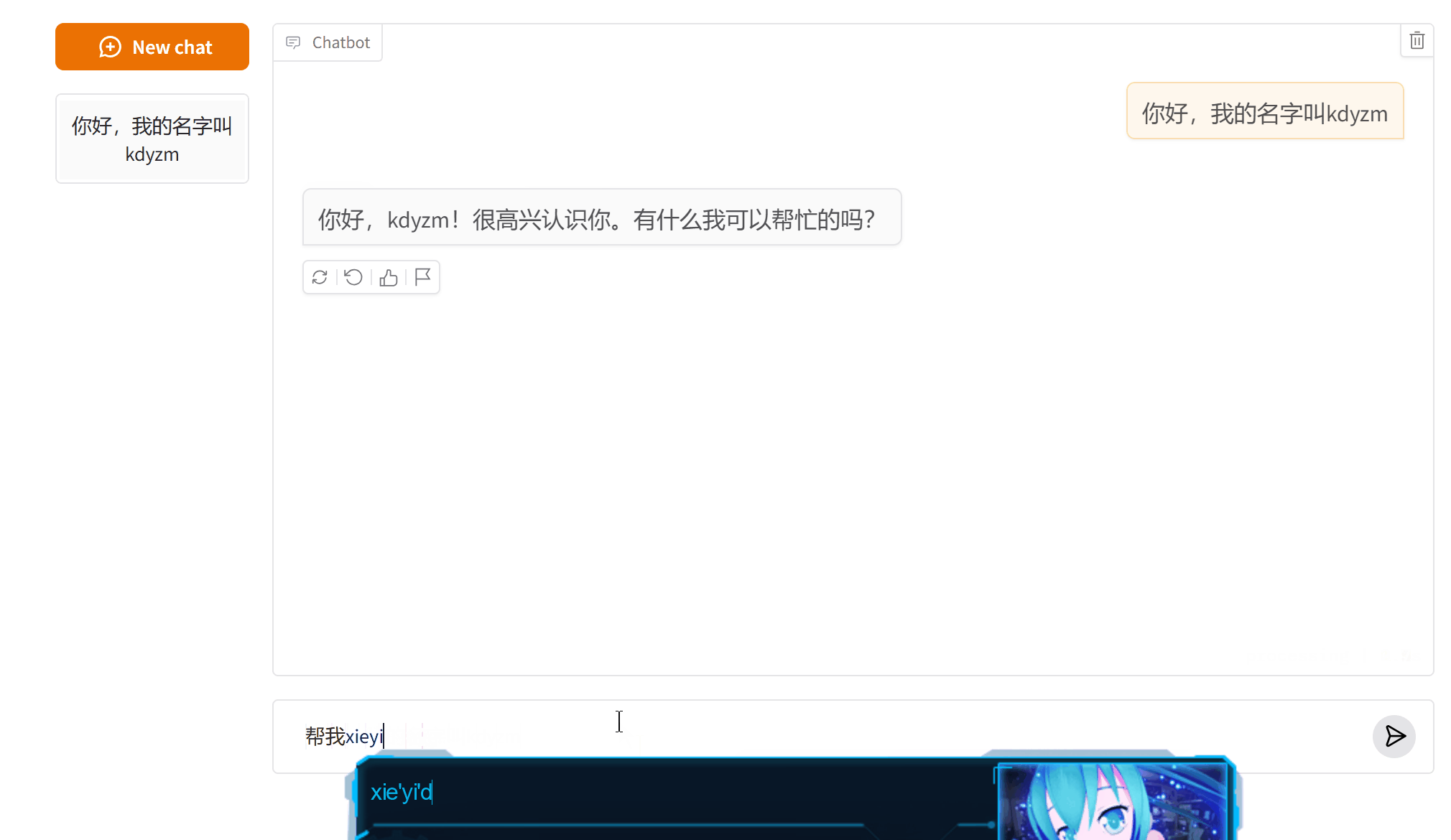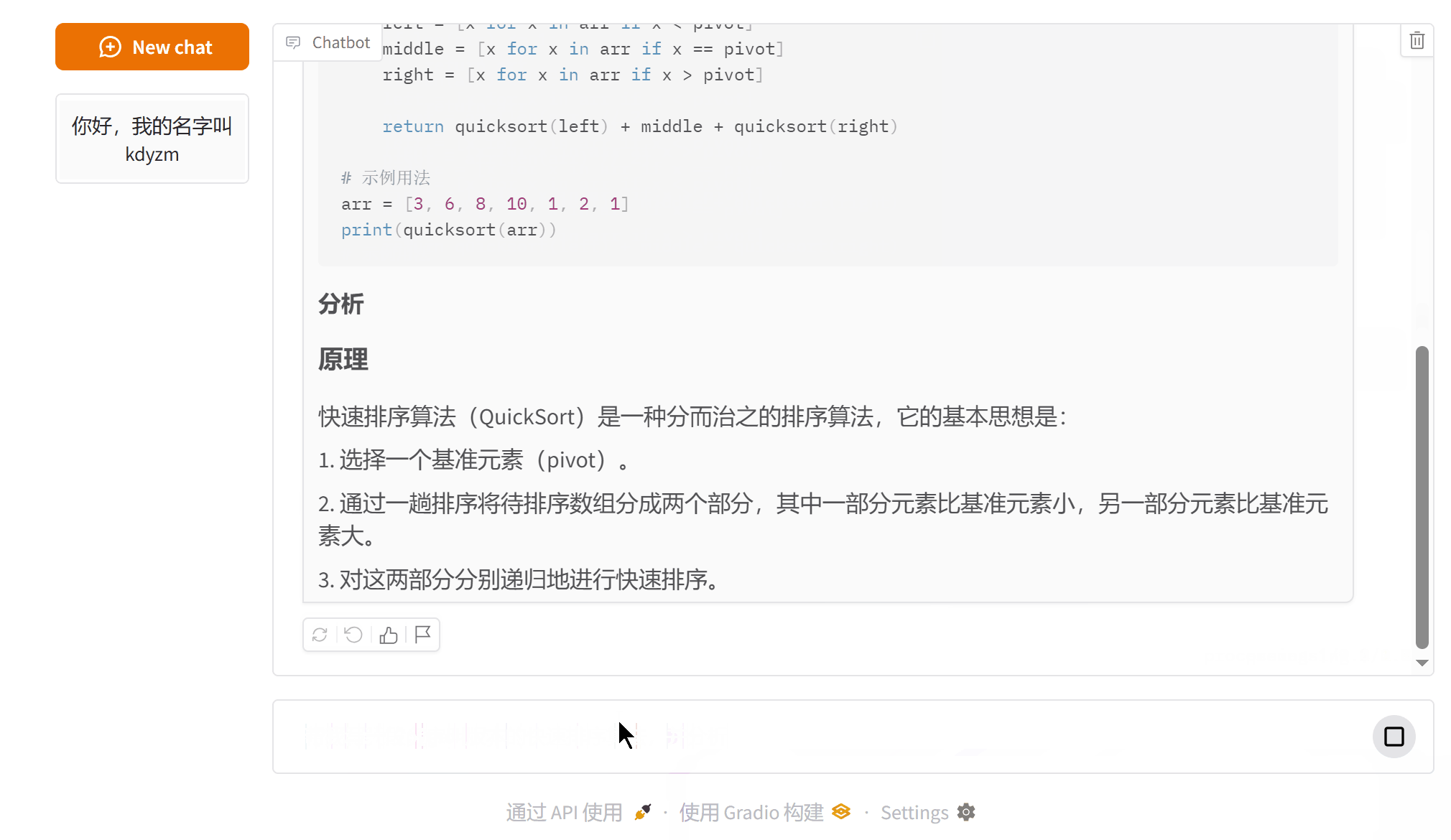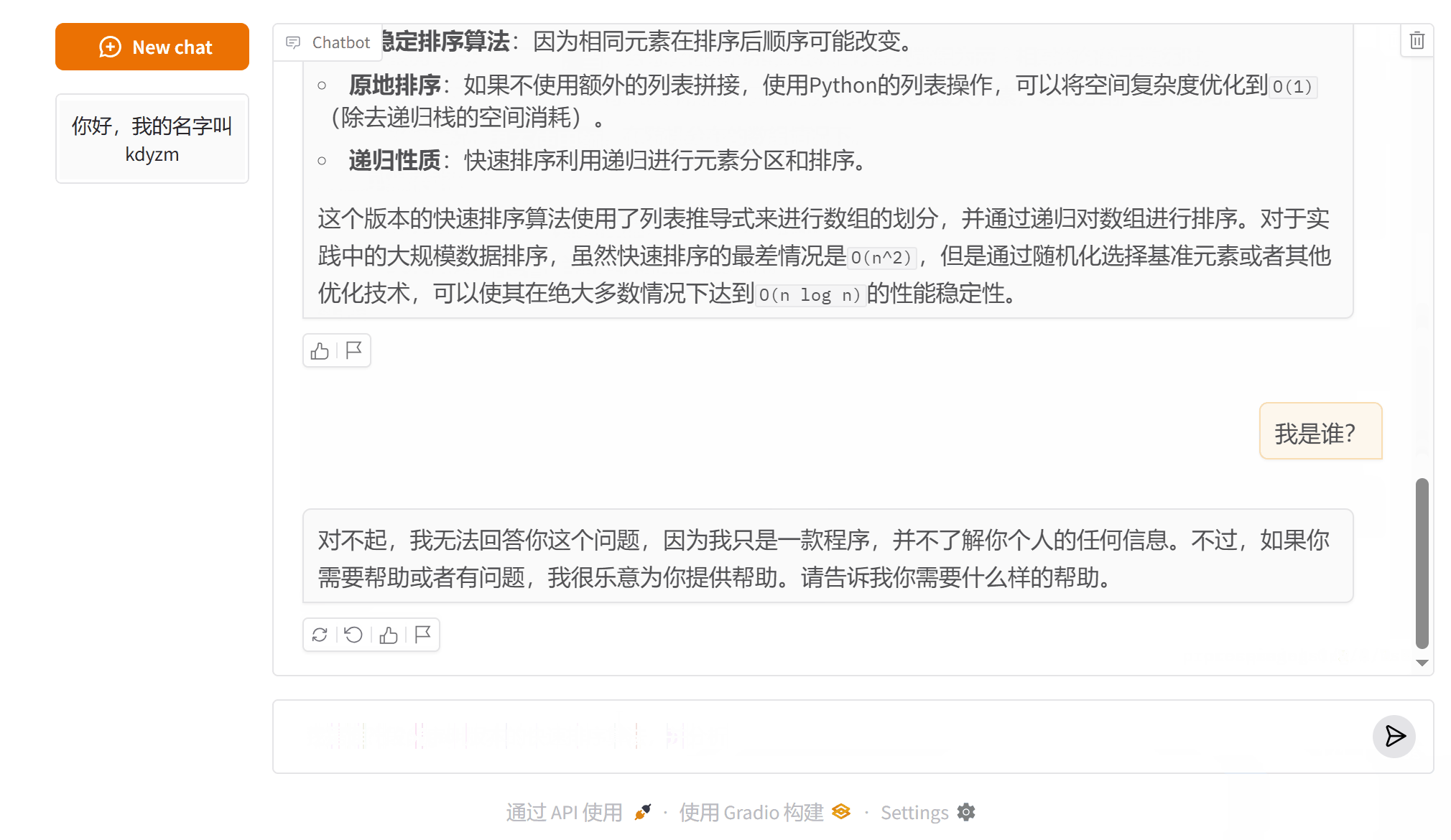
后台打印的被优化的消息:- [HumanMessage(content='你好,我的名字叫kdyzm', additional_kwargs={}, response_metadata={})]
- [HumanMessage(content='你好,我的名字叫kdyzm', additional_kwargs={}, response_metadata={}), AIMessage(content='你好,kdyzm!很高兴认识你。有什么我可以帮忙的吗?', additional_kwargs={}, response_metadata={}), HumanMessage(content='帮我写一段python版本的快速排序算法,并分析', additional_kwargs={}, response_metadata={})]
- [HumanMessage(content='我是谁?', additional_kwargs={}, response_metadata={})]
最后,欢迎关注我的博客呀:一枝梅的博客
END.
来源:程序园用户自行投稿发布,如果侵权,请联系站长删除
免责声明:如果侵犯了您的权益,请联系站长,我们会及时删除侵权内容,谢谢合作! |