1. 简介
1.1 运行环境
- 浏览器是 js 的前端运行环境
- Node.js 是 js 的后端运行环境
- Node.js 中无法调用 DOM 和 BOM 等浏览器内置 API
1.2 Node.js 可以做什么
- 基于 Express 框架可以快速构建 Web 应用
- 基于 Electron 框架可以快速构建跨平台的桌面应用
- 基于 restify 框架可以快速构建 API 接口项目
- 读取和操作数据库,创建实用的命令行工具辅助前端开发
- ...
1.3 安装与运行
- 下载稳定版node.js
- 安装完查看 node.js 的版本
- 创建测试文件,通过命令行运行(需要切换到文件所在目录)
2. fs 文件系统模块
fs 模块是 Node.js 官方提供的用来操作文件的模块,提供了一系列的方法和属性,用来满足用户对文件的操作需求
- 如果要在 js 代码中使用 fs 模块来操作文件,则需要先导入
- const fs = require("fs");
- 使用fs.readFile()读取指定文件中的内容
- fs.readFile(path[, options), callback)
- 参数解读
- path:必选,读取的文件路径(字符串)
- options:可选,以什么编码格式来读取文件,默认指定utf8
- callback:必选,文件读取完成后,通过回调函数拿到读取的失败和成功的结果,err 和 dataObj
- 示例:
- const fs = require("fs");
- fs.readFile("./files/1.txt", "utf-8", function (err, dataObj) {
- // 读取成功,err为null,否则为错误对象。因此能以此进行判断
- if (err) {
- return console.log("文件读取失败!" + err.message);
- }
- // 读取成功的结果,失败则为undefined
- console.log("文件读取成功,内容是:" + dataObj);
- });
2.2 向指定文件中写入内容
- 使用fs.writeFile()向指定文件写入内容
- fs.writeFile(file, data[, options], callback)
- 参数解读
- file:必选,文件存放的路径(字符串)
- data:必选,要写入的内容
- options:可选,以什么格式写入文件内容,默认utf8
- callback:必选,文件写入完成后的回调函数
- 示例
- const fs = require("fs");
- fs.writeFile("F:/files/2.txt", "hello world", function (err) {
- // 写入成功,err为null,否则为错误对象
- if (err) {
- return console.log("写入文件失败!" + err.message);
- }
- console.log("文件写入成功!");
- });
2.3 小练习
- 需求:整理成绩.txt中的数据,并写入成绩-ok.txt
- 源数据与期望格式数据如下:
- const fs = require("fs");
- fs.readFile("./files/成绩.txt", function (err, dataObj) {
- if (err) {
- return console.log("文件读取失败!" + err.message);
- }
- let dataStr = dataObj.toString();
- dataStr = dataStr.replaceAll("=", ":");
- dataStr = dataStr.replaceAll(" ", "\n");
- fs.writeFile("./files/成绩-ok.txt", dataStr, function (err) {
- if (err) {
- return console.log("文件写入失败!" + err.message);
- }
- });
- });
- 在使用 fs 模块操作文件时,如果使用相对路径,很容易出现动态路径拼接错误的问题
- 原因:代码在运行时,会以执行 node 命令所处的目录,动态拼接出被操作文件的完整路径
- 解决
- 提供完整路径:移植性差,不利于维护
- 使用__dirname_ + '/files/data.txt':__dirname表示当前文件所在的目录
- 使用相对路径,并在文件所在目录上一级执行命令
- const fs = require("fs");
- fs.readFile(__dirname + "/files/data.txt", function (err, dataObj) {
- if (err) {
- return console.log("文件读取失败!" + err.message);
- }
- console.log(dataObj.toString());
- });
3. Path 路径模块
path 模块是 Node.js 官方提供的用来处理路径的模块。它提供了一系列的方法和属性,用来满足用户对路径的处理需求
- 如果要在 js 代码中使用 path 模块来处理路径,则需要先导入
- const path = require("path");
- 使用path.join()把多个路径片段拼接为完整的路径字符串
- const fs = require("fs");
- const path = require("path");
- // ../ 会抵消一级路径
- const pathStr = path.join("/a", "/b/c", "../", "./d", "e");
- console.log(pathStr);
- fs.readFile(path.join(__dirname, "/files/data.txt"), function (err, dataObj) {
- if (err) {
- return console.log("文件读取失败!" + err.message);
- }
- console.log(dataObj.toString());
- });
- 注:以后涉及路径拼接的操作,都要用path.join()进行处理,如果直接使用+进行拼接,可能会有问题,如下图所示
3.2 获取路径中的文件名
- 使用path.basename()方法获取路径中的最后一部分,经常用它获取路径中的文件名
- path.basename(path[, ext])
- 参数解读
- path:必选,表示一个路径的字符串
- ext:可选,表示文件扩展名
- 返回值:表示路径中的最后一部分
- 示例
- const path = require("path");
- // 不加第二个参数,会连扩展名一起输出
- const fileName = path.basename("/a/b/c/index.html", ".html");
- console.log(fileName);
3.3 获取路径中的文件扩展名
- 使用path.extname()获取路径中的扩展名
- const path = require("path");
- const extName = path.extname("/a/b/c/index.html");
- console.log(extName);
- 参数解读
- path:必选,表示路径字符串
- 返回值:扩展名字符串
- 示例
- const path = require("path");
- const extName = path.extname("/a/b/c/index.html");
- console.log(extName);
- 需求:将Clock.html拆分为三个文件,clock/index.html、clock/index.js、clock/index.css,并引入 css、js 文件(找一个含 html、css、js 的文件进行练习即可)
- 思路
- 设置正则表达式匹配和中的内容
- 使用 fs 模块读取Clock.html文件
- 编写三个方法处理 css、js、html 内容写入文件中
- 目录结构

- const fs = require("fs");
- const path = require("path");
- // 先设置正则表达式,提取和的内容
- const regStyle = /", "");
- fs.writeFile(path.join(__dirname, "./clock/index.css"), cssStr[0], function (err) {
- if (err) return console.log("文件写入失败!" + cssStr);
- });
- console.log("css文件写入成功!");
- }
- // 处理js
- function resolveJs(htmlStr) {
- const jsStr = regScript.exec(htmlStr);
- jsStr[0] = jsStr[0].replace("", "");
- fs.writeFile(path.join(__dirname, "./clock/index.js"), jsStr[0], function (err) {
- if (err) return console.log("文件写入失败!" + jsStr);
- });
- console.log("js文件写入成功!");
- }
- // 处理html
- function resolveHtml(htmlStr) {
- const newStr = htmlStr
- .replace(regStyle, '<link rel="stylesheet" href="index.css">')
- .replace(regScript, '');
- fs.writeFile(path.join(__dirname, "./clock/index.html"), newStr, function (err) {
- if (err) console.log("文件写入失败!" + err.message);
- console.log("html文件写入成功!");
- });
- }
- 两个注意点
- fs.writeFile()只能用来创建文件,不能用来创建路径
- 重复调用fs.writeFile()写入同一个文件,新写入的内容会覆盖之前的内容
4. http 模块
4.1 简介
http 模块是 Node.js 官方提供的用来创建 web 服务器的模块
- 客户端:在网络节点中,负责消费资源的电脑
- 服务器:负责对外提供网络资源的电脑
- 服务器和普通电脑的区别在于:服务器上安装了 web 服务器软件,如 IIS、Apache 等,通过安装这些服务器软件,就能把一台普通的电脑变成一台 web 服务器
- 在 Node.js 中不需要使用 IIS、Apache 等第三方 web 服务器软件,可以基于 Node.js 提供的 http 模块轻松手写一个服务器软件
4.2 创建最基本的 web 服务器
- const http = require("http");
- 调用http.createServer()创建 web 服务器实例
- const server = http.createServer();
- 为服务器实例绑定request事件,监听客户端的请求
- server.on("request", (req, res) => {
- // 只要有客户端来请求服务器,就会触发request事件,从而调用这个事件处理函数
- console.log("Someone visit our web server.");
- });
- server.listen("8080", () => {
- console.log("http server running at http://127.0.0.1:8080");
- });
4.3 req 请求对象
- 只要服务器收到了客户端的请求,就会调用通过server.on()为服务器绑定的request事件处理函数
- req是请求对象,包含了与客户端相关的数据和属性
- req.url:客户端请求的 url 地址
- req.method:客户端的 method 请求类型
- 示例
- const http = require("http");const server = http.createServer();server.on("request", (req, res) => { console.log(`Your request url is ${req.url}, and request method is ${req.method}`);});server.listen("8080", () => {
- console.log("http server running at http://127.0.0.1:8080");
- });
- res是响应对象,包含与服务器相关的数据和属性
- res.end():向客户端发送指定的内容,并结束本次请求的处理过程
- 示例
- const http = require("http");const server = http.createServer();server.on("request", (req, res) => { const str = `Your request url is ${req.url}, and request method is ${req.method}`; res.end(str);});server.listen("8080", () => {
- console.log("http server running at http://127.0.0.1:8080");
- });
- 通过一些接口测试软件测试一下其他请求方式,此处使用Apifox
4.5 解决中文乱码问题
- 当调用res.end()向客户端发送中文内容时,会出现乱码,此时需要手动设置内容的编码格式
- res.setHeader("Content-Type", "text-html; charset=utf-8");
- const http = require("http");const server = http.createServer();server.on("request", (req, res) => { const str = `您的请求地址是:${req.url},请求方式是:${req.method}`; res.setHeader("Content-Type", "text/html; charset=utf-8"); res.end(str);});server.listen("8080", () => {
- console.log("http server running at http://127.0.0.1:8080");
- });
4.6 小练习
4.6.1 根据不同的 url 响应不同的 html 内容
- 实现步骤
- 获取请求的 url
- 路径为/或/index.html,访问的是首页
- 路径为/about.html,访问的是关于页面
- 其他则显示404 Not Found
- 设置Content-Type响应头,防止中文乱码
- 使用res.end()响应给客户端
- 代码实现
- const http = require("http");const server = http.createServer();server.on("request", (req, res) => { let content = "[size=6]404 Not Found[/size]
- "; console.log(req.url); if (req.url === "/" || req.url === "/index.html") { content = "[size=6]首页[/size]
- "; } else if (req.url === "/about.html") { content = "[size=6]关于[/size]
- "; } res.setHeader("Content-Type", "text/html; charset=utf-8"); res.end(content);});server.listen("8080", () => {
- console.log("http server running at http://127.0.0.1:8080");
- });
- 思路:把文件的实际存放路径,作为每个资源的请求 url 地址
- const http = require("http");const fs = require("fs");const path = require("path");const server = http.createServer();server.on("request", (req, res) => { if (req.url !== "/favicon.ico") { fs.readFile(path.join(__dirname, req.url), function (err, dataObj) { if (err) { return res.end(`[size=6]404 Not Found[/size]
- `); } res.end(dataObj.toString()); }); }});server.listen("8080", () => {
- console.log("http server running at http://127.0.0.1:8080");
- });
- 优化资源请求路径
- 访问/时默认也访问/clock/index.html
- 简化路径输入/clock/index.html --> /index.html
- const http = require("http");const fs = require("fs");const path = require("path");const server = http.createServer();server.on("request", (req, res) => { // 优化资源请求路径 let fpath = ""; if (req.url === "/") { fpath = path.join(__dirname, "./clock/index.html"); } else { fpath = path.join(__dirname, "/clock", req.url); } if (req.url !== "/favicon.ico") { fs.readFile(fpath, function (err, dataObj) { if (err) { return res.end(`[size=6]404 Not Found[/size]
- `); } res.end(dataObj.toString()); }); }});server.listen("8080", () => {
- console.log("http server running at http://127.0.0.1:8080");
- });
5.1 模块化概述
5.1.1 什么是模块化
- 将程序⽂件依据⼀定规则拆分成多个⽂件,这种编码⽅式就是模块化的编码方式
- 拆分出来每个⽂件就是⼀个模块,模块中的数据都是私有的,模块之间互相隔离
- 同时也能通过一些手段,可以把模块内的指定数据“交出去”,供其他模块使用
5.1.2 为什么需要模块化
- 随着应用的复杂度越来越高,其代码量和文件数量都会急剧增加,会逐渐引发以下问题:
- 好处
5.2 有哪些模块化规范
- CommonJS——服务端应用广泛
- AMD(了解)
- CMD(了解)
- ES6 模块化——浏览器端应用广泛
5.3 导入和导出的概念
模块化的核心思想就是:模块之间是隔离的,通过导入和导出进行数据和功能的共享
- 导出(暴露):模块公开其内部的⼀部分(如变量、函数等),使这些内容可以被其他模块使用
- 导入(引入):模块引入和使用其他模块导出的内容,以重用代码和功能
5.4 Node.js 中的模块化
5.4.1 分类
- 根据来源的不同,分为三大类
- 内置模块:如 fs、path、http 等
- 自定义模块:用户创建的每个.js文件都是自定义模块
- 第三方模块:由第三方开发出来的模块,使用前需要提前下载
5.4.2 加载模块
- // 1、加载内置的fs模块
- const fs = require("fs");
- // 2、加载自定义模块,.js后缀可省略
- const custom = require("./custom.js");
- // 3、加载第三方模块
- const moment = require("moment");
- 模块作用域:只能在当前模块内被访问
- 好处:防止全局变量污染问题
- module 对象:每个.js自定义模块中都有一个module对象,里面存储了和当前模块有关的信息
5.5 CommonJS 规范
Node.js 遵循了 CommonJS 模块化规范,CommonJS 规定了模块的特性和各模块之间如何相互依赖
- CommonJS 规定
- 每个模块内部,module 变量代表当前模块
- module 变量是一个对象,其exports属性(即module.exports)是对外的接口
- 加载某个模块,其实就是加载该模块的module.exports属性,require()方法用于加载模块
5.5.1 初步体验
- const name = "尚硅谷";
- const slogan = "让天下没有难学的技术!";
- function getTel() {
- return "010-56253825";
- }
- function getCities() {
- return ["北京", "上海", "深圳", "成都", "武汉", "西安"];
- }
- // 通过给exports对象添加属性的方式,来导出数据
- // 此处不导出getCities
- exports.name = name;
- exports.slogan = slogan;
- exports.getTel = getTel;
- const name = "张三";
- const motto = "相信明天会更好!";
- function getTel() {
- return "13877889900";
- }
- function getHobby() {
- return ["抽烟", "喝酒", "烫头"];
- }
- // 通过给exports对象添加属性的方式,来导出数据
- // 此处不导出getHobby
- exports.name = name;
- exports.motto = motto;
- exports.getTel = getTel;
- // 引入school模块暴露的所有内容
- const school = require("./school.js");
- // 引入student模块暴露的所有内容
- const student = require("./student.js");
- console.log(school);
- console.log(student);
- 在CommonJS标准中,导出数据有两种方式:
- 第一种方式:module.exports = value
- 第二种方式:exports.name = value
- 注:
- 每个模块内部的:this、exports、modules.exports在初始时,都指向同一个空对象,该空对象就是当前模块导出的数据,如下图:
- 无论如何修改导出对象,最终导出的都是module.exports的值
- exports是对module.exports的初始引用,仅为了方便给导出添加属性,所以不能用exports={}的形式导出数据,但是可以用module.exports={}导出数据
- 注:为了防止混乱,建议不要在同一模块中同时使用exports和module.exports
- school.js
- const name = "尚硅谷";
- const slogan = "让天下没有难学的技术!";
- function getTel() {
- return "010-56253825";
- }
- function getCities() {
- return ["北京", "上海", "深圳", "成都", "武汉", "西安"];
- }
- module.exports = { name, slogan, getTel };
- // this.c =789
- // exports = {a:1}
- // exports.b = 2
- // module.exports.c = 3
- // module.exports = {d:4} // 最终导出成功的是这个
- // console.log(this)
- // console.log(exports)
- // console.log(module.exports)
- // console.log(this === exports && exports === module.exports)
- exports.name = name;
- exports.slogan = slogan;
- exports.getTel = getTel;
- 解释
- 一开始module.exports和exports指向同一个空对象
- exports = {a:1}:exports就指向了{a:1}这个新对象,module.exports仍指向空对象
- exports.b = 2:向exports指向的对象添加属性b
- module.exports.c = 3:向module.exports指向的对象添加属性c
- module.exports = {d:4}:module.exports指向了新对象{d:4}
- 无论如何修改导出对象,最终导出的都是module.exports的值
5.5.3 导入数据
在 CJS 模块化标准中,使用内置的 require 函数进行导入数据
- //直接引入模块
- const school = require("./school.js");
- //引入同时解构出要用的数据
- const { name, slogan, getTel } = require("./school.js");
- //引入同时解构+重命名
- const { name: stuName, motto, getTel: stuTel } = require("./student.js");
- 一个 JS 模块在执行时,是被包裹在一个内置函数中执行的,所以每个模块都有自己的作用域,可以通过如下方式验证这一说法:
- console.log(arguments);
- console.log(arguments.callee.toString());
- function (exports, require, module, __filename, __dirname){
- /**************************/
- }
- Node.js 默认是支持 CommonJS 规范的,但浏览器端不支持,所以需要经过编译,步骤如下:
- browserify index.js -o build.js
- 注:index.js 是源文件,build.js 是输出的目标文件
- 第三步:页面中引入使用
- [/code]
- [/list][size=4]5.6 ES6 模块化规范[/size]
- [indent]ES6 模块化规范是一个官方标准的规范,它是在语言标准的层面上实现了模块化功能,是目前最流行的模块化规范,且浏览器与服务端均支持该规范
- [/indent][size=3]5.6.1 初步体验[/size]
- [list]
- [*]school.js
- [/list][code]// 导出name
- export const name = "尚硅谷";
- // 导出slogan
- export const slogan = "让天下没有难学的技术!";
- // 导出getTel
- export function getTel() {
- return "010-56253825";
- }
- function getCities() {
- return ["北京", "上海", "深圳", "成都", "武汉", "西安"];
- }
- export const name = "张三";
- export const motto = "相信明天会更好!";
- export function getTel() {
- return "13877889900";
- }
- function getHobby() {
- return ["抽烟", "喝酒", "烫头"];
- }
- // 引入school模块暴露的所有内容
- import * as school from "./school.js";
- // 引入student模块暴露的所有内容
- import * as student from "./student.js";
- [/code][size=3]5.6.2 Node 中运行 ES6 模块[/size]
- [list]
- [*]Node.js 中运行 ES6 模块代码有两种方式:
- [list]
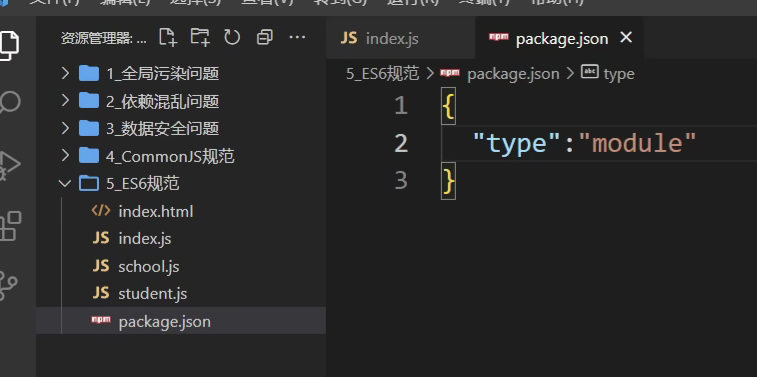
- [*]方式一:将 JavaScript 文件后缀从.js改为.mjs,Node 则会自动识别 ES6 模块
- [*]方式二:在package.json中设置type属性值为module
- [/list]
- [/list][align=center]
 [/align][size=3]5.6.3 导出数据[/size]
[/align][size=3]5.6.3 导出数据[/size] - [indent]ES6 模块化提供 3 种导出方式:① 分别导出、② 统一导出、③ 默认导出
- [/indent]
- [list]
- [*]分别导出
- [/list][code]// 导出name
- export const name = "尚硅谷";
- // 导出slogan
- export const slogan = "让天下没有难学的技术!";
- // 导出getTel
- export function getTel() {
- return "010-56253825";
- }
- const name = "尚硅谷";
- const slogan = "让天下没有难学的技术!";
- function getTel() {
- return "010-56253825";
- }
- function getCities() {
- return ["北京", "上海", "深圳", "成都", "武汉", "西安"];
- }
- // 统一导出了:name、slogan、getTel
- export { name, slogan, getTel };
- const name = "尚硅谷";
- const slogan = "让天下没有难学的技术!";
- function getTel() {
- return "010-56253825";
- }
- function getCities() {
- return ["北京", "上海", "深圳", "成都", "武汉", "西安"];
- }
- //默认导出了:name、slogan、getTel
- export default { name, slogan, getTel };
- // 导出name —— 分别导出
- export const name = "尚硅谷";
- const slogan = "让天下没有难学的技术!";
- function getTel() {
- return "010-56253825";
- }
- function getCities() {
- return ["北京", "上海", "深圳", "成都", "武汉", "西安"];
- }
- // 导出slogan —— 统一导出
- export { slogan };
- // 导出getTel —— 默认导出
- export default getTel;
对于 ES6 模块化来说,使用何种导入方式,要根据导出方式决定
来源:程序园用户自行投稿发布,如果侵权,请联系站长删除
免责声明:如果侵犯了您的权益,请联系站长,我们会及时删除侵权内容,谢谢合作!
|