大纲
1.Seata的Resource资源接口源码
2.Seata数据源连接池代理的实现源码
3.Client向Server发起注册RM的源码
4.Client向Server注册RM时的交互源码
5.数据源连接代理与SQL句柄代理的初始化源码
6.Seata基于SQL句柄代理执行SQL的源码
7.执行SQL语句前取消自动提交事务的源码
8.执行SQL语句前后构建数据镜像的源码
9.构建全局锁的key和UndoLog数据的源码
10.Seata Client发起分支事务注册的源码
11.Seata Server处理分支事务注册请求的源码
12.将UndoLog写入到数据库与提交事务的源码
13.通过全局锁重试策略组件执行事务的提交
14.注册分支事务时获取全局锁的入口源码
15.Seata Server获取全局锁的具体逻辑源码
16.全局锁和分支事务及本地事务总结
17.提交全局事务以及提交各分支事务的源码
18.全局事务回滚的过程源码
1.Seata的Resource资源接口源码
数据源代理DataSourceProxy不仅实现了Seata的Resource资源接口,同时还继承了实现了SeataDataSourceProxy接口的抽象类AbstractDataSourceProxy。
由于SeataDataSourceProxy接口又继承自JDK提供的DataSource接口,所以通过数据源连接池DataSource接口的方法,可以获取数据源的连接。
注意:这里的数据源==数据库。- public class DataSourceProxy extends AbstractDataSourceProxy implements Resource {
- ...
- }
- public abstract class AbstractDataSourceProxy implements SeataDataSourceProxy {
- ...
- }
- public interface SeataDataSourceProxy extends DataSource {
- ...
- }
- public interface DataSource extends CommonDataSource, Wrapper {
- //获取数据源连接
- Connection getConnection() throws SQLException;
- Connection getConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException;
- }
一.getResourceGroupId()方法用来获取资源分组
比如主从节点同属一个分组。
二.getResourceId()方法用来获取数据源ID
比如数据源连接URL可作为数据源ID。
三.getBranchType()方法用来获取分支事务类型
比如类型有:AT、TCC、SAGA、XA。- //Resource that can be managed by Resource Manager and involved into global transaction.
- //资源是由RM资源管理组件来负责管理的
- //RM资源管理器组件会负责把一个个的资源纳入到全局事务里去
- //比如RM可以管理数据库资源,把一个数据库本地事务纳入到全局事务里去
- public interface Resource {
- //Get the resource group id.
- //e.g. master and slave data-source should be with the same resource group id.
- //获取到资源分组ID
- //主从架构的数据源关联到同一个资源分组ID
- //比如MySQL部署了主从架构,主节点和从节点是两个数据源,但是关联到一个分组ID
- String getResourceGroupId();
- //Get the resource id.
- //e.g. url of a data-source could be the id of the db data-source resource.
- //比如数据源连接URL可以作为数据源的ID
- String getResourceId();
- //get resource type, AT, TCC, SAGA and XA
- //branchType表示分支事务类型:AT、TCC、SAGA、XA
- BranchType getBranchType();
- }
2.Seata数据源连接池代理的实现源码
(1)Seata的数据源连接池代理接口SeataDataSourceProxy
(2)Seata的数据源连接池代理抽象类AbstractDataSourceProxy
(3)Seata的数据源连接池代理DataSourceProxy的变量和初始化
(1)Seata的数据源连接池代理接口SeataDataSourceProxy
SeataDataSourceProxy数据源代理在继承DataSource数据源连接池的基础上,增加了两个方法:一个是获取代理的目标数据源连接池的方法,一个是获取代理的目标数据源连接池对应的分支事务类型的方法。- public interface SeataDataSourceProxy extends DataSource {
- //Gets target data source.
- //获取代理的目标数据源连接池
- DataSource getTargetDataSource();
- //Gets branch type.
- //获取代理的目标数据源连接池对应的分支事务类型
- BranchType getBranchType();
- }
AbstractDataSourceProxy抽象类的主要工作是封装代理的目标数据源连接池targetDataSource。- //The type Abstract data source proxy.
- //AbstractDataSourceProxy主要的工作就是:
- //封装了代理的目标数据源连接池targetDataSource
- public abstract class AbstractDataSourceProxy implements SeataDataSourceProxy {
- //The Target data source.
- //代理目标的连接池,可以通过targetDataSource来获取连接
- protected DataSource targetDataSource;
- //Instantiates a new Abstract data source proxy.
- public AbstractDataSourceProxy(){ }
- //Instantiates a new Abstract data source proxy.
- public AbstractDataSourceProxy(DataSource targetDataSource) {
- this.targetDataSource = targetDataSource;
- }
- //Gets target data source.
- @Override
- public DataSource getTargetDataSource() {
- return targetDataSource;
- }
- @Override
- public <T> T unwrap(Class<T> iface) throws SQLException {
- return targetDataSource.unwrap(iface);
- }
- //判断目标连接池targetDataSource是否包装了指定的接口iface
- @Override
- public boolean isWrapperFor(Class<?> iface) throws SQLException {
- return targetDataSource.isWrapperFor(iface);
- }
- @Override
- public PrintWriter getLogWriter() throws SQLException {
- return targetDataSource.getLogWriter();
- }
- @Override
- public void setLogWriter(PrintWriter out) throws SQLException {
- targetDataSource.setLogWriter(out);
- }
- @Override
- public void setLoginTimeout(int seconds) throws SQLException {
- targetDataSource.setLoginTimeout(seconds);
- }
- @Override
- public int getLoginTimeout() throws SQLException {
- return targetDataSource.getLoginTimeout();
- }
- @Override
- public Logger getParentLogger() throws SQLFeatureNotSupportedException {
- return targetDataSource.getParentLogger();
- }
- }
初始化数据源连接池代理DataSourceProxy的具体逻辑是:首先从目标数据库连接池dataSource中获取一个数据库连接,然后根据这个数据库连接Connection去初始化jdbcUrl和dbType,接着根据数据库连接地址jdbcUrl初始化resourceId,然后把当前数据库连接池代理DataSourceProxy作为一个资源注册到默认的RM即DefaultResourceManager里去,最后设置RootContext上下文即线程本地变量副本中的分支事务类型。- public class DataSourceProxy extends AbstractDataSourceProxy implements Resource {
- private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(DataSourceProxy.class);
- //默认资源分组ID
- private static final String DEFAULT_RESOURCE_GROUP_ID = "DEFAULT";
- //Enable the table meta checker,默认是不启用的
- private static boolean ENABLE_TABLE_META_CHECKER_ENABLE = ConfigurationFactory.getInstance().getBoolean(ConfigurationKeys.CLIENT_TABLE_META_CHECK_ENABLE, DEFAULT_CLIENT_TABLE_META_CHECK_ENABLE);
- //Table meta checker interval,默认是60s
- private static final long TABLE_META_CHECKER_INTERVAL = ConfigurationFactory.getInstance().getLong(ConfigurationKeys.CLIENT_TABLE_META_CHECKER_INTERVAL, DEFAULT_TABLE_META_CHECKER_INTERVAL);
- //资源组ID,比如MySQL部署了主从架构,主节点和从节点是两个数据源,但是关联到一个分组ID
- private String resourceGroupId;
- //代理的目标数据源连接url,这个数据源连接url也可以作为resourceId
- private String jdbcUrl;
- //数据源ID,比如数据库连接url就可以作为一个数据源ID
- private String resourceId;
- //数据源类型
- private String dbType;
- //数据源连接用户名
- private String userName;
- //定时调度的线程池,定时检查表里的元数据
- private final ScheduledExecutorService tableMetaExecutor = new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(1, new NamedThreadFactory("tableMetaChecker", 1, true));
- //Instantiates a new Data source proxy.
- public DataSourceProxy(DataSource targetDataSource) {
- this(targetDataSource, DEFAULT_RESOURCE_GROUP_ID);
- }
- //Instantiates a new Data source proxy.
- //@param targetDataSource the target data source
- //@param resourceGroupId the resource group id
- public DataSourceProxy(DataSource targetDataSource, String resourceGroupId) {
- if (targetDataSource instanceof SeataDataSourceProxy) {
- LOGGER.info("Unwrap the target data source, because the type is: {}", targetDataSource.getClass().getName());
- targetDataSource = ((SeataDataSourceProxy) targetDataSource).getTargetDataSource();
- }
- this.targetDataSource = targetDataSource;
- init(targetDataSource, resourceGroupId);
- }
- //初始化数据源连接池代理DataSourceProxy
- private void init(DataSource dataSource, String resourceGroupId) {
- //资源分组ID
- this.resourceGroupId = resourceGroupId;
- //从目标数据库连接池dataSource中,获取一个数据库连接
- try (Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection()) {
- //获取数据库连接connection里的元数据的连接url
- jdbcUrl = connection.getMetaData().getURL();
- //根据连接url获取到数据库类型
- dbType = JdbcUtils.getDbType(jdbcUrl);
- if (JdbcConstants.ORACLE.equals(dbType)) {
- //如果数据库类型等于oracle,则需要获取数据库连接connection的元数据的用户名
- userName = connection.getMetaData().getUserName();
- } else if (JdbcConstants.MARIADB.equals(dbType)) {
- //如果数据库类型等于mariadb,则需要对数据库类型进行赋值为MySQL
- dbType = JdbcConstants.MYSQL;
- }
- } catch (SQLException e) {
- throw new IllegalStateException("can not init dataSource", e);
- }
- //初始化资源ID,也就是获取数据库连接url来初始化resourceID
- initResourceId();
- //把当前数据库连接池代理,作为一个资源,注册到默认的RM里,也就是DefaultResourceManager
- DefaultResourceManager.get().registerResource(this);
- if (ENABLE_TABLE_META_CHECKER_ENABLE) {
- tableMetaExecutor.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> {
- try (Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection()) {
- TableMetaCacheFactory.getTableMetaCache(DataSourceProxy.this.getDbType()).refresh(connection, DataSourceProxy.this.getResourceId());
- } catch (Exception ignore) {
-
- }
- }, 0, TABLE_META_CHECKER_INTERVAL, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
- }
- //Set the default branch type to 'AT' in the RootContext.
- //设置RootContext上下文,即线程本地变量副本中的分支事务类型
- RootContext.setDefaultBranchType(this.getBranchType());
- }
-
- private void initResourceId() {
- if (JdbcConstants.POSTGRESQL.equals(dbType)) {
- initPGResourceId();
- } else if (JdbcConstants.ORACLE.equals(dbType) && userName != null) {
- initDefaultResourceId();
- resourceId = resourceId + "/" + userName;
- } else if (JdbcConstants.MYSQL.equals(dbType)) {
- initMysqlResourceId();
- } else {
- initDefaultResourceId();
- }
- }
-
- private void initMysqlResourceId() {
- String startsWith = "jdbc:mysql:loadbalance://";
- if (jdbcUrl.startsWith(startsWith)) {
- String url;
- if (jdbcUrl.contains("?")) {
- url = jdbcUrl.substring(0, jdbcUrl.indexOf('?'));
- } else {
- url = jdbcUrl;
- }
- resourceId = url.replace(",", "|");
- } else {
- initDefaultResourceId();
- }
- }
- ...
- }
3.Client向Server发起注册RM的源码
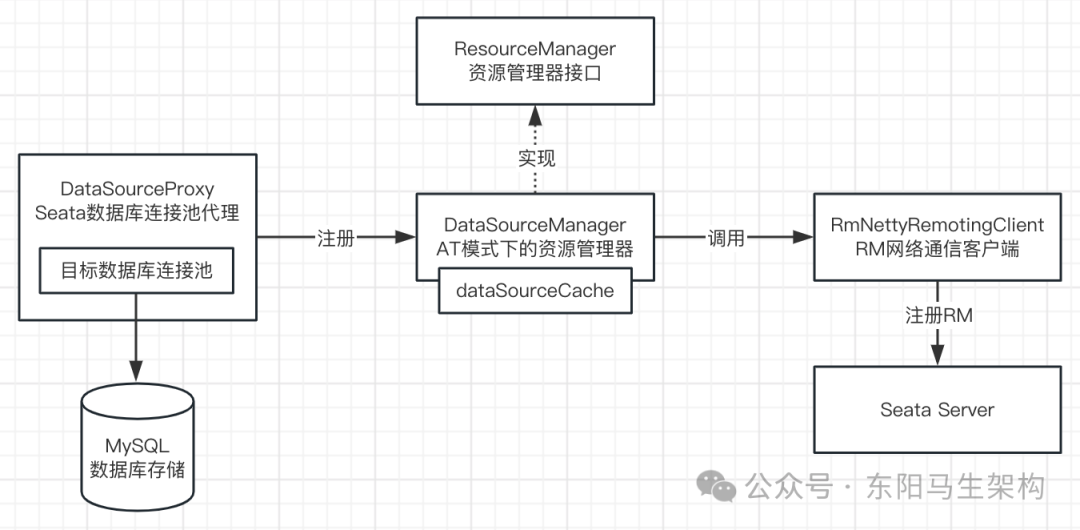
初始化数据源连接池代理DataSourceProxy时,会将数据库连接池代理作为资源,注册到DefaultResourceManager资源管理器中。
而初始化DefaultResourceManager时,会通过SPI机制加载所有的ResourceManager。
因此在执行DataSourceProxy的init()方法进行初始化时,由于会调用DefaultResourceManager的registerResource()方法,所以最后会执行到DataSourceManager的registerResource()方法。
在DataSourceManager的registerResource()方法中,首先会把数据源连接池代理DataSourceProxy放入一个Map中进行缓存,然后通过RmNettyRemotingClient构造一个注册RM的请求把数据源连接池代理DataSourceProxy作为资源注册到Seata Server中。
- public class DefaultResourceManager implements ResourceManager {
- //all resource managers
- protected static Map<BranchType, ResourceManager> resourceManagers = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
-
- private static class SingletonHolder {
- private static DefaultResourceManager INSTANCE = new DefaultResourceManager();
- }
-
- //Get resource manager.
- public static DefaultResourceManager get() {
- return SingletonHolder.INSTANCE;
- }
-
- private DefaultResourceManager() {
- initResourceManagers();
- }
-
- protected void initResourceManagers() {
- //init all resource managers
- //通过SPI加载所有的ResourceManager资源管理器
- //比如:DataSourceManager、TCCResourceManager、SagaResourceManager、ResourceManagerXA
- List<ResourceManager> allResourceManagers = EnhancedServiceLoader.loadAll(ResourceManager.class);
- if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(allResourceManagers)) {
- for (ResourceManager rm : allResourceManagers) {
- resourceManagers.put(rm.getBranchType(), rm);
- }
- }
- }
-
- @Override
- public void registerResource(Resource resource) {
- getResourceManager(resource.getBranchType()).registerResource(resource);
- }
-
- public ResourceManager getResourceManager(BranchType branchType) {
- ResourceManager rm = resourceManagers.get(branchType);
- if (rm == null) {
- throw new FrameworkException("No ResourceManager for BranchType:" + branchType.name());
- }
- return rm;
- }
- ...
- }
- //The type Data source manager.
- //DataSourceManager是AT模式下的资源管理器
- public class DataSourceManager extends AbstractResourceManager {
- //异步化worker
- private final AsyncWorker asyncWorker = new AsyncWorker(this);
- //RM负责管理的一些resource资源
- private final Map<String, Resource> dataSourceCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
- ...
-
- @Override
- public void registerResource(Resource resource) {
- DataSourceProxy dataSourceProxy = (DataSourceProxy) resource;
- //根据资源ID和数据源代理,把数据源连接池代理DataSourceProxy放入到map里去
- dataSourceCache.put(dataSourceProxy.getResourceId(), dataSourceProxy);
- super.registerResource(dataSourceProxy);
- }
- ...
- }
- public abstract class AbstractResourceManager implements ResourceManager {
- ...
- @Override
- public void registerResource(Resource resource) {
- //通过RmNettyRemotingClient把RM注册到Seata Server中
- RmNettyRemotingClient.getInstance().registerResource(resource.getResourceGroupId(), resource.getResourceId());
- }
- ...
- }
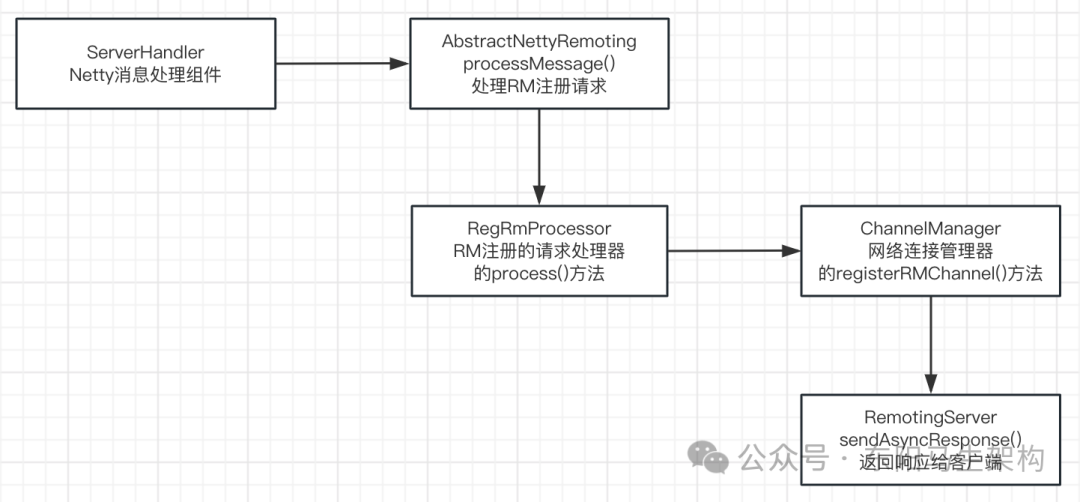
4.Client向Server注册RM时的交互源码
(1)Client异步发送注册RM的请求给Server
(2)Server收到注册RM的请求后的处理及异步响应
(1)Client异步发送注册RM的请求给Server- public final class RmNettyRemotingClient extends AbstractNettyRemotingClient {
- ...
- //Register new db key.
- public void registerResource(String resourceGroupId, String resourceId) {
- //Resource registration cannot be performed until the RM client is initialized
- if (StringUtils.isBlank(transactionServiceGroup)) {
- return;
- }
- if (getClientChannelManager().getChannels().isEmpty()) {
- getClientChannelManager().reconnect(transactionServiceGroup);
- return;
- }
- synchronized (getClientChannelManager().getChannels()) {
- //向每一个Server发起注册
- for (Map.Entry<String, Channel> entry : getClientChannelManager().getChannels().entrySet()) {
- String serverAddress = entry.getKey();
- Channel rmChannel = entry.getValue();
- if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
- LOGGER.info("will register resourceId:{}", resourceId);
- }
- sendRegisterMessage(serverAddress, rmChannel, resourceId);
- }
- }
- }
-
- public void sendRegisterMessage(String serverAddress, Channel channel, String resourceId) {
- RegisterRMRequest message = new RegisterRMRequest(applicationId, transactionServiceGroup);
- message.setResourceIds(resourceId);
- try {
- //异步发送注册RM的请求
- super.sendAsyncRequest(channel, message);
- } catch (FrameworkException e) {
- if (e.getErrcode() == FrameworkErrorCode.ChannelIsNotWritable && serverAddress != null) {
- getClientChannelManager().releaseChannel(channel, serverAddress);
- if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
- LOGGER.info("remove not writable channel:{}", channel);
- }
- } else {
- LOGGER.error("register resource failed, channel:{},resourceId:{}", channel, resourceId, e);
- }
- }
- }
- ...
- }
- public abstract class AbstractNettyRemotingClient extends AbstractNettyRemoting implements RemotingClient {
- ...
- @Override
- public void sendAsyncRequest(Channel channel, Object msg) {
- if (channel == null) {
- LOGGER.warn("sendAsyncRequest nothing, caused by null channel.");
- return;
- }
- RpcMessage rpcMessage = buildRequestMessage(msg, msg instanceof HeartbeatMessage
- ? ProtocolConstants.MSGTYPE_HEARTBEAT_REQUEST
- : ProtocolConstants.MSGTYPE_RESQUEST_ONEWAY);
- if (rpcMessage.getBody() instanceof MergeMessage) {
- mergeMsgMap.put(rpcMessage.getId(), (MergeMessage) rpcMessage.getBody());
- }
- super.sendAsync(channel, rpcMessage);
- }
- ...
- }
- public abstract class AbstractNettyRemoting implements Disposable {
- ...
- //rpc async request.
- protected void sendAsync(Channel channel, RpcMessage rpcMessage) {
- channelWritableCheck(channel, rpcMessage.getBody());
- if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
- LOGGER.debug("write message:" + rpcMessage.getBody() + ", channel:" + channel + ",active?" + channel.isActive() + ",writable?" + channel.isWritable() + ",isopen?" + channel.isOpen());
- }
- doBeforeRpcHooks(ChannelUtil.getAddressFromChannel(channel), rpcMessage);
- channel.writeAndFlush(rpcMessage).addListener((ChannelFutureListener) future -> {
- if (!future.isSuccess()) {
- destroyChannel(future.channel());
- }
- });
- }
- ...
- }
- public abstract class AbstractNettyRemotingServer extends AbstractNettyRemoting implements RemotingServer {
- ...
- @ChannelHandler.Sharable
- class ServerHandler extends ChannelDuplexHandler {
- @Override
- public void channelRead(final ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
- if (!(msg instanceof RpcMessage)) {
- return;
- }
- //接下来调用processMessage()方法对解码完毕的RpcMessage对象进行处理
- processMessage(ctx, (RpcMessage) msg);
- }
- ...
- }
- ...
- }
- public abstract class AbstractNettyRemoting implements Disposable {
- ...
- //Rpc message processing.
- protected void processMessage(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RpcMessage rpcMessage) throws Exception {
- if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
- LOGGER.debug(String.format("%s msgId:%s, body:%s", this, rpcMessage.getId(), rpcMessage.getBody()));
- }
- Object body = rpcMessage.getBody();
- if (body instanceof MessageTypeAware) {
- MessageTypeAware messageTypeAware = (MessageTypeAware) body;
- //根据消息类型获取到一个Pair对象,该Pair对象是由请求处理组件和请求处理线程池组成的
- //processorTable里的内容,是NettyRemotingServer在初始化时,通过调用registerProcessor()方法put进去的
- final Pair<RemotingProcessor, ExecutorService> pair = this.processorTable.get((int) messageTypeAware.getTypeCode());
- if (pair != null) {
- if (pair.getSecond() != null) {
- try {
- pair.getSecond().execute(() -> {
- try {
- pair.getFirst().process(ctx, rpcMessage);
- } catch (Throwable th) {
- LOGGER.error(FrameworkErrorCode.NetDispatch.getErrCode(), th.getMessage(), th);
- } finally {
- MDC.clear();
- }
- });
- } catch (RejectedExecutionException e) {
- ...
- }
- } else {
- try {
- pair.getFirst().process(ctx, rpcMessage);
- } catch (Throwable th) {
- LOGGER.error(FrameworkErrorCode.NetDispatch.getErrCode(), th.getMessage(), th);
- }
- }
- } else {
- LOGGER.error("This message type [{}] has no processor.", messageTypeAware.getTypeCode());
- }
- } else {
- LOGGER.error("This rpcMessage body[{}] is not MessageTypeAware type.", body);
- }
- }
- ...
- }
- public class RegRmProcessor implements RemotingProcessor {
- ...
- @Override
- public void process(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RpcMessage rpcMessage) throws Exception {
- onRegRmMessage(ctx, rpcMessage);
- }
- private void onRegRmMessage(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RpcMessage rpcMessage) {
- RegisterRMRequest message = (RegisterRMRequest) rpcMessage.getBody();
- //获取请求的发送地址
- String ipAndPort = NetUtil.toStringAddress(ctx.channel().remoteAddress());
- boolean isSuccess = false;
- String errorInfo = StringUtils.EMPTY;
- try {
- if (null == checkAuthHandler || checkAuthHandler.regResourceManagerCheckAuth(message)) {
- //通过Channel管理组件ChannelManager,注册RM网络连接
- ChannelManager.registerRMChannel(message, ctx.channel());
- Version.putChannelVersion(ctx.channel(), message.getVersion());
- isSuccess = true;
- if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
- LOGGER.debug("RM checkAuth for client:{},vgroup:{},applicationId:{} is OK", ipAndPort, message.getTransactionServiceGroup(), message.getApplicationId());
- }
- } else {
- if (LOGGER.isWarnEnabled()) {
- LOGGER.warn("RM checkAuth for client:{},vgroup:{},applicationId:{} is FAIL", ipAndPort, message.getTransactionServiceGroup(), message.getApplicationId());
- }
- }
- } catch (Exception exx) {
- isSuccess = false;
- errorInfo = exx.getMessage();
- LOGGER.error("RM register fail, error message:{}", errorInfo);
- }
- RegisterRMResponse response = new RegisterRMResponse(isSuccess);
- if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(errorInfo)) {
- response.setMsg(errorInfo);
- }
- //返回响应给客户端
- remotingServer.sendAsyncResponse(rpcMessage, ctx.channel(), response);
- if (isSuccess && LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
- LOGGER.info("RM register success,message:{},channel:{},client version:{}", message, ctx.channel(), message.getVersion());
- }
- }
- ...
- }
- public class ChannelManager {
- ...
- public static void registerRMChannel(RegisterRMRequest resourceManagerRequest, Channel channel) throws IncompatibleVersionException {
- Version.checkVersion(resourceManagerRequest.getVersion());
- Set<String> dbkeySet = dbKeytoSet(resourceManagerRequest.getResourceIds());
- RpcContext rpcContext;
- if (!IDENTIFIED_CHANNELS.containsKey(channel)) {
- rpcContext = buildChannelHolder(NettyPoolKey.TransactionRole.RMROLE, resourceManagerRequest.getVersion(),
- resourceManagerRequest.getApplicationId(), resourceManagerRequest.getTransactionServiceGroup(),
- resourceManagerRequest.getResourceIds(), channel);
- rpcContext.holdInIdentifiedChannels(IDENTIFIED_CHANNELS);
- } else {
- rpcContext = IDENTIFIED_CHANNELS.get(channel);
- rpcContext.addResources(dbkeySet);
- }
- if (dbkeySet == null || dbkeySet.isEmpty()) {
- return;
- }
- for (String resourceId : dbkeySet) {
- String clientIp;
- ConcurrentMap<Integer, RpcContext> portMap =
- CollectionUtils.computeIfAbsent(RM_CHANNELS, resourceId, key -> new ConcurrentHashMap<>())
- .computeIfAbsent(resourceManagerRequest.getApplicationId(), key -> new ConcurrentHashMap<>())
- .computeIfAbsent(clientIp = ChannelUtil.getClientIpFromChannel(channel), key -> new ConcurrentHashMap<>());
- rpcContext.holdInResourceManagerChannels(resourceId, portMap);
- updateChannelsResource(resourceId, clientIp, resourceManagerRequest.getApplicationId());
- }
- }
- ...
- }
- public abstract class AbstractNettyRemotingServer extends AbstractNettyRemoting implements RemotingServer {
- ...
- @Override
- public void sendAsyncResponse(RpcMessage rpcMessage, Channel channel, Object msg) {
- Channel clientChannel = channel;
- if (!(msg instanceof HeartbeatMessage)) {
- clientChannel = ChannelManager.getSameClientChannel(channel);
- }
- if (clientChannel != null) {
- RpcMessage rpcMsg = buildResponseMessage(rpcMessage, msg, msg instanceof HeartbeatMessage
- ? ProtocolConstants.MSGTYPE_HEARTBEAT_RESPONSE : ProtocolConstants.MSGTYPE_RESPONSE);
- super.sendAsync(clientChannel, rpcMsg);
- } else {
- throw new RuntimeException("channel is error.");
- }
- }
- ...
- }
- public abstract class AbstractNettyRemoting implements Disposable {
- ...
- //rpc async request.
- protected void sendAsync(Channel channel, RpcMessage rpcMessage) {
- channelWritableCheck(channel, rpcMessage.getBody());
- if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
- LOGGER.debug("write message:" + rpcMessage.getBody() + ", channel:" + channel + ",active?" + channel.isActive() + ",writable?" + channel.isWritable() + ",isopen?" + channel.isOpen());
- }
- doBeforeRpcHooks(ChannelUtil.getAddressFromChannel(channel), rpcMessage);
- channel.writeAndFlush(rpcMessage).addListener((ChannelFutureListener) future -> {
- if (!future.isSuccess()) {
- destroyChannel(future.channel());
- }
- });
- }
- ...
- }
5.数据源连接代理与SQL句柄代理的初始化源码
(1)数据库操作的三剑客之连接、句柄和结果
(2)数据源连接代理的初始化
(3)数据源连接代理对SQL进行预编译
(4)SQL句柄代理的初始化
(5)SQL句柄代理执行SQL
(1)数据库操作的三剑客之连接、句柄和结果
Seata Client或者Seata Server进行数据库操作的大致流程如下所示:
- public class LogStoreDataBaseDAO implements LogStore {
- //The Log store data source. 数据源连接池
- protected DataSource logStoreDataSource = null;
- ...
- @Override
- public GlobalTransactionDO queryGlobalTransactionDO(long transactionId) {
- String sql = LogStoreSqlsFactory.getLogStoreSqls(dbType).getQueryGlobalTransactionSQLByTransactionId(globalTable);
- Connection conn = null;//连接
- PreparedStatement ps = null;//句柄
- ResultSet rs = null;//结果
- try {
- //1.从数据源连接池中获取数据源连接
- conn = logStoreDataSource.getConnection();
- conn.setAutoCommit(true);
- //2.对sql语句进行预编译
- ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
- ps.setLong(1, transactionId);
- //3.执行sql语句
- rs = ps.executeQuery();
- if (rs.next()) {
- return convertGlobalTransactionDO(rs);
- } else {
- return null;
- }
- } catch (SQLException e) {
- throw new DataAccessException(e);
- } finally {
- IOUtil.close(rs, ps, conn);
- }
- }
- ...
- }
Seata Client或者Seata Server进行数据库操作时,首先会通过数据库连接池代理DataSourceProxy获取数据库连接,也就是会通过DataSourceProxy的getConnection()方法获取数据源连接代理ConnectionProxy,其中就会根据获取到的一个数据源连接Connection初始化一个数据源连接代理ConnectionProxy。- public class DataSourceProxy extends AbstractDataSourceProxy implements Resource {
- ...
- @Override
- public ConnectionProxy getConnection() throws SQLException {
- //从目标数据源连接池中获取一个数据库连接,然后封装到ConnectionProxy数据源连接代理中,并进行返回
- Connection targetConnection = targetDataSource.getConnection();
- return new ConnectionProxy(this, targetConnection);
- }
- @Override
- public ConnectionProxy getConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException {
- //从目标数据源连接池中获取一个数据库连接,然后封装到ConnectionProxy数据源连接代理中,并进行返回
- Connection targetConnection = targetDataSource.getConnection(username, password);
- return new ConnectionProxy(this, targetConnection);
- }
- ...
- }
- public class ConnectionProxy extends AbstractConnectionProxy {
- //Instantiates a new Connection proxy.
- public ConnectionProxy(DataSourceProxy dataSourceProxy, Connection targetConnection) {
- super(dataSourceProxy, targetConnection);
- }
- ...
- }
- public abstract class AbstractConnectionProxy implements Connection {
- //The Data source proxy. 数据源连接池代理
- protected DataSourceProxy dataSourceProxy;
- //The Target connection. 目标数据源连接
- protected Connection targetConnection;
- //Instantiates a new Abstract connection proxy.
- public AbstractConnectionProxy(DataSourceProxy dataSourceProxy, Connection targetConnection) {
- this.dataSourceProxy = dataSourceProxy;
- this.targetConnection = targetConnection;
- }
- ...
- }
数据源连接代理ConnectionProxy在进行数据库操作时,获取到数据库连接Connection之后,就需要对要执行的SQL进行预编译,也就是会调用AbstractConnectionProxy的prepareStatement()方法。- public abstract class AbstractConnectionProxy implements Connection {
- ...
- //对SQL进行预编译
- @Override
- public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql) throws SQLException {
- String dbType = getDbType();
- //support oracle 10.2+
- PreparedStatement targetPreparedStatement = null;
- //如果是AT模式
- if (BranchType.AT == RootContext.getBranchType()) {
- List<SQLRecognizer> sqlRecognizers = SQLVisitorFactory.get(sql, dbType);
- if (sqlRecognizers != null && sqlRecognizers.size() == 1) {
- SQLRecognizer sqlRecognizer = sqlRecognizers.get(0);
- if (sqlRecognizer != null && sqlRecognizer.getSQLType() == SQLType.INSERT) {
- TableMeta tableMeta = TableMetaCacheFactory.getTableMetaCache(dbType).getTableMeta(
- getTargetConnection(),
- sqlRecognizer.getTableName(), getDataSourceProxy().getResourceId()
- );
- String[] pkNameArray = new String[tableMeta.getPrimaryKeyOnlyName().size()];
- tableMeta.getPrimaryKeyOnlyName().toArray(pkNameArray);
- targetPreparedStatement = getTargetConnection().prepareStatement(sql, pkNameArray);
- }
- }
- }
- if (targetPreparedStatement == null) {
- targetPreparedStatement = getTargetConnection().prepareStatement(sql);
- }
- //返回一个SQL句柄代理
- return new PreparedStatementProxy(this, targetPreparedStatement, sql);
- }
- ...
- }
SQL句柄代理PreparedStatementProxy的初始化主要是设置目标SQL、目标句柄和数据源连接代理。- public class PreparedStatementProxy extends AbstractPreparedStatementProxy implements PreparedStatement, ParametersHolder {
- //Instantiates a new Prepared statement proxy.
- public PreparedStatementProxy(AbstractConnectionProxy connectionProxy, PreparedStatement targetStatement, String targetSQL) throws SQLException {
- super(connectionProxy, targetStatement, targetSQL);
- }
- ...
- }
- public abstract class AbstractPreparedStatementProxy extends StatementProxy<PreparedStatement> implements PreparedStatement {
- protected Map<Integer, ArrayList<Object>> parameters;
-
- private void initParameterHolder() {
- this.parameters = new HashMap<>();
- }
-
- //Instantiates a new Abstract prepared statement proxy.
- public AbstractPreparedStatementProxy(AbstractConnectionProxy connectionProxy, PreparedStatement targetStatement, String targetSQL) throws SQLException {
- super(connectionProxy, targetStatement, targetSQL);
- initParameterHolder();
- }
- ...
- }
- public class StatementProxy<T extends Statement> extends AbstractStatementProxy<T> {
- //Instantiates a new Statement proxy.
- public StatementProxy(AbstractConnectionProxy connectionWrapper, T targetStatement, String targetSQL) throws SQLException {
- super(connectionWrapper, targetStatement, targetSQL);
- }
- ...
- }
- public abstract class AbstractStatementProxy<T extends Statement> implements Statement {
- //The Connection proxy.
- protected AbstractConnectionProxy connectionProxy;
- //The Target statement.
- protected T targetStatement;
- //The Target sql.
- protected String targetSQL;
- ...
- //Instantiates a new Abstract statement proxy.
- public AbstractStatementProxy(AbstractConnectionProxy connectionProxy, T targetStatement, String targetSQL) throws SQLException {
- this.connectionProxy = connectionProxy;
- this.targetStatement = targetStatement;
- this.targetSQL = targetSQL;
- }
- ...
- }
从数据源连接池中获取到数据源连接,以及对SQL语句进行预编译后,就可以调用SQL句柄代理PreparedStatementProxy的executeQuery()等方法执行SQL语句。
6.Seata基于SQL句柄代理执行SQL的源码
(1)Spring的JdbcTemplate操作数据库的三剑客
(2)基于SQL句柄代理执行SQL的流程
(1)Spring的JdbcTemplate操作数据库的三剑客
连接、句柄和结果。- @Disabled
- public class LocalTransactionWithGlobalLockDataSourceBasicTest {
- private static ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context;
- private static JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
-
- @BeforeAll
- public static void before() {
- context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("basic-test-context.xml");
- jdbcTemplate = (JdbcTemplate) context.getBean("jdbcTemplate");
- }
-
- @Test
- public void testInsert() {
- RootContext.bindGlobalLockFlag();
- jdbcTemplate.update("insert into user0 (id, name, gmt) values (?, ?, ?)", new Object[]{2, "xxx", new Date()});
- }
- ...
- }
- public class JdbcTemplate extends JdbcAccessor implements JdbcOperations {
- ...
- @Override
- public int update(String sql, @Nullable Object... args) throws DataAccessException {
- return update(sql, newArgPreparedStatementSetter(args));
- }
-
- @Override
- public int update(String sql, @Nullable PreparedStatementSetter pss) throws DataAccessException {
- return update(new SimplePreparedStatementCreator(sql), pss);
- }
-
- protected int update(final PreparedStatementCreator psc, @Nullable final PreparedStatementSetter pss) throws DataAccessException {
- logger.debug("Executing prepared SQL update");
- return updateCount(execute(psc, ps -> {
- try {
- if (pss != null) {
- pss.setValues(ps);
- }
- //PreparedStatement执行SQL
- int rows = ps.executeUpdate();
- if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
- logger.trace("SQL update affected " + rows + " rows");
- }
- return rows;
- } finally {
- if (pss instanceof ParameterDisposer) {
- ((ParameterDisposer) pss).cleanupParameters();
- }
- }
- }, true));
- }
-
- @Nullable
- private <T> T execute(PreparedStatementCreator psc, PreparedStatementCallback<T> action, boolean closeResources) throws DataAccessException {
- Assert.notNull(psc, "PreparedStatementCreator must not be null");
- Assert.notNull(action, "Callback object must not be null");
- if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
- String sql = getSql(psc);
- logger.debug("Executing prepared SQL statement" + (sql != null ? " [" + sql + "]" : ""));
- }
- //1.获取连接
- Connection con = DataSourceUtils.getConnection(obtainDataSource());
- PreparedStatement ps = null;
- try {
- //2.创建句柄
- ps = psc.createPreparedStatement(con);
- applyStatementSettings(ps);
- //3.执行SQL的结果
- T result = action.doInPreparedStatement(ps);
- handleWarnings(ps);
- return result;
- } catch (SQLException ex) {
- if (psc instanceof ParameterDisposer) {
- ((ParameterDisposer) psc).cleanupParameters();
- }
- String sql = getSql(psc);
- psc = null;
- JdbcUtils.closeStatement(ps);
- ps = null;
- DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection(con, getDataSource());
- con = null;
- throw translateException("PreparedStatementCallback", sql, ex);
- } finally {
- if (closeResources) {
- if (psc instanceof ParameterDisposer) {
- ((ParameterDisposer) psc).cleanupParameters();
- }
- JdbcUtils.closeStatement(ps);
- DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection(con, getDataSource());
- }
- }
- }
- ...
- }
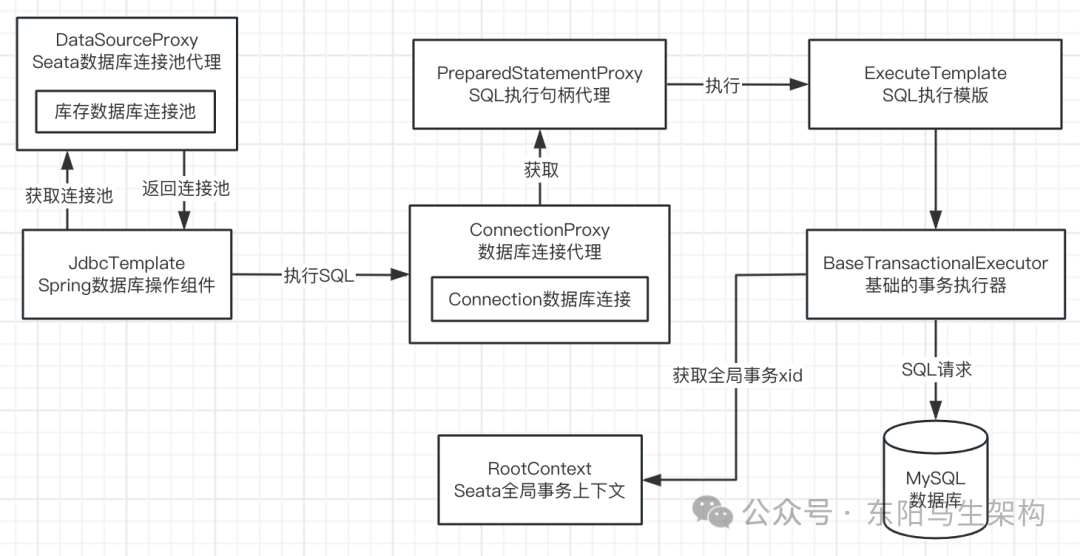
SQL句柄代理PreparedStatementProxy在调用execute()方法执行SQL时,就会调用到ExecuteTemplate执行模版的execute()方法。
而ExecuteTemplate执行模版的execute()方法,如果发现不需要全局锁 + 没有开启全局事务,那么就普通执行本地事务。否则,最终就会调用到BaseTransactionalExecutor的excute()方法。
在BaseTransactionalExecutor的excute()方法中,首先会从线程本地变量副本中获取xid,然后再执行SQL。
- public class PreparedStatementProxy extends AbstractPreparedStatementProxy implements PreparedStatement, ParametersHolder {
- ...
- @Override
- public boolean execute() throws SQLException {
- return ExecuteTemplate.execute(this, (statement, args) -> statement.execute());
- }
-
- @Override
- public ResultSet executeQuery() throws SQLException {
- return ExecuteTemplate.execute(this, (statement, args) -> statement.executeQuery());
- }
-
- @Override
- public int executeUpdate() throws SQLException {
- return ExecuteTemplate.execute(this, (statement, args) -> statement.executeUpdate());
- }
- ...
- }
- public class ExecuteTemplate {
- ...
- public static <T, S extends Statement> T execute(StatementProxy<S> statementProxy, StatementCallback<T, S> statementCallback, Object... args) throws SQLException {
- return execute(null, statementProxy, statementCallback, args);
- }
-
- public static <T, S extends Statement> T execute(List<SQLRecognizer> sqlRecognizers, StatementProxy<S> statementProxy, StatementCallback<T, S> statementCallback, Object... args) throws SQLException {
- //如果发现不需要全局锁,而且没有开启AT模式下的全局事务,那么就普通执行本地事务
- if (!RootContext.requireGlobalLock() && BranchType.AT != RootContext.getBranchType()) {
- //Just work as original statement
- return statementCallback.execute(statementProxy.getTargetStatement(), args);
- }
- //获取到DB的类型
- String dbType = statementProxy.getConnectionProxy().getDbType();
- if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(sqlRecognizers)) {
- sqlRecognizers = SQLVisitorFactory.get(statementProxy.getTargetSQL(), dbType);
- }
- Executor<T> executor;
- if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(sqlRecognizers)) {
- executor = new PlainExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback);
- } else {
- if (sqlRecognizers.size() == 1) {
- SQLRecognizer sqlRecognizer = sqlRecognizers.get(0);
- switch (sqlRecognizer.getSQLType()) {
- case INSERT:
- //通过SPI机制加载InsertExecutor
- executor = EnhancedServiceLoader.load(InsertExecutor.class, dbType, new Class[]{StatementProxy.class, StatementCallback.class, SQLRecognizer.class}, new Object[]{statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizer});
- break;
- case UPDATE:
- executor = new UpdateExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizer);
- break;
- case DELETE:
- executor = new DeleteExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizer);
- break;
- case SELECT_FOR_UPDATE:
- executor = new SelectForUpdateExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizer);
- break;
- case INSERT_ON_DUPLICATE_UPDATE:
- switch (dbType) {
- case JdbcConstants.MYSQL:
- case JdbcConstants.MARIADB:
- executor = new MySQLInsertOrUpdateExecutor(statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizer);
- break;
- default:
- throw new NotSupportYetException(dbType + " not support to INSERT_ON_DUPLICATE_UPDATE");
- }
- break;
- default:
- executor = new PlainExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback);
- break;
- }
- } else {
- executor = new MultiExecutor<>(statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizers);
- }
- }
- T rs;
- try {
- //比如下面最终会调用BaseTransactionalExecutor.excute()方法
- rs = executor.execute(args);
- } catch (Throwable ex) {
- if (!(ex instanceof SQLException)) {
- // Turn other exception into SQLException
- ex = new SQLException(ex);
- }
- throw (SQLException) ex;
- }
- return rs;
- }
- ...
- }
- @LoadLevel(name = JdbcConstants.MYSQL, scope = Scope.PROTOTYPE)
- public class MySQLInsertExecutor extends BaseInsertExecutor implements Defaultable {
- ...
- //Instantiates a new Abstract dml base executor.
- public MySQLInsertExecutor(StatementProxy statementProxy, StatementCallback statementCallback, SQLRecognizer sqlRecognizer) {
- super(statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizer);
- }
- ...
- }
- public abstract class BaseInsertExecutor<T, S extends Statement> extends AbstractDMLBaseExecutor<T, S> implements InsertExecutor<T> {
- ...
- public BaseInsertExecutor(StatementProxy<S> statementProxy, StatementCallback<T, S> statementCallback, SQLRecognizer sqlRecognizer) {
- super(statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizer);
- }
- ...
- }
- public abstract class AbstractDMLBaseExecutor<T, S extends Statement> extends BaseTransactionalExecutor<T, S> {
- ...
- public AbstractDMLBaseExecutor(StatementProxy<S> statementProxy, StatementCallback<T, S> statementCallback, SQLRecognizer sqlRecognizer) {
- super(statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizer);
- }
-
- @Override
- public T doExecute(Object... args) throws Throwable {
- AbstractConnectionProxy connectionProxy = statementProxy.getConnectionProxy();
- //判断是否是自动提交本地事务,默认情况本地事务都是自动提交的,此时需要阻止自动提交
- if (connectionProxy.getAutoCommit()) {
- return executeAutoCommitTrue(args);
- } else {
- return executeAutoCommitFalse(args);
- }
- }
- ...
- }
- public abstract class BaseTransactionalExecutor<T, S extends Statement> implements Executor<T> {
- //The Statement proxy.
- protected StatementProxy<S> statementProxy;
- //The Statement callback.
- protected StatementCallback<T, S> statementCallback;
- //The Sql recognizer.
- protected SQLRecognizer sqlRecognizer;
- ...
- public BaseTransactionalExecutor(StatementProxy<S> statementProxy, StatementCallback<T, S> statementCallback,
- SQLRecognizer sqlRecognizer) {
- this.statementProxy = statementProxy;
- this.statementCallback = statementCallback;
- this.sqlRecognizer = sqlRecognizer;
- }
- ...
- @Override
- public T execute(Object... args) throws Throwable {
- //获取xid
- String xid = RootContext.getXID();
- if (xid != null) {
- statementProxy.getConnectionProxy().bind(xid);
- }
- statementProxy.getConnectionProxy().setGlobalLockRequire(RootContext.requireGlobalLock());
- return doExecute(args);
- }
-
- //Do execute object.
- protected abstract T doExecute(Object... args) throws Throwable;
- ...
- }
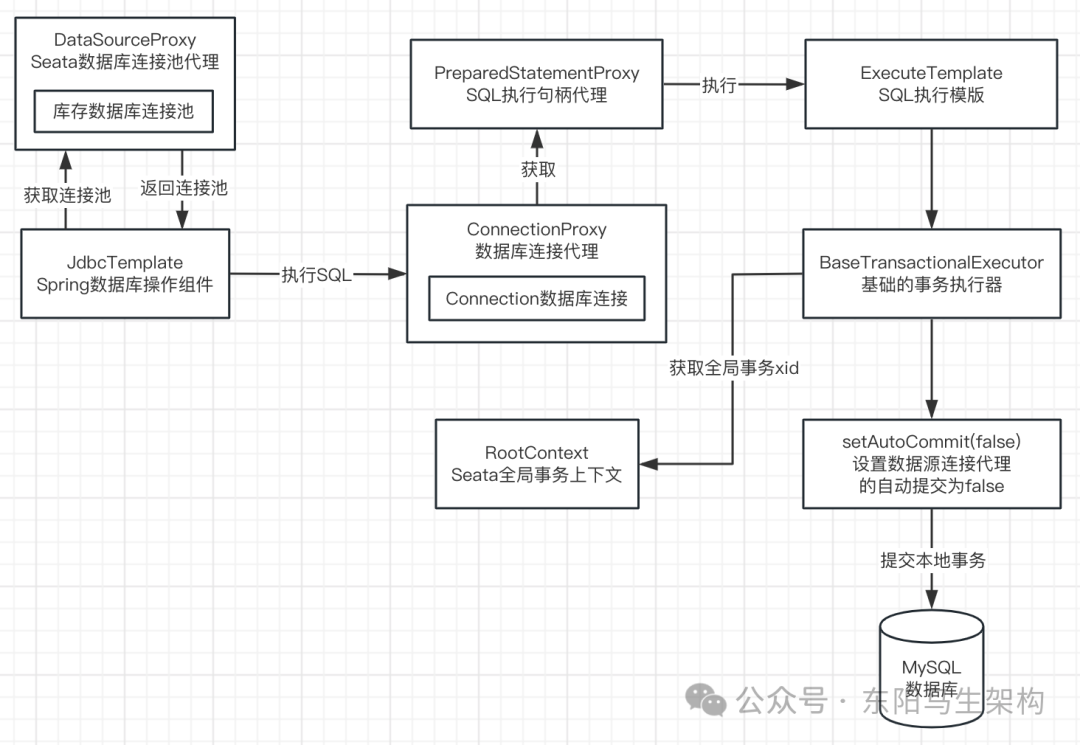
7.执行SQL语句前取消自动提交事务的源码
执行ExecuteTemplate执行模版的execute()方法时,最终会调用到BaseTransactionalExecutor基础事务执行器的excute()方法。
执行BaseTransactionalExecutor的execute()方法时,又会执行到AbstractDMLBaseExecutor的doExecute()方法。该方法会判断目标数据库连接是否会自动提交本地事务,默认情况下本地事务都是自动提交的。如果是,则取消自动提交本地事务。
- public abstract class BaseTransactionalExecutor<T, S extends Statement> implements Executor<T> {
- //The Statement proxy.
- protected StatementProxy<S> statementProxy;
- //The Statement callback.
- protected StatementCallback<T, S> statementCallback;
- //The Sql recognizer.
- protected SQLRecognizer sqlRecognizer;
- ...
- public BaseTransactionalExecutor(StatementProxy<S> statementProxy, StatementCallback<T, S> statementCallback,
- SQLRecognizer sqlRecognizer) {
- this.statementProxy = statementProxy;
- this.statementCallback = statementCallback;
- this.sqlRecognizer = sqlRecognizer;
- }
- ...
- @Override
- public T execute(Object... args) throws Throwable {
- //获取xid
- String xid = RootContext.getXID();
- if (xid != null) {
- statementProxy.getConnectionProxy().bind(xid);
- }
- statementProxy.getConnectionProxy().setGlobalLockRequire(RootContext.requireGlobalLock());
- return doExecute(args);
- }
-
- //Do execute object.
- protected abstract T doExecute(Object... args) throws Throwable;
- ...
- }
- public abstract class AbstractDMLBaseExecutor<T, S extends Statement> extends BaseTransactionalExecutor<T, S> {
- ...
- public AbstractDMLBaseExecutor(StatementProxy<S> statementProxy, StatementCallback<T, S> statementCallback, SQLRecognizer sqlRecognizer) {
- super(statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizer);
- }
-
- @Override
- public T doExecute(Object... args) throws Throwable {
- AbstractConnectionProxy connectionProxy = statementProxy.getConnectionProxy();
- //判断是否是自动提交本地事务,默认情况本地事务都是自动提交的,此时需要阻止自动提交
- if (connectionProxy.getAutoCommit()) {
- return executeAutoCommitTrue(args);
- } else {
- return executeAutoCommitFalse(args);
- }
- }
- ...
- }
- public abstract class AbstractConnectionProxy implements Connection {
- ...
- @Override
- public boolean getAutoCommit() throws SQLException {
- //判断目标数据库连接是否是自动提交,默认情况是都是自动提交的
- return targetConnection.getAutoCommit();
- }
- ...
- }
- public abstract class AbstractDMLBaseExecutor<T, S extends Statement> extends BaseTransactionalExecutor<T, S> {
- ...
- //Execute auto commit true t.
- protected T executeAutoCommitTrue(Object[] args) throws Throwable {
- ConnectionProxy connectionProxy = statementProxy.getConnectionProxy();
- try {
- //修改自动提交事务的设置,此时需要阻止自动提交事务
- connectionProxy.changeAutoCommit();
- return new LockRetryPolicy(connectionProxy).execute(() -> {
- T result = executeAutoCommitFalse(args);//执行SQL语句
- connectionProxy.commit();//手动提交本地事务
- return result;
- });
- } catch (Exception e) {
- //when exception occur in finally,this exception will lost, so just print it here
- LOGGER.error("execute executeAutoCommitTrue error:{}", e.getMessage(), e);
- if (!LockRetryPolicy.isLockRetryPolicyBranchRollbackOnConflict()) {
- connectionProxy.getTargetConnection().rollback();
- }
- throw e;
- } finally {
- connectionProxy.getContext().reset();
- connectionProxy.setAutoCommit(true);
- }
- }
- ...
- }
- public class ConnectionProxy extends AbstractConnectionProxy {
- private final ConnectionContext context = new ConnectionContext();
- ...
- //change connection autoCommit to false by seata
- public void changeAutoCommit() throws SQLException {
- getContext().setAutoCommitChanged(true);
- setAutoCommit(false);
- }
-
- //Gets context.
- public ConnectionContext getContext() {
- return context;
- }
-
- @Override
- public void setAutoCommit(boolean autoCommit) throws SQLException {
- if ((context.inGlobalTransaction() || context.isGlobalLockRequire()) && autoCommit && !getAutoCommit()) {
- //change autocommit from false to true, we should commit() first according to JDBC spec.
- doCommit();
- }
- //把目标数据源连接的自动提交事务设置为false
- targetConnection.setAutoCommit(autoCommit);
- }
- ...
- }
8.执行SQL语句前后构建数据镜像的源码
(1)AbstractDMLBaseExecutor的doExecute()方法的执行流程
(2)以UpdateExecuto为例构建前后镜像
(1)AbstractDMLBaseExecutor的doExecute()方法的执行流程
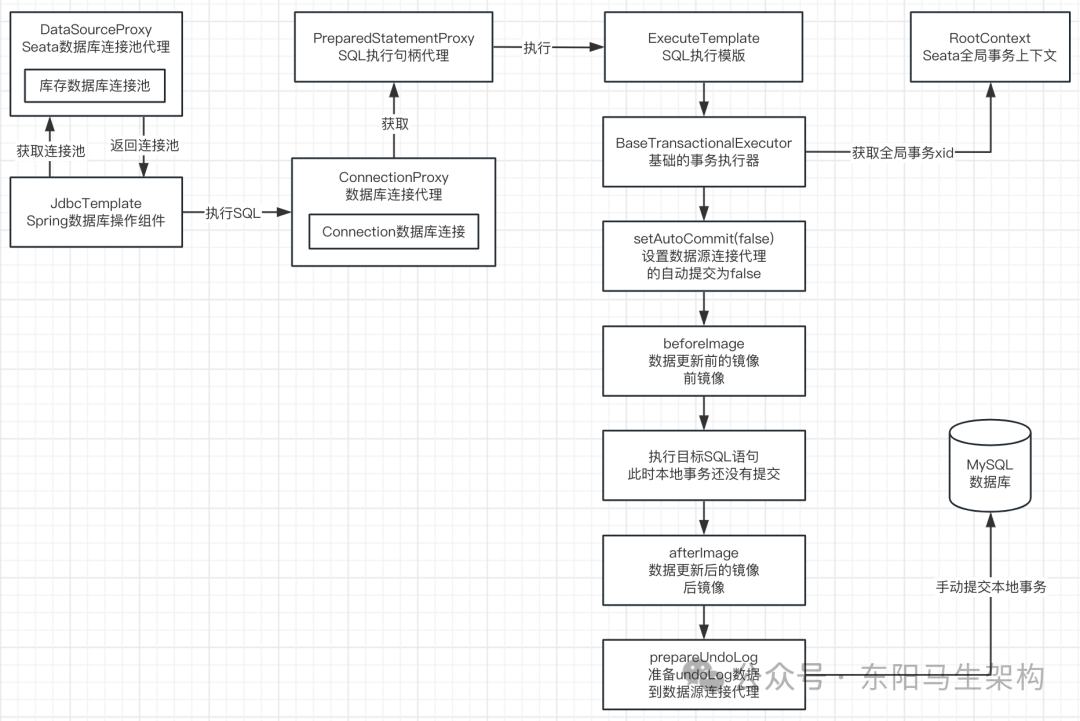
一.首先设置数据源连接阻止其自动提交事务
二.根据目标SQL语句构建beforeImage前镜像
三.执行目标SQL语句(但还没提交其对应的事务)
四.根据beforeImage前镜像构建afterImage后镜像
五.根据前镜像和后镜像构建UndoLog数据
六.手动提交数据源连接代理的事务
- public abstract class AbstractDMLBaseExecutor<T, S extends Statement> extends BaseTransactionalExecutor<T, S> {
- ...
- //Execute auto commit true t.
- protected T executeAutoCommitTrue(Object[] args) throws Throwable {
- ConnectionProxy connectionProxy = statementProxy.getConnectionProxy();
- try {
- //修改数据源连接的自动提交事务的设置,此时需要阻止自动提交事务
- connectionProxy.changeAutoCommit();
- return new LockRetryPolicy(connectionProxy).execute(() -> {
- T result = executeAutoCommitFalse(args);//执行SQL语句
- connectionProxy.commit();//手动提交本地事务
- return result;
- });
- } catch (Exception e) {
- // when exception occur in finally,this exception will lost, so just print it here
- LOGGER.error("execute executeAutoCommitTrue error:{}", e.getMessage(), e);
- if (!LockRetryPolicy.isLockRetryPolicyBranchRollbackOnConflict()) {
- connectionProxy.getTargetConnection().rollback();
- }
- throw e;
- } finally {
- connectionProxy.getContext().reset();
- connectionProxy.setAutoCommit(true);
- }
- }
-
- //Execute auto commit false t.
- protected T executeAutoCommitFalse(Object[] args) throws Exception {
- if (!JdbcConstants.MYSQL.equalsIgnoreCase(getDbType()) && isMultiPk()) {
- throw new NotSupportYetException("multi pk only support mysql!");
- }
- //根据目标SQL语句构建beforeImage,表示目标SQL执行前的数据镜像
- TableRecords beforeImage = beforeImage();
- //接下来真正去执行这条SQL语句,但是此时本地事务还不会提交
- T result = statementCallback.execute(statementProxy.getTargetStatement(), args);
- int updateCount = statementProxy.getUpdateCount();
- if (updateCount > 0) {
- //根据beforeImage构建afterImage,表示目标SQL执行后的数据镜像
- TableRecords afterImage = afterImage(beforeImage);
- //根据beforeImage和afterImage准备undoLog数据到数据源连接代理中
- prepareUndoLog(beforeImage, afterImage);
- }
- return result;
- }
- ...
- }
- public class TableRecords implements java.io.Serializable {
- //表的元数据
- private transient TableMeta tableMeta;
- //表的名称
- private String tableName;
- //表的多行数据
- private List<Row> rows = new ArrayList<Row>();
- ...
- }
- public class UpdateExecutor<T, S extends Statement> extends AbstractDMLBaseExecutor<T, S> {
- private static final Configuration CONFIG = ConfigurationFactory.getInstance();
- private static final boolean ONLY_CARE_UPDATE_COLUMNS = CONFIG.getBoolean(ConfigurationKeys.TRANSACTION_UNDO_ONLY_CARE_UPDATE_COLUMNS, DefaultValues.DEFAULT_ONLY_CARE_UPDATE_COLUMNS);
-
- //Instantiates a new Update executor.
- public UpdateExecutor(StatementProxy<S> statementProxy, StatementCallback<T, S> statementCallback, SQLRecognizer sqlRecognizer) {
- super(statementProxy, statementCallback, sqlRecognizer);
- }
- @Override
- protected TableRecords beforeImage() throws SQLException {
- ArrayList<List<Object>> paramAppenderList = new ArrayList<>();
- TableMeta tmeta = getTableMeta();
- //根据主键ID值拼接一个SQL语句,查询这条数据更新前的镜像
- String selectSQL = buildBeforeImageSQL(tmeta, paramAppenderList);
- return buildTableRecords(tmeta, selectSQL, paramAppenderList);
- }
- private String buildBeforeImageSQL(TableMeta tableMeta, ArrayList<List<Object>> paramAppenderList) {
- SQLUpdateRecognizer recognizer = (SQLUpdateRecognizer) sqlRecognizer;
- List<String> updateColumns = recognizer.getUpdateColumns();
- StringBuilder prefix = new StringBuilder("SELECT ");
- StringBuilder suffix = new StringBuilder(" FROM ").append(getFromTableInSQL());
- String whereCondition = buildWhereCondition(recognizer, paramAppenderList);
- String orderByCondition = buildOrderCondition(recognizer, paramAppenderList);
- String limitCondition = buildLimitCondition(recognizer, paramAppenderList);
- if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(whereCondition)) {
- suffix.append(WHERE).append(whereCondition);
- }
- if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(orderByCondition)) {
- suffix.append(" ").append(orderByCondition);
- }
- if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(limitCondition)) {
- suffix.append(" ").append(limitCondition);
- }
- suffix.append(" FOR UPDATE");
- StringJoiner selectSQLJoin = new StringJoiner(", ", prefix.toString(), suffix.toString());
- if (ONLY_CARE_UPDATE_COLUMNS) {
- if (!containsPK(updateColumns)) {
- selectSQLJoin.add(getColumnNamesInSQL(tableMeta.getEscapePkNameList(getDbType())));
- }
- for (String columnName : updateColumns) {
- selectSQLJoin.add(columnName);
- }
- //The on update xxx columns will be auto update by db, so it's also the actually updated columns
- List<String> onUpdateColumns = tableMeta.getOnUpdateColumnsOnlyName();
- onUpdateColumns.removeAll(updateColumns);
- for (String onUpdateColumn : onUpdateColumns) {
- selectSQLJoin.add(ColumnUtils.addEscape(onUpdateColumn, getDbType()));
- }
- } else {
- for (String columnName : tableMeta.getAllColumns().keySet()) {
- selectSQLJoin.add(ColumnUtils.addEscape(columnName, getDbType()));
- }
- }
- return selectSQLJoin.toString();
- }
- @Override
- protected TableRecords afterImage(TableRecords beforeImage) throws SQLException {
- TableMeta tmeta = getTableMeta();
- if (beforeImage == null || beforeImage.size() == 0) {
- return TableRecords.empty(getTableMeta());
- }
- String selectSQL = buildAfterImageSQL(tmeta, beforeImage);
- ResultSet rs = null;
- try (PreparedStatement pst = statementProxy.getConnection().prepareStatement(selectSQL)) {
- SqlGenerateUtils.setParamForPk(beforeImage.pkRows(), getTableMeta().getPrimaryKeyOnlyName(), pst);
- rs = pst.executeQuery();
- return TableRecords.buildRecords(tmeta, rs);
- } finally {
- IOUtil.close(rs);
- }
- }
- private String buildAfterImageSQL(TableMeta tableMeta, TableRecords beforeImage) throws SQLException {
- StringBuilder prefix = new StringBuilder("SELECT ");
- String whereSql = SqlGenerateUtils.buildWhereConditionByPKs(tableMeta.getPrimaryKeyOnlyName(), beforeImage.pkRows().size(), getDbType());
- String suffix = " FROM " + getFromTableInSQL() + " WHERE " + whereSql;
- StringJoiner selectSQLJoiner = new StringJoiner(", ", prefix.toString(), suffix);
- if (ONLY_CARE_UPDATE_COLUMNS) {
- SQLUpdateRecognizer recognizer = (SQLUpdateRecognizer) sqlRecognizer;
- List<String> updateColumns = recognizer.getUpdateColumns();
- if (!containsPK(updateColumns)) {
- selectSQLJoiner.add(getColumnNamesInSQL(tableMeta.getEscapePkNameList(getDbType())));
- }
- for (String columnName : updateColumns) {
- selectSQLJoiner.add(columnName);
- }
- //The on update xxx columns will be auto update by db, so it's also the actually updated columns
- List<String> onUpdateColumns = tableMeta.getOnUpdateColumnsOnlyName();
- onUpdateColumns.removeAll(updateColumns);
- for (String onUpdateColumn : onUpdateColumns) {
- selectSQLJoiner.add(ColumnUtils.addEscape(onUpdateColumn, getDbType()));
- }
- } else {
- for (String columnName : tableMeta.getAllColumns().keySet()) {
- selectSQLJoiner.add(ColumnUtils.addEscape(columnName, getDbType()));
- }
- }
- return selectSQLJoiner.toString();
- }
- }
9.构建全局锁的key和UndoLog数据的源码
(1)prepareUndoLog()方法会构建全局锁的key和UndoLog数据
(2)构建全局锁的key的源码
(3)构建UndoLog数据的源码
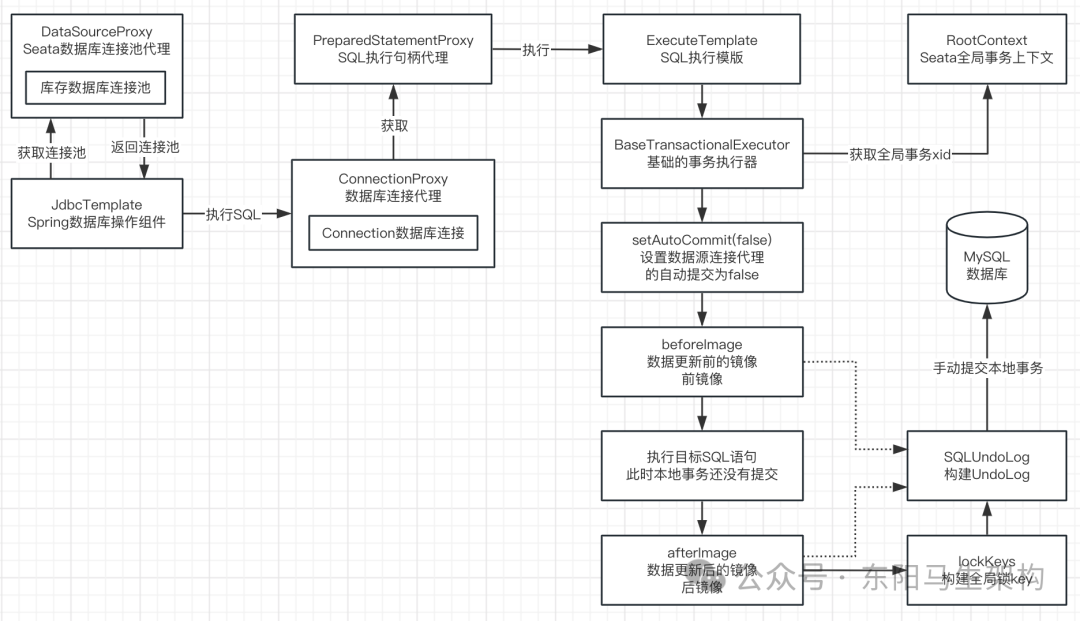
(1)prepareUndoLog()方法会构建全局锁的key和UndoLog数据
在基础事务执行器BaseTransactionalExecutor的prepareUndoLog()方法中,会构建全局锁的key和构建UndoLog数据,并把它们设置到数据源连接代理ConnectionProxy中。
- public abstract class BaseTransactionalExecutor<T, S extends Statement> implements Executor<T> {
- ...
- //prepare undo log.
- //@param beforeImage the before image
- //@param afterImage the after image
- protected void prepareUndoLog(TableRecords beforeImage, TableRecords afterImage) throws SQLException {
- if (beforeImage.getRows().isEmpty() && afterImage.getRows().isEmpty()) {
- return;
- }
- if (SQLType.UPDATE == sqlRecognizer.getSQLType()) {
- if (beforeImage.getRows().size() != afterImage.getRows().size()) {
- throw new ShouldNeverHappenException("Before image size is not equaled to after image size, probably because you updated the primary keys.");
- }
- }
- ConnectionProxy connectionProxy = statementProxy.getConnectionProxy();
- TableRecords lockKeyRecords = sqlRecognizer.getSQLType() == SQLType.DELETE ? beforeImage : afterImage;
- //构建全局锁的key
- //比如更新了一批数据,那么需要针对这批数据的主键ID,来构建这批数据的全局锁的key
- String lockKeys = buildLockKey(lockKeyRecords);
- if (null != lockKeys) {
- //将全局锁key设置到数据源连接代理ConnectionProxy中
- connectionProxy.appendLockKey(lockKeys);
- //构建UndoLog
- SQLUndoLog sqlUndoLog = buildUndoItem(beforeImage, afterImage);
- //将UndoLog设置到数据源连接代理ConnectionProxy中
- connectionProxy.appendUndoLog(sqlUndoLog);
- }
- }
- ...
- }
- public abstract class BaseTransactionalExecutor<T, S extends Statement> implements Executor<T> {
- ...
- //build lockKey
- //@param rowsIncludingPK the records
- //@return the string as local key. the local key example(multi pk): "t_user:1_a,2_b"
- protected String buildLockKey(TableRecords rowsIncludingPK) {
- if (rowsIncludingPK.size() == 0) {
- return null;
- }
- //构建出来的全局锁的key形式为:table_name:id_11001
- StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
- sb.append(rowsIncludingPK.getTableMeta().getTableName());
- sb.append(":");
- int filedSequence = 0;
- //pksRows指的是,更新的每一行数据主键字段和主键的值
- List<Map<String, Field>> pksRows = rowsIncludingPK.pkRows();
- //获取到主键字段名称,主键可能是联合主键,主键字段的名称可能有多个
- List<String> primaryKeysOnlyName = getTableMeta().getPrimaryKeyOnlyName();
- //rowMap就是一行数据,rowMap中的key是字段名称,value是字段值
- for (Map<String, Field> rowMap : pksRows) {
- int pkSplitIndex = 0;
- //遍历和提取这行数据里多个主键字段的名称
- for (String pkName : primaryKeysOnlyName) {
- if (pkSplitIndex > 0) {
- sb.append("_");
- }
- //获取到多个主键字段的value,然后拼接在一起
- sb.append(rowMap.get(pkName).getValue());
- pkSplitIndex++;
- }
- filedSequence++;
- if (filedSequence < pksRows.size()) {
- sb.append(",");
- }
- }
- //最终拼成的key形如:table_name:1101_aadd,table_name:xxxx_xxx
- return sb.toString();
- }
- ...
- }
- public abstract class BaseTransactionalExecutor<T, S extends Statement> implements Executor<T> {
- ...
- //build a SQLUndoLog
- //@param beforeImage the before image
- //@param afterImage the after image
- protected SQLUndoLog buildUndoItem(TableRecords beforeImage, TableRecords afterImage) {
- SQLType sqlType = sqlRecognizer.getSQLType();
- String tableName = sqlRecognizer.getTableName();
- SQLUndoLog sqlUndoLog = new SQLUndoLog();
- sqlUndoLog.setSqlType(sqlType);//SQL的类型可能为insert、update、delete
- sqlUndoLog.setTableName(tableName);//表的名称
- sqlUndoLog.setBeforeImage(beforeImage);//SQL执行前的数据镜像
- sqlUndoLog.setAfterImage(afterImage);//SQL执行后的数据镜像
- return sqlUndoLog;
- }
- ...
- }
- public class SQLUndoLog implements java.io.Serializable {
- private SQLType sqlType;
- private String tableName;
- private TableRecords beforeImage;
- private TableRecords afterImage;
- ...
- }
10.Seata Client发起分支事务注册的源码
(1)ConnectionProxy.commit()提交事务
(2)ConnectionProxy.register()注册分支事务
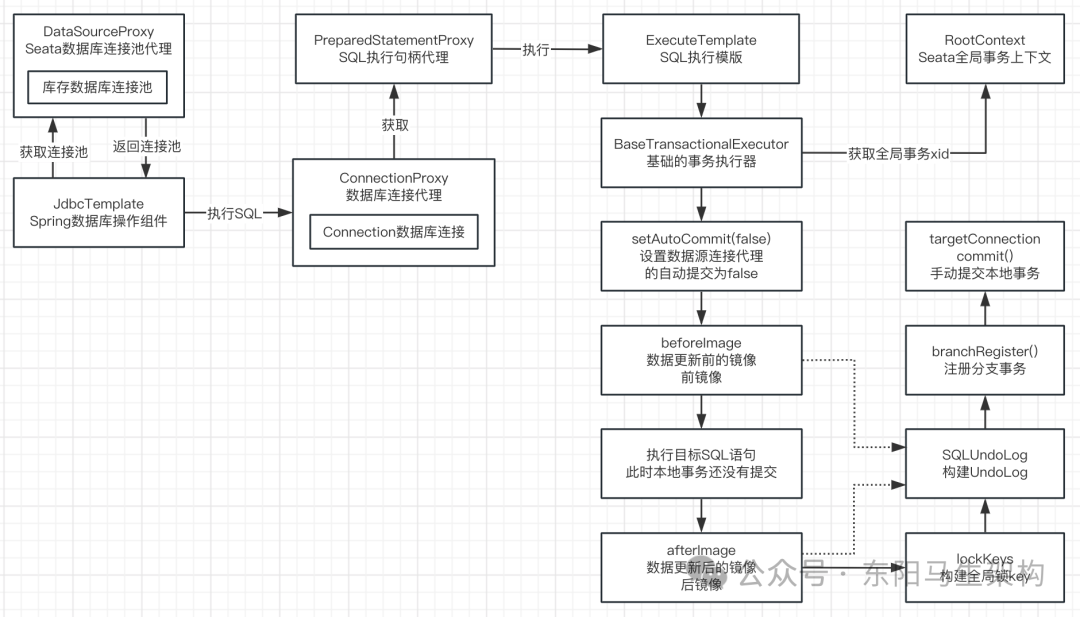
(1)ConnectionProxy.commit()提交事务
执行数据源连接代理ConnectionProxy的commit()方法提交事务的时候,首先会先调用数据源连接代理ConnectionProxy的register()方法注册分支事务。
- public class ConnectionProxy extends AbstractConnectionProxy {
- private final ConnectionContext context = new ConnectionContext();
- ...
- @Override
- public void commit() throws SQLException {
- try {
- //通过全局锁重试策略组件来执行本地事务的提交
- lockRetryPolicy.execute(() -> {
- doCommit();
- return null;
- });
- } catch (SQLException e) {
- if (targetConnection != null && !getAutoCommit() && !getContext().isAutoCommitChanged()) {
- rollback();
- }
- throw e;
- } catch (Exception e) {
- throw new SQLException(e);
- }
- }
-
- private void doCommit() throws SQLException {
- if (context.inGlobalTransaction()) {
- processGlobalTransactionCommit();
- } else if (context.isGlobalLockRequire()) {
- processLocalCommitWithGlobalLocks();
- } else {
- targetConnection.commit();
- }
- }
- private void processLocalCommitWithGlobalLocks() throws SQLException {
- //检查全局锁keys
- checkLock(context.buildLockKeys());
- try {
- //目标数据源连接提交事务
- targetConnection.commit();
- } catch (Throwable ex) {
- throw new SQLException(ex);
- }
- context.reset();
- }
- private void processGlobalTransactionCommit() throws SQLException {
- try {
- //注册分支事务
- register();
- } catch (TransactionException e) {
- recognizeLockKeyConflictException(e, context.buildLockKeys());
- }
- try {
- UndoLogManagerFactory.getUndoLogManager(this.getDbType()).flushUndoLogs(this);
- //目标数据源连接提交事务
- targetConnection.commit();
- } catch (Throwable ex) {
- LOGGER.error("process connectionProxy commit error: {}", ex.getMessage(), ex);
- report(false);
- throw new SQLException(ex);
- }
- if (IS_REPORT_SUCCESS_ENABLE) {
- report(true);
- }
- context.reset();
- }
- ...
- }
执行数据源连接代理ConnectionProxy的register()方法注册分支事务的时候,会调用资源管理器DefaultResourceManager的branchRegister()方法,然后会继续调用AbstractResourceManager的branchRegister()方法来注册分支事务。
在AbstractResourceManager的branchRegister()方法中,首先会构造分支事务注册请求,然后通过RmNettyRemotingClient将分支事务注册请求发送给Seata Server。- //The type Connection proxy.
- //数据源连接代理
- public class ConnectionProxy extends AbstractConnectionProxy {
- private final ConnectionContext context = new ConnectionContext();
- ...
- private void register() throws TransactionException {
- if (!context.hasUndoLog() || !context.hasLockKey()) {
- return;
- }
- //分支事务注册
- Long branchId = DefaultResourceManager.get().branchRegister(
- BranchType.AT,//事务类型
- getDataSourceProxy().getResourceId(),//资源id,资源是已经注册过了的
- null,
- context.getXid(),
- context.getApplicationData(),
- context.buildLockKeys()//注册分支事物时带上全局锁keys
- );
- context.setBranchId(branchId);
- }
- ...
- }
- public class DefaultResourceManager implements ResourceManager {
- protected static Map<BranchType, ResourceManager> resourceManagers = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
-
- private static class SingletonHolder {
- private static DefaultResourceManager INSTANCE = new DefaultResourceManager();
- }
-
- public static DefaultResourceManager get() {
- return SingletonHolder.INSTANCE;
- }
-
- private DefaultResourceManager() {
- initResourceManagers();
- }
-
- protected void initResourceManagers() {
- //通过SPI加载所有的ResourceManager资源管理器
- //比如:DataSourceManager、TCCResourceManager、SagaResourceManager、ResourceManagerXA
- List<ResourceManager> allResourceManagers = EnhancedServiceLoader.loadAll(ResourceManager.class);
- if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(allResourceManagers)) {
- for (ResourceManager rm : allResourceManagers) {
- resourceManagers.put(rm.getBranchType(), rm);
- }
- }
- }
-
- //注册分支事务
- @Override
- public Long branchRegister(BranchType branchType, String resourceId, String clientId, String xid, String applicationData, String lockKeys) throws TransactionException {
- return getResourceManager(branchType).branchRegister(branchType, resourceId, clientId, xid, applicationData, lockKeys);
- }
-
- public ResourceManager getResourceManager(BranchType branchType) {
- ResourceManager rm = resourceManagers.get(branchType);
- if (rm == null) {
- throw new FrameworkException("No ResourceManager for BranchType:" + branchType.name());
- }
- return rm;
- }
- ...
- }
- public abstract class AbstractResourceManager implements ResourceManager {
- ...
- @Override
- public Long branchRegister(BranchType branchType, String resourceId, String clientId, String xid, String applicationData, String lockKeys) throws TransactionException {
- try {
- BranchRegisterRequest request = new BranchRegisterRequest();
- request.setXid(xid);//xid是全局事务id
- request.setLockKey(lockKeys);//这次分支事务要更新数据全局锁key
- request.setResourceId(resourceId);//分支事务对应的资源id
- request.setBranchType(branchType);//分支事务类型
- request.setApplicationData(applicationData);//应用数据
- BranchRegisterResponse response = (BranchRegisterResponse) RmNettyRemotingClient.getInstance().sendSyncRequest(request);
- if (response.getResultCode() == ResultCode.Failed) {
- throw new RmTransactionException(response.getTransactionExceptionCode(), String.format("Response[ %s ]", response.getMsg()));
- }
- return response.getBranchId();
- } catch (TimeoutException toe) {
- throw new RmTransactionException(TransactionExceptionCode.IO, "RPC Timeout", toe);
- } catch (RuntimeException rex) {
- throw new RmTransactionException(TransactionExceptionCode.BranchRegisterFailed, "Runtime", rex);
- }
- }
- ...
- }
11.Seata Server处理分支事务注册请求的源码
(1)Seata Server收到分支事务注册请求后的处理
(2)BranchRegisterRequest.handle()的处理
(3)DefaultCore.branchRegister()的处理
(1)Seata Server收到分支事务注册请求后的处理
Seata Server收到Seata Client发送过来的分支事务注册请求后,首先会将分支事务注册请求交给ServerOnRequestProcessor的process()方法进行处理,然后再将请求交给DefaultCoordinator的onRequest()方法进行处理。- public abstract class AbstractNettyRemotingServer extends AbstractNettyRemoting implements RemotingServer {
- ...
- @ChannelHandler.Sharable
- class ServerHandler extends ChannelDuplexHandler {
- @Override
- public void channelRead(final ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
- if (!(msg instanceof RpcMessage)) {
- return;
- }
- //接下来调用processMessage()方法对解码完毕的RpcMessage对象进行处理
- processMessage(ctx, (RpcMessage) msg);
- }
- }
- }
- public abstract class AbstractNettyRemoting implements Disposable {
- ...
- protected void processMessage(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RpcMessage rpcMessage) throws Exception {
- if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
- LOGGER.debug(String.format("%s msgId:%s, body:%s", this, rpcMessage.getId(), rpcMessage.getBody()));
- }
- Object body = rpcMessage.getBody();
- if (body instanceof MessageTypeAware) {
- MessageTypeAware messageTypeAware = (MessageTypeAware) body;
- //根据消息类型获取到一个Pair对象,该Pair对象是由请求处理组件和请求处理线程池组成的
- //processorTable里的内容,是NettyRemotingServer在初始化时,通过调用registerProcessor()方法put进去的
- //所以下面的代码实际上会由ServerOnRequestProcessor的process()方法进行处理
- final Pair<RemotingProcessor, ExecutorService> pair = this.processorTable.get((int) messageTypeAware.getTypeCode());
- if (pair != null) {
- if (pair.getSecond() != null) {
- try {
- pair.getSecond().execute(() -> {
- try {
- pair.getFirst().process(ctx, rpcMessage);
- } catch (Throwable th) {
- LOGGER.error(FrameworkErrorCode.NetDispatch.getErrCode(), th.getMessage(), th);
- } finally {
- MDC.clear();
- }
- });
- } catch (RejectedExecutionException e) {
- ...
- }
- } else {
- try {
- pair.getFirst().process(ctx, rpcMessage);
- } catch (Throwable th) {
- LOGGER.error(FrameworkErrorCode.NetDispatch.getErrCode(), th.getMessage(), th);
- }
- }
- } else {
- LOGGER.error("This message type [{}] has no processor.", messageTypeAware.getTypeCode());
- }
- } else {
- LOGGER.error("This rpcMessage body[{}] is not MessageTypeAware type.", body);
- }
- }
- ...
- }
- public class ServerOnRequestProcessor implements RemotingProcessor, Disposable {
- private final RemotingServer remotingServer;
- ...
- @Override
- public void process(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RpcMessage rpcMessage) throws Exception {
- if (ChannelManager.isRegistered(ctx.channel())) {
- onRequestMessage(ctx, rpcMessage);
- } else {
- try {
- if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
- LOGGER.info("closeChannelHandlerContext channel:" + ctx.channel());
- }
- ctx.disconnect();
- ctx.close();
- } catch (Exception exx) {
- LOGGER.error(exx.getMessage());
- }
- if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
- LOGGER.info(String.format("close a unhandled connection! [%s]", ctx.channel().toString()));
- }
- }
- }
-
- private void onRequestMessage(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RpcMessage rpcMessage) {
- Object message = rpcMessage.getBody();
- //RpcContext线程本地变量副本
- RpcContext rpcContext = ChannelManager.getContextFromIdentified(ctx.channel());
- if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
- LOGGER.debug("server received:{},clientIp:{},vgroup:{}", message, NetUtil.toIpAddress(ctx.channel().remoteAddress()), rpcContext.getTransactionServiceGroup());
- } else {
- try {
- BatchLogHandler.INSTANCE.getLogQueue().put(message + ",clientIp:" + NetUtil.toIpAddress(ctx.channel().remoteAddress()) + ",vgroup:" + rpcContext.getTransactionServiceGroup());
- } catch (InterruptedException e) {
- LOGGER.error("put message to logQueue error: {}", e.getMessage(), e);
- }
- }
- if (!(message instanceof AbstractMessage)) {
- return;
- }
- //the batch send request message
- if (message instanceof MergedWarpMessage) {
- ...
- } else {
- //the single send request message
- final AbstractMessage msg = (AbstractMessage) message;
- //最终调用到DefaultCoordinator的onRequest()方法来处理RpcMessage
- //此时传入的msg其实就是客户端发送请求时的BranchRegisterRequest对象
- AbstractResultMessage result = transactionMessageHandler.onRequest(msg, rpcContext);
- //返回响应给客户端
- remotingServer.sendAsyncResponse(rpcMessage, ctx.channel(), result);
- }
- }
- ...
- }
- public class DefaultCoordinator extends AbstractTCInboundHandler implements TransactionMessageHandler, Disposable {
- ...
- @Override
- public AbstractResultMessage onRequest(AbstractMessage request, RpcContext context) {
- if (!(request instanceof AbstractTransactionRequestToTC)) {
- throw new IllegalArgumentException();
- }
- //此时传入的request其实就是客户端发送请求时的BranchRegisterRequest对象
- AbstractTransactionRequestToTC transactionRequest = (AbstractTransactionRequestToTC) request;
- transactionRequest.setTCInboundHandler(this);
- return transactionRequest.handle(context);
- }
- ...
- }
在DefaultCoordinator的onRequest()方法中,会调用BranchRegisterRequest的handle()方法来处理分支事务注册请求,该handle()方法又会调用DefaultCoordinator的doBranchRegister()方法,所以最后会调用DefaultCore的branchRegister()方法来具体处理分支事务注册请求。- public class BranchRegisterRequest extends AbstractTransactionRequestToTC {
- ...
- @Override
- public AbstractTransactionResponse handle(RpcContext rpcContext) {
- return handler.handle(this, rpcContext);
- }
- ...
- }
- public interface TCInboundHandler {
- ...
- //Handle branch register response.
- BranchRegisterResponse handle(BranchRegisterRequest branchRegister, RpcContext rpcContext);
- }
- public abstract class AbstractTCInboundHandler extends AbstractExceptionHandler implements TCInboundHandler {
- ...
- @Override
- public BranchRegisterResponse handle(BranchRegisterRequest request, final RpcContext rpcContext) {
- BranchRegisterResponse response = new BranchRegisterResponse();
- exceptionHandleTemplate(new AbstractCallback<BranchRegisterRequest, BranchRegisterResponse>() {
- @Override
- public void execute(BranchRegisterRequest request, BranchRegisterResponse response) throws TransactionException {
- try {
- doBranchRegister(request, response, rpcContext);
- } catch (StoreException e) {
- throw new TransactionException(TransactionExceptionCode.FailedStore, String.format("branch register request failed. xid=%s, msg=%s", request.getXid(), e.getMessage()), e);
- }
- }
- }, request, response);
- return response;
- }
-
- //Do branch register.
- protected abstract void doBranchRegister(BranchRegisterRequest request, BranchRegisterResponse response, RpcContext rpcContext) throws TransactionException;
- ...
- }
- public class DefaultCoordinator extends AbstractTCInboundHandler implements TransactionMessageHandler, Disposable {
- private final DefaultCore core;
- ...
- @Override
- protected void doBranchRegister(BranchRegisterRequest request, BranchRegisterResponse response, RpcContext rpcContext) throws TransactionException {
- MDC.put(RootContext.MDC_KEY_XID, request.getXid());
- //调用DefaultCore的branchRegister()方法处理分支事务注册请求
- response.setBranchId(core.branchRegister(request.getBranchType(), request.getResourceId(), rpcContext.getClientId(), request.getXid(), request.getApplicationData(), request.getLockKey()));
- }
- ...
- }
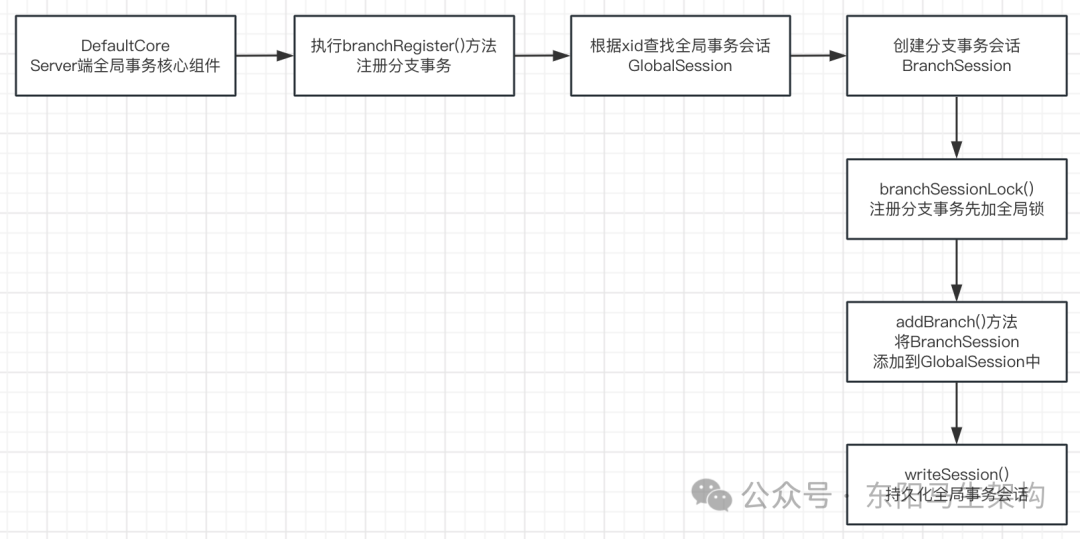
DefaultCore的branchRegister()方法其实会继续调用其抽象父类AbstractCore的branchRegister()方法来处理注册分支事务请求,具体的过程如下:
一.根据xid获取全局事务会话
二.根据全局事务会话创建分支事务会话
三.通过MDC将分支事务ID存到线程本地变量副本
四.注册分支事务需要先获取全局锁
五.把分支事务会话加入到全局事务会话中并持久化
- public class DefaultCore implements Core {
- private static Map<BranchType, AbstractCore> coreMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
-
- public DefaultCore(RemotingServer remotingServer) {
- List allCore = EnhancedServiceLoader.loadAll(AbstractCore.class, new Class[] {RemotingServer.class}, new Object[] {remotingServer});
- if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(allCore)) {
- for (AbstractCore core : allCore) {
- coreMap.put(core.getHandleBranchType(), core);
- }
- }
- }
-
- @Override
- public Long branchRegister(BranchType branchType, String resourceId, String clientId, String xid, String applicationData, String lockKeys) throws TransactionException {
- return getCore(branchType).branchRegister(branchType, resourceId, clientId, xid, applicationData, lockKeys);
- }
-
- public AbstractCore getCore(BranchType branchType) {
- AbstractCore core = coreMap.get(branchType);
- if (core == null) {
- throw new NotSupportYetException("unsupported type:" + branchType.name());
- }
- return core;
- }
- ...
- }
- public abstract class AbstractCore implements Core {
- protected RemotingServer remotingServer;
-
- public AbstractCore(RemotingServer remotingServer) {
- if (remotingServer == null) {
- throw new IllegalArgumentException("remotingServer must be not null");
- }
- this.remotingServer = remotingServer;
- }
-
- //注册分支事务
- @Override
- public Long branchRegister(BranchType branchType, String resourceId, String clientId, String xid, String applicationData, String lockKeys) throws TransactionException {
- //1.根据xid获取全局事务会话GlobalSession
- GlobalSession globalSession = assertGlobalSessionNotNull(xid, false);
- return SessionHolder.lockAndExecute(globalSession, () -> {
- globalSessionStatusCheck(globalSession);
- globalSession.addSessionLifecycleListener(SessionHolder.getRootSessionManager());
- //2.创建分支事务会话BranchSession,根据全局事务开启一个分支事务
- //传入的参数依次是:全局事务会话、事务类型、资源ID、应用数据、全局锁keys、客户端ID
- BranchSession branchSession = SessionHelper.newBranchByGlobal(globalSession, branchType, resourceId, applicationData, lockKeys, clientId);
- //3.把分支事务的ID存放到线程本地变量副本中,也就是MDC中
- MDC.put(RootContext.MDC_KEY_BRANCH_ID, String.valueOf(branchSession.getBranchId()));
- //4.注册分支事务时会获取全局锁
- //分支事务会话branchSession尝试获取一个全局锁,获取失败会抛异常,说明分支事务注册失败
- branchSessionLock(globalSession, branchSession);
- try {
- //5.把分支事务会话加入到全局事务会话中
- globalSession.addBranch(branchSession);
- } catch (RuntimeException ex) {
- branchSessionUnlock(branchSession);
- throw new BranchTransactionException(FailedToAddBranch, String.format("Failed to store branch xid = %s branchId = %s", globalSession.getXid(), branchSession.getBranchId()), ex);
- }
- if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
- LOGGER.info("Register branch successfully, xid = {}, branchId = {}, resourceId = {} ,lockKeys = {}", globalSession.getXid(), branchSession.getBranchId(), resourceId, lockKeys);
- }
- return branchSession.getBranchId();
- });
- }
-
- private GlobalSession assertGlobalSessionNotNull(String xid, boolean withBranchSessions) throws TransactionException {
- //根据xid寻找全局事务会话GlobalSession
- GlobalSession globalSession = SessionHolder.findGlobalSession(xid, withBranchSessions);
- if (globalSession == null) {
- throw new GlobalTransactionException(TransactionExceptionCode.GlobalTransactionNotExist, String.format("Could not found global transaction xid = %s, may be has finished.", xid));
- }
- return globalSession;
- }
-
- //获取全局锁,获取全局锁失败则抛异常
- protected void branchSessionLock(GlobalSession globalSession, BranchSession branchSession) throws TransactionException {
- }
- ...
- }
- public class SessionHolder {
- ...
- //根据xid获取全局事务会话GlobalSession
- public static GlobalSession findGlobalSession(String xid, boolean withBranchSessions) {
- return getRootSessionManager().findGlobalSession(xid, withBranchSessions);
- }
- ...
- }
- @LoadLevel(name = "db", scope = Scope.PROTOTYPE)
- public class DataBaseSessionManager extends AbstractSessionManager implements Initialize {
- ...
- //根据xid获取全局事务会话GlobalSession
- @Override
- public GlobalSession findGlobalSession(String xid, boolean withBranchSessions) {
- return transactionStoreManager.readSession(xid, withBranchSessions);
- }
- ...
- }
- public class DataBaseTransactionStoreManager extends AbstractTransactionStoreManager implements TransactionStoreManager {
- ...
- //根据xid获取全局事务会话GlobalSession
- @Override
- public GlobalSession readSession(String xid, boolean withBranchSessions) {
- //global transaction
- GlobalTransactionDO globalTransactionDO = logStore.queryGlobalTransactionDO(xid);
- if (globalTransactionDO == null) {
- return null;
- }
- //branch transactions
- List<BranchTransactionDO> branchTransactionDOs = null;
- //reduce rpc with db when branchRegister and getGlobalStatus
- if (withBranchSessions) {
- branchTransactionDOs = logStore.queryBranchTransactionDO(globalTransactionDO.getXid());
- }
- return getGlobalSession(globalTransactionDO, branchTransactionDOs);
- }
- ...
- }
- public class SessionHelper {
- ...
- //创建分支事务会话
- public static BranchSession newBranchByGlobal(GlobalSession globalSession, BranchType branchType, String resourceId, String applicationData, String lockKeys, String clientId) {
- BranchSession branchSession = new BranchSession();
- branchSession.setXid(globalSession.getXid());
- branchSession.setTransactionId(globalSession.getTransactionId());
- branchSession.setBranchId(UUIDGenerator.generateUUID());
- branchSession.setBranchType(branchType);
- branchSession.setResourceId(resourceId);
- branchSession.setLockKey(lockKeys);
- branchSession.setClientId(clientId);
- branchSession.setApplicationData(applicationData);
- return branchSession;
- }
- ...
- }
- public class GlobalSession implements SessionLifecycle, SessionStorable {
- private List<BranchSession> branchSessions;
- ...
- //把分支事务会话加入到全局事务会话中
- @Override
- public void addBranch(BranchSession branchSession) throws TransactionException {
- for (SessionLifecycleListener lifecycleListener : lifecycleListeners) {
- lifecycleListener.onAddBranch(this, branchSession);
- }
- branchSession.setStatus(BranchStatus.Registered);
- add(branchSession);
- }
-
- //把分支事务会话加入到全局事务会话中
- public boolean add(BranchSession branchSession) {
- if (null != branchSessions) {
- return branchSessions.add(branchSession);
- } else {
- //db and redis no need to deal with
- return true;
- }
- }
- ...
- }
- public abstract class AbstractSessionManager implements SessionManager, SessionLifecycleListener {
- ...
- @Override
- public void onAddBranch(GlobalSession globalSession, BranchSession branchSession) throws TransactionException {
- addBranchSession(globalSession, branchSession);
- }
-
- @Override
- public void addBranchSession(GlobalSession session, BranchSession branchSession) throws TransactionException {
- if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
- LOGGER.debug("MANAGER[{}] SESSION[{}] {}", name, branchSession, LogOperation.BRANCH_ADD);
- }
- writeSession(LogOperation.BRANCH_ADD, branchSession);
- }
-
- //持久化全局事务会话
- private void writeSession(LogOperation logOperation, SessionStorable sessionStorable) throws TransactionException {
- //transactionStoreManager.writeSession()会对全局事务会话进行持久化
- if (!transactionStoreManager.writeSession(logOperation, sessionStorable)) {
- ...
- }
- }
- ...
- }
12.将UndoLog写入到数据库与提交事务的源码
在数据源连接代理ConnectionProxy的processGlobalTransactionCommit()方法中:
一.首先会注册完分支事务
二.然后会将UndoLog写入到数据库
三.最后才提交目标数据源连接的事务
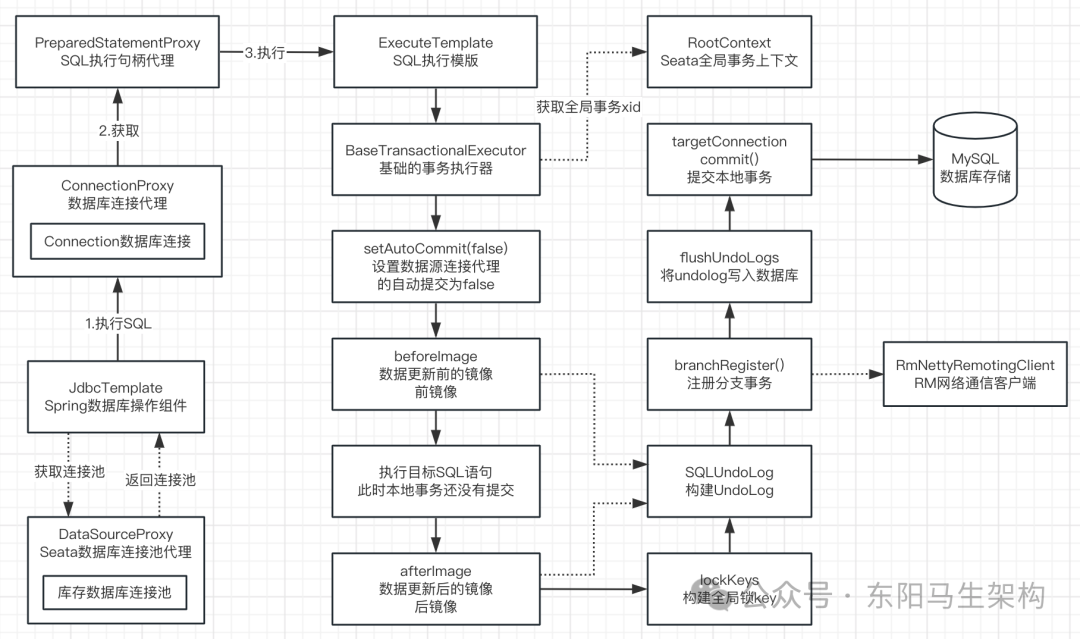
- //数据源连接代理
- public class ConnectionProxy extends AbstractConnectionProxy {
- private final LockRetryPolicy lockRetryPolicy = new LockRetryPolicy(this);
- ...
- @Override
- public void commit() throws SQLException {
- try {
- //通过全局锁重试策略组件LockRetryPolicy来执行本地事务的提交
- lockRetryPolicy.execute(() -> {
- doCommit();
- return null;
- });
- } catch (SQLException e) {
- if (targetConnection != null && !getAutoCommit() && !getContext().isAutoCommitChanged()) {
- rollback();
- }
- throw e;
- } catch (Exception e) {
- throw new SQLException(e);
- }
- }
-
- private void doCommit() throws SQLException {
- if (context.inGlobalTransaction()) {
- processGlobalTransactionCommit();
- } else if (context.isGlobalLockRequire()) {
- processLocalCommitWithGlobalLocks();
- } else {
- targetConnection.commit();
- }
- }
-
- private void processLocalCommitWithGlobalLocks() throws SQLException {
- //检查全局锁keys
- checkLock(context.buildLockKeys());
- try {
- //目标数据源连接提交事务
- targetConnection.commit();
- } catch (Throwable ex) {
- throw new SQLException(ex);
- }
- context.reset();
- }
-
- private void processGlobalTransactionCommit() throws SQLException {
- try {
- //1.注册分支事务
- register();
- } catch (TransactionException e) {
- recognizeLockKeyConflictException(e, context.buildLockKeys());
- }
- try {
- //2.将UndoLog写入到数据库
- UndoLogManagerFactory.getUndoLogManager(this.getDbType()).flushUndoLogs(this);
- //3.目标数据源连接提交事务
- targetConnection.commit();
- } catch (Throwable ex) {
- LOGGER.error("process connectionProxy commit error: {}", ex.getMessage(), ex);
- report(false);
- throw new SQLException(ex);
- }
- if (IS_REPORT_SUCCESS_ENABLE) {
- report(true);
- }
- context.reset();
- }
- ...
- }
- public class UndoLogManagerFactory {
- private static final Map<String, UndoLogManager> UNDO_LOG_MANAGER_MAP = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
- //获取UndoLog管理器
- public static UndoLogManager getUndoLogManager(String dbType) {
- return CollectionUtils.computeIfAbsent(UNDO_LOG_MANAGER_MAP, dbType,
- key -> EnhancedServiceLoader.load(UndoLogManager.class, dbType));
- }
- }
- public abstract class AbstractUndoLogManager implements UndoLogManager {
- ...
- @Override
- public void flushUndoLogs(ConnectionProxy cp) throws SQLException {
- ConnectionContext connectionContext = cp.getContext();
- if (!connectionContext.hasUndoLog()) {
- return;
- }
- String xid = connectionContext.getXid();
- long branchId = connectionContext.getBranchId();
- BranchUndoLog branchUndoLog = new BranchUndoLog();
- branchUndoLog.setXid(xid);
- branchUndoLog.setBranchId(branchId);
- branchUndoLog.setSqlUndoLogs(connectionContext.getUndoItems());
- UndoLogParser parser = UndoLogParserFactory.getInstance();
- byte[] undoLogContent = parser.encode(branchUndoLog);
- if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
- LOGGER.debug("Flushing UNDO LOG: {}", new String(undoLogContent, Constants.DEFAULT_CHARSET));
- }
- CompressorType compressorType = CompressorType.NONE;
- if (needCompress(undoLogContent)) {
- compressorType = ROLLBACK_INFO_COMPRESS_TYPE;
- undoLogContent = CompressorFactory.getCompressor(compressorType.getCode()).compress(undoLogContent);
- }
- //插入UndoLog到数据库
- insertUndoLogWithNormal(xid, branchId, buildContext(parser.getName(), compressorType), undoLogContent, cp.getTargetConnection());
- }
-
- //insert uodo log when normal
- protected abstract void insertUndoLogWithNormal(String xid, long branchId, String rollbackCtx, byte[] undoLogContent, Connection conn) throws SQLException;
- ...
- }
- @LoadLevel(name = JdbcConstants.MYSQL)
- public class MySQLUndoLogManager extends AbstractUndoLogManager {
- ...
- @Override
- protected void insertUndoLogWithNormal(String xid, long branchId, String rollbackCtx, byte[] undoLogContent, Connection conn) throws SQLException {
- insertUndoLog(xid, branchId, rollbackCtx, undoLogContent, State.Normal, conn);
- }
-
- private void insertUndoLog(String xid, long branchId, String rollbackCtx, byte[] undoLogContent, State state, Connection conn) throws SQLException {
- try (PreparedStatement pst = conn.prepareStatement(INSERT_UNDO_LOG_SQL)) {
- pst.setLong(1, branchId);
- pst.setString(2, xid);
- pst.setString(3, rollbackCtx);
- pst.setBytes(4, undoLogContent);
- pst.setInt(5, state.getValue());
- pst.executeUpdate();
- } catch (Exception e) {
- if (!(e instanceof SQLException)) {
- e = new SQLException(e);
- }
- throw (SQLException) e;
- }
- }
- ...
- }
13.通过全局锁重试策略组件执行事务的提交
当设置完禁止自动提交事务、构建前镜像、执行SQL、构建后镜像,执行到数据源连接代理ConnectionProxy的commit()方法提交本地事务时,便会通过全局锁重试策略LockRetryPolicy来执行本地事务的提交。
全局锁重试策略LockRetryPolicy,会确保先获取到全局锁才提交本地事务。也就是如果获取不到全局锁,则重试获取。此外,注册分支事务时,获取到全局锁才能注册成功。- public class ConnectionProxy extends AbstractConnectionProxy {
- private final LockRetryPolicy lockRetryPolicy = new LockRetryPolicy(this);
- ...
- @Override
- public void commit() throws SQLException {
- try {
- //通过全局锁重试策略组件LockRetryPolicy来执行本地事务的提交
- lockRetryPolicy.execute(() -> {
- doCommit();
- return null;
- });
- } catch (SQLException e) {
- if (targetConnection != null && !getAutoCommit() && !getContext().isAutoCommitChanged()) {
- rollback();
- }
- throw e;
- } catch (Exception e) {
- throw new SQLException(e);
- }
- }
- ...
- public static class LockRetryPolicy {
- protected static final boolean LOCK_RETRY_POLICY_BRANCH_ROLLBACK_ON_CONFLICT = ConfigurationFactory.getInstance().
- getBoolean(ConfigurationKeys.CLIENT_LOCK_RETRY_POLICY_BRANCH_ROLLBACK_ON_CONFLICT, DEFAULT_CLIENT_LOCK_RETRY_POLICY_BRANCH_ROLLBACK_ON_CONFLICT);
- protected final ConnectionProxy connection;
- public LockRetryPolicy(ConnectionProxy connection) {
- this.connection = connection;
- }
- public <T> T execute(Callable<T> callable) throws Exception {
- //the only case that not need to retry acquire lock hear is
- //LOCK_RETRY_POLICY_BRANCH_ROLLBACK_ON_CONFLICT == true && connection#autoCommit == true
- //because it has retry acquire lock when AbstractDMLBaseExecutor#executeAutoCommitTrue
- if (LOCK_RETRY_POLICY_BRANCH_ROLLBACK_ON_CONFLICT && connection.getContext().isAutoCommitChanged()) {
- //不需要重试
- return callable.call();
- } else {
- //LOCK_RETRY_POLICY_BRANCH_ROLLBACK_ON_CONFLICT == false
- //or LOCK_RETRY_POLICY_BRANCH_ROLLBACK_ON_CONFLICT == true && autoCommit == false
- return doRetryOnLockConflict(callable);
- }
- }
- protected <T> T doRetryOnLockConflict(Callable<T> callable) throws Exception {
- LockRetryController lockRetryController = new LockRetryController();
- while (true) {
- try {
- return callable.call();
- } catch (LockConflictException lockConflict) {
- onException(lockConflict);
- //AbstractDMLBaseExecutor#executeAutoCommitTrue the local lock is released
- if (connection.getContext().isAutoCommitChanged() && lockConflict.getCode() == TransactionExceptionCode.LockKeyConflictFailFast) {
- lockConflict.setCode(TransactionExceptionCode.LockKeyConflict);
- }
- //休眠一会再去重试
- lockRetryController.sleep(lockConflict);
- } catch (Exception e) {
- onException(e);
- throw e;
- }
- }
- }
-
- //Callback on exception in doLockRetryOnConflict.
- protected void onException(Exception e) throws Exception {
- }
- }
- ...
- }
- public abstract class AbstractDMLBaseExecutor<T, S extends Statement> extends BaseTransactionalExecutor<T, S> {
- ...
- private static class LockRetryPolicy extends ConnectionProxy.LockRetryPolicy {
- LockRetryPolicy(final ConnectionProxy connection) {
- super(connection);
- }
- @Override
- public <T> T execute(Callable<T> callable) throws Exception {
- if (LOCK_RETRY_POLICY_BRANCH_ROLLBACK_ON_CONFLICT) {
- return doRetryOnLockConflict(callable);
- } else {
- return callable.call();
- }
- }
- @Override
- protected void onException(Exception e) throws Exception {
- ConnectionContext context = connection.getContext();
- //UndoItems can't use the Set collection class to prevent ABA
- context.removeSavepoint(null);
- //回滚目标数据源连接对SQL的执行
- connection.getTargetConnection().rollback();
- }
- public static boolean isLockRetryPolicyBranchRollbackOnConflict() {
- return LOCK_RETRY_POLICY_BRANCH_ROLLBACK_ON_CONFLICT;
- }
- }
- ...
- }
14.注册分支事务时获取全局锁的入口源码
在Seata Server中,只有当全局锁获取成功后,分支事务才能注册成功。AbstractCore的branchRegister()方法会通过调用ATCore的branchSessionLock()方法来获取全局锁,而ATCore的branchSessionLock()方法最终则是靠调用AbstractLockManager的acquireLock()方法来尝试获取全局锁的。获取全局锁失败会抛出异常,说明注册分支事务失败。- public abstract class AbstractCore implements Core {
- ...
- //注册分支事务
- @Override
- public Long branchRegister(BranchType branchType, String resourceId, String clientId, String xid, String applicationData, String lockKeys) throws TransactionException {
- //1.根据xid获取全局事务会话GlobalSession
- GlobalSession globalSession = assertGlobalSessionNotNull(xid, false);
- return SessionHolder.lockAndExecute(globalSession, () -> {
- globalSessionStatusCheck(globalSession);
- globalSession.addSessionLifecycleListener(SessionHolder.getRootSessionManager());
- //2.创建分支事务会话,根据全局事务开启一个分支事务
- //传入的参数依次是:全局事务会话、事务类型、资源ID、应用数据、全局锁keys、客户端ID
- BranchSession branchSession = SessionHelper.newBranchByGlobal(globalSession, branchType, resourceId, applicationData, lockKeys, clientId);
- //3.把分支事务的ID存放到线程本地变量副本中,也就是MDC中
- MDC.put(RootContext.MDC_KEY_BRANCH_ID, String.valueOf(branchSession.getBranchId()));
- //4.注册分支事务时会加全局锁
- //分支事务会话branchSession尝试获取一个全局锁,获取失败会抛异常,说明分支事务注册失败
- branchSessionLock(globalSession, branchSession);
- try {
- //5.把分支事务会话加入到全局事务会话中
- globalSession.addBranch(branchSession);
- } catch (RuntimeException ex) {
- branchSessionUnlock(branchSession);
- throw new BranchTransactionException(FailedToAddBranch, String.format("Failed to store branch xid = %s branchId = %s", globalSession.getXid(), branchSession.getBranchId()), ex);
- }
- if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
- LOGGER.info("Register branch successfully, xid = {}, branchId = {}, resourceId = {} ,lockKeys = {}", globalSession.getXid(), branchSession.getBranchId(), resourceId, lockKeys);
- }
- return branchSession.getBranchId();
- });
- }
- ...
- }
- public class ATCore extends AbstractCore {
- ...
- @Override
- protected void branchSessionLock(GlobalSession globalSession, BranchSession branchSession) throws TransactionException {
- //从应用程序数据里提取出一些属性进行属性赋值
- String applicationData = branchSession.getApplicationData();
- boolean autoCommit = true;
- boolean skipCheckLock = false;
- if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(applicationData)) {
- if (objectMapper == null) {
- objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
- }
- try {
- //ObjectMapper是一个对象映射框架,它可以把ApplicationData对象里的属性值读取出来,然后写入到HashMap里
- Map<String, Object> data = objectMapper.readValue(applicationData, HashMap.class);
- Object clientAutoCommit = data.get(AUTO_COMMIT);
- if (clientAutoCommit != null && !(boolean)clientAutoCommit) {
- autoCommit = (boolean)clientAutoCommit;
- }
- Object clientSkipCheckLock = data.get(SKIP_CHECK_LOCK);
- if (clientSkipCheckLock instanceof Boolean) {
- skipCheckLock = (boolean)clientSkipCheckLock;
- }
- } catch (IOException e) {
- LOGGER.error("failed to get application data: {}", e.getMessage(), e);
- }
- }
- try {
- //分支事务会话branchSession尝试获取一个全局锁,获取失败会抛异常,说明分支事务注册失败
- if (!branchSession.lock(autoCommit, skipCheckLock)) {
- throw new BranchTransactionException(LockKeyConflict, String.format("Global lock acquire failed xid = %s branchId = %s", globalSession.getXid(), branchSession.getBranchId()));
- }
- } catch (StoreException e) {
- if (e.getCause() instanceof BranchTransactionException) {
- throw new BranchTransactionException(((BranchTransactionException)e.getCause()).getCode(), String.format("Global lock acquire failed xid = %s branchId = %s", globalSession.getXid(), branchSession.getBranchId()));
- }
- throw e;
- }
- }
- ...
- }
- public class BranchSession implements Lockable, Comparable<BranchSession>, SessionStorable {
- ...
- public boolean lock(boolean autoCommit, boolean skipCheckLock) throws TransactionException {
- if (this.getBranchType().equals(BranchType.AT)) {
- //尝试获取全局锁
- return LockerManagerFactory.getLockManager().acquireLock(this, autoCommit, skipCheckLock);
- }
- return true;
- }
- ...
- }
- public class LockerManagerFactory {
- private static final Configuration CONFIG = ConfigurationFactory.getInstance();
- private static volatile LockManager LOCK_MANAGER;
-
- public static LockManager getLockManager() {
- if (LOCK_MANAGER == null) {
- init();
- }
- return LOCK_MANAGER;
- }
-
- public static void init() {
- init(null);
- }
-
- public static void init(String lockMode) {
- if (LOCK_MANAGER == null) {
- synchronized (LockerManagerFactory.class) {
- if (LOCK_MANAGER == null) {
- if (StringUtils.isBlank(lockMode)) {
- lockMode = CONFIG.getConfig(ConfigurationKeys.STORE_LOCK_MODE, CONFIG.getConfig(ConfigurationKeys.STORE_MODE, SERVER_DEFAULT_STORE_MODE));
- }
- if (StoreMode.contains(lockMode)) {
- LOCK_MANAGER = EnhancedServiceLoader.load(LockManager.class, lockMode);
- }
- }
- }
- }
- }
- }
- public abstract class AbstractLockManager implements LockManager {
- ...
- @Override
- public boolean acquireLock(BranchSession branchSession, boolean autoCommit, boolean skipCheckLock) throws TransactionException {
- if (branchSession == null) {
- throw new IllegalArgumentException("branchSession can't be null for memory/file locker.");
- }
- String lockKey = branchSession.getLockKey();
- if (StringUtils.isNullOrEmpty(lockKey)) {
- //no lock
- return true;
- }
- //get locks of branch
- //获取到分支事务里需要的所有行锁
- List<RowLock> locks = collectRowLocks(branchSession);
- if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(locks)) {
- //no lock
- return true;
- }
- //具体进行获取锁
- return getLocker(branchSession).acquireLock(locks, autoCommit, skipCheckLock);
- }
-
- @Override
- public List<RowLock> collectRowLocks(BranchSession branchSession) {
- if (branchSession == null || StringUtils.isBlank(branchSession.getLockKey())) {
- return Collections.emptyList();
- }
- String lockKey = branchSession.getLockKey();
- String resourceId = branchSession.getResourceId();
- String xid = branchSession.getXid();
- long transactionId = branchSession.getTransactionId();
- long branchId = branchSession.getBranchId();
- return collectRowLocks(lockKey, resourceId, xid, transactionId, branchId);
- }
-
- protected List<RowLock> collectRowLocks(String lockKey, String resourceId, String xid, Long transactionId, Long branchID) {
- List<RowLock> locks = new ArrayList<>();
- String[] tableGroupedLockKeys = lockKey.split(";");
- for (String tableGroupedLockKey : tableGroupedLockKeys) {
- int idx = tableGroupedLockKey.indexOf(":");
- if (idx < 0) {
- return locks;
- }
- String tableName = tableGroupedLockKey.substring(0, idx);
- String mergedPKs = tableGroupedLockKey.substring(idx + 1);
- if (StringUtils.isBlank(mergedPKs)) {
- return locks;
- }
- String[] pks = mergedPKs.split(",");
- if (pks == null || pks.length == 0) {
- return locks;
- }
- for (String pk : pks) {
- if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(pk)) {
- RowLock rowLock = new RowLock();
- rowLock.setXid(xid);
- rowLock.setTransactionId(transactionId);
- rowLock.setBranchId(branchID);
- rowLock.setTableName(tableName);
- rowLock.setPk(pk);
- rowLock.setResourceId(resourceId);
- locks.add(rowLock);
- }
- }
- }
- return locks;
- }
- ...
- }
- public class RowLock {
- private String xid;//全局事务xid
- private Long transactionId;//全局事务ID
- private Long branchId;//分支事务ID
- private String resourceId;//资源ID
- private String tableName;//表名称
- private String pk;//主键
- private String rowKey;//行键
- private String feature;//功能特性
- ...
- }
15.Seata Server获取全局锁的具体逻辑源码
调用AbstractLockManager的acquireLock()方法获取全局锁时,其实调用的是DataBaseLocker的acquireLock()方法 -> LockStoreDataBaseDAO的acquireLock()方法。
在LockStoreDataBaseDAO的acquireLock()方法中,首先会查询数据库中是否存在要申请的全局锁的记录,然后根据这些锁记录 + xid判断是否由当前全局事务获取的(这是核心)。
如果不是,则说明其他全局事务先获取到了要申请的全局锁,此时当前事务获取全局锁失败。
如果是,则把当前事务已经获取过的全局锁过滤出来,然后尝试写入当前分支事务还需获取的全局锁记录到数据库。如果写入成功,则表示当前分支事务成功获取到全局锁。如果写入失败,则表示其他分支事务已经获取到全局锁。- @LoadLevel(name = "db")
- public class DataBaseLockManager extends AbstractLockManager implements Initialize {
- private Locker locker;
-
- @Override
- public void init() {
- //init dataSource
- String datasourceType = ConfigurationFactory.getInstance().getConfig(ConfigurationKeys.STORE_DB_DATASOURCE_TYPE);
- DataSource lockStoreDataSource = EnhancedServiceLoader.load(DataSourceProvider.class, datasourceType).provide();
- locker = new DataBaseLocker(lockStoreDataSource);
- }
- @Override
- public Locker getLocker(BranchSession branchSession) {
- return locker;
- }
- ...
- }
- public class DataBaseLocker extends AbstractLocker {
- private LockStore lockStore;
-
- public DataBaseLocker(DataSource logStoreDataSource) {
- lockStore = new LockStoreDataBaseDAO(logStoreDataSource);
- }
- ...
-
- @Override
- public boolean acquireLock(List<RowLock> locks, boolean autoCommit, boolean skipCheckLock) {
- if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(locks)) {
- //no lock
- return true;
- }
- try {
- //通过执行MySQL来获取全局锁
- return lockStore.acquireLock(convertToLockDO(locks), autoCommit, skipCheckLock);
- } catch (StoreException e) {
- throw e;
- } catch (Exception t) {
- LOGGER.error("AcquireLock error, locks:{}", CollectionUtils.toString(locks), t);
- return false;
- }
- }
- ...
- }
- public class LockStoreDataBaseDAO implements LockStore {
- ...
- @Override
- public boolean acquireLock(List<LockDO> lockDOs, boolean autoCommit, boolean skipCheckLock) {
- //数据库操作三剑客:连接、句柄、结果
- Connection conn = null;
- PreparedStatement ps = null;
- ResultSet rs = null;
- Set<String> dbExistedRowKeys = new HashSet<>();
- boolean originalAutoCommit = true;
- if (lockDOs.size() > 1) {
- lockDOs = lockDOs.stream().filter(LambdaUtils.distinctByKey(LockDO::getRowKey)).collect(Collectors.toList());
- }
- try {
- //从全局锁数据源里获取到一个连接
- conn = lockStoreDataSource.getConnection();
- //关闭自动提交事务
- if (originalAutoCommit = conn.getAutoCommit()) {
- conn.setAutoCommit(false);
- }
- //需要获取的锁,有可能多个
- List<LockDO> unrepeatedLockDOs = lockDOs;
- //check lock
- if (!skipCheckLock) {
- boolean canLock = true;
- //query,针对全局锁表查询某个数据加了全局锁的全局事务xid
- //LockStoreSqlFactory是全局锁存储的SQL工厂
- String checkLockSQL = LockStoreSqlFactory.getLogStoreSql(dbType).getCheckLockableSql(lockTable, lockDOs.size());
- ps = conn.prepareStatement(checkLockSQL);
- for (int i = 0; i < lockDOs.size(); i++) {
- ps.setString(i + 1, lockDOs.get(i).getRowKey());
- }
- //执行查询
- rs = ps.executeQuery();
- //获取到当前要加全局锁的事务xid
- String currentXID = lockDOs.get(0).getXid();
- boolean failFast = false;
- //如果查询到的结果rs是空,则表示当前全局锁没有被事务获取占用
- while (rs.next()) {
- String dbXID = rs.getString(ServerTableColumnsName.LOCK_TABLE_XID);
- //如果获取到全局锁的是别的全局事务xid,那么获取全局锁失败,设置canLock为false
- if (!StringUtils.equals(dbXID, currentXID)) {
- if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
- String dbPk = rs.getString(ServerTableColumnsName.LOCK_TABLE_PK);
- String dbTableName = rs.getString(ServerTableColumnsName.LOCK_TABLE_TABLE_NAME);
- long dbBranchId = rs.getLong(ServerTableColumnsName.LOCK_TABLE_BRANCH_ID);
- LOGGER.info("Global lock on [{}:{}] is holding by xid {} branchId {}", dbTableName, dbPk, dbXID, dbBranchId);
- }
- if (!autoCommit) {
- int status = rs.getInt(ServerTableColumnsName.LOCK_TABLE_STATUS);
- if (status == LockStatus.Rollbacking.getCode()) {
- failFast = true;
- }
- }
- canLock = false;
- break;
- }
- dbExistedRowKeys.add(rs.getString(ServerTableColumnsName.LOCK_TABLE_ROW_KEY));
- }
- if (!canLock) {
- conn.rollback();
- if (failFast) {
- throw new StoreException(new BranchTransactionException(LockKeyConflictFailFast));
- }
- return false;
- }
- //If the lock has been exists in db, remove it from the lockDOs
- if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(dbExistedRowKeys)) {
- //过滤当前事务已经获取过的全局锁
- unrepeatedLockDOs = lockDOs.stream().filter(lockDO -> !dbExistedRowKeys.contains(lockDO.getRowKey())).collect(Collectors.toList());
- }
- if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(unrepeatedLockDOs)) {
- conn.rollback();
- return true;
- }
- }
- //lock
- if (unrepeatedLockDOs.size() == 1) {
- LockDO lockDO = unrepeatedLockDOs.get(0);
- //尝试加锁,表示全局锁被当前的分支事务获取了
- if (!doAcquireLock(conn, lockDO)) {
- if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
- LOGGER.info("Global lock acquire failed, xid {} branchId {} pk {}", lockDO.getXid(), lockDO.getBranchId(), lockDO.getPk());
- }
- conn.rollback();
- return false;
- }
- } else {
- if (!doAcquireLocks(conn, unrepeatedLockDOs)) {
- if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
- LOGGER.info("Global lock batch acquire failed, xid {} branchId {} pks {}", unrepeatedLockDOs.get(0).getXid(), unrepeatedLockDOs.get(0).getBranchId(), unrepeatedLockDOs.stream().map(lockDO -> lockDO.getPk()).collect(Collectors.toList()));
- }
- conn.rollback();
- return false;
- }
- }
- conn.commit();
- return true;
- } catch (SQLException e) {
- throw new StoreException(e);
- } finally {
- IOUtil.close(rs, ps);
- if (conn != null) {
- try {
- if (originalAutoCommit) {
- conn.setAutoCommit(true);
- }
- conn.close();
- } catch (SQLException e) {
- }
- }
- }
- }
-
- protected boolean doAcquireLock(Connection conn, LockDO lockDO) {
- PreparedStatement ps = null;
- try {
- //insert
- String insertLockSQL = LockStoreSqlFactory.getLogStoreSql(dbType).getInsertLockSQL(lockTable);
- ps = conn.prepareStatement(insertLockSQL);
- ps.setString(1, lockDO.getXid());//全局事务xid
- ps.setLong(2, lockDO.getTransactionId());//全局事务id
- ps.setLong(3, lockDO.getBranchId());//分支事务id
- ps.setString(4, lockDO.getResourceId());//资源id
- ps.setString(5, lockDO.getTableName());//表名称
- ps.setString(6, lockDO.getPk());//主键
- ps.setString(7, lockDO.getRowKey());//rowkey
- ps.setInt(8, LockStatus.Locked.getCode());//locked
- return ps.executeUpdate() > 0;
- } catch (SQLException e) {
- throw new StoreException(e);
- } finally {
- IOUtil.close(ps);
- }
- }
- ...
- }
16.全局锁和分支事务及本地事务总结
获取到全局锁,才能注册分支事务成功,否则LockRetryPolicy重试。获取到全局锁,才能提交本地事务成功,否则LockRetryPolicy重试。
全局锁没有被其他事务(xid)获取,则当前事务(xid)才能获取全局锁成功。获取全局锁,会将当前分支事务申请全局锁的记录写入到数据库中。
17.提交全局事务以及提交各分支事务的源码
(1)Seata Client发起提交全局事务的请求
(2)Server向Client发送提交分支事务的请求
(3)Seata Client处理提交分支事务的请求
(4)全局事务的提交主要就是让各个分支事务把本地的UndoLog删除
(1)Seata Client发起提交全局事务的请求- -> TransactionalTemplate.execute()发起全局事务的提交
- -> TransactionalTemplate.commitTransaction()
- -> DefaultGlobalTransaction.commit()
- -> DefaultTransactionManager.commit()
- -> DefaultTransactionManager.syncCall()
- -> TmNettyRemotingClient.sendSyncRequest()
- 把全局事务提交请求GlobalCommitRequest发送给Seata Server进行处理
- //Template of executing business logic with a global transaction. 全局事务执行模版
- public class TransactionalTemplate {
- private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(TransactionalTemplate.class);
-
- public Object execute(TransactionalExecutor business) throws Throwable {
- //1.Get transactionInfo
- TransactionInfo txInfo = business.getTransactionInfo();
- if (txInfo == null) {
- throw new ShouldNeverHappenException("transactionInfo does not exist");
- }
- //1.1 Get current transaction, if not null, the tx role is 'GlobalTransactionRole.Participant'.
- //根据线程本地变量副本,获取当前线程本地变量副本里是否存在xid,如果存在则创建一个全局事务
- //刚开始在开启一个全局事务的时候,是没有全局事务的
- GlobalTransaction tx = GlobalTransactionContext.getCurrent();
- //1.2 Handle the transaction propagation.
- //从全局事务配置里,可以获取到全局事务的传播级别,默认是REQUIRED
- //也就是如果存在一个全局事务,就直接执行业务;如果不存在一个全局事务,就开启一个新的全局事务;
- Propagation propagation = txInfo.getPropagation();
- //不同的全局事务传播级别,会采取不同的处理方式
- //比如挂起当前事务 + 开启新的事务,或者是直接不使用事务执行业务,挂起其实就是解绑当前线程的xid
- //可以通过@GlobalTransactional注解,定制业务方法的全局事务,比如指定业务方法全局事务的传播级别
- SuspendedResourcesHolder suspendedResourcesHolder = null;
- try {
- switch (propagation) {
- ...
- }
- //1.3 If null, create new transaction with role 'GlobalTransactionRole.Launcher'.
- if (tx == null) {
- tx = GlobalTransactionContext.createNew();
- }
- //set current tx config to holder
- GlobalLockConfig previousConfig = replaceGlobalLockConfig(txInfo);
- try {
- //2. If the tx role is 'GlobalTransactionRole.Launcher', send the request of beginTransaction to TC,
- //else do nothing. Of course, the hooks will still be triggered.
- //开启一个全局事务
- beginTransaction(txInfo, tx);
-
- Object rs;
- try {
- //Do Your Business
- //执行业务方法,把全局事务xid通过Dubbo RPC传递下去,开启并提交一个一个分支事务
- rs = business.execute();
- } catch (Throwable ex) {
- //3. The needed business exception to rollback.
- //发生异常时需要完成的事务
- completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, tx, ex);
- throw ex;
- }
- //4. everything is fine, commit.
- //如果一切执行正常就会在这里提交全局事务
- commitTransaction(tx);
- return rs;
- } finally {
- //5. clear
- //执行一些全局事务完成后的回调,比如清理等工作
- resumeGlobalLockConfig(previousConfig);
- triggerAfterCompletion();
- cleanUp();
- }
- } finally {
- //If the transaction is suspended, resume it.
- if (suspendedResourcesHolder != null) {
- //如果之前挂起了一个全局事务,此时可以恢复这个全局事务
- tx.resume(suspendedResourcesHolder);
- }
- }
- }
-
- //提交事务
- private void commitTransaction(GlobalTransaction tx) throws TransactionalExecutor.ExecutionException {
- try {
- triggerBeforeCommit();
- tx.commit();
- triggerAfterCommit();
- } catch (TransactionException txe) {
- // 4.1 Failed to commit
- throw new TransactionalExecutor.ExecutionException(tx, txe, TransactionalExecutor.Code.CommitFailure);
- }
- }
- ...
- }
- //The type Default global transaction. 默认的全局事务
- public class DefaultGlobalTransaction implements GlobalTransaction {
- private TransactionManager transactionManager;
-
- DefaultGlobalTransaction(String xid, GlobalStatus status, GlobalTransactionRole role) {
- this.transactionManager = TransactionManagerHolder.get();//全局事务管理者
- this.xid = xid;
- this.status = status;
- this.role = role;
- }
- ...
- @Override
- public void commit() throws TransactionException {
- if (role == GlobalTransactionRole.Participant) {
- //Participant has no responsibility of committing
- if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
- LOGGER.debug("Ignore Commit(): just involved in global transaction [{}]", xid);
- }
- return;
- }
- assertXIDNotNull();
- int retry = COMMIT_RETRY_COUNT <= 0 ? DEFAULT_TM_COMMIT_RETRY_COUNT : COMMIT_RETRY_COUNT;
- try {
- while (retry > 0) {
- try {
- retry--;
- status = transactionManager.commit(xid);
- break;
- } catch (Throwable ex) {
- LOGGER.error("Failed to report global commit [{}],Retry Countdown: {}, reason: {}", this.getXid(), retry, ex.getMessage());
- if (retry == 0) {
- throw new TransactionException("Failed to report global commit", ex);
- }
- }
- }
- } finally {
- if (xid.equals(RootContext.getXID())) {
- suspend();
- }
- }
- if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
- LOGGER.info("[{}] commit status: {}", xid, status);
- }
- }
- ...
- }
- public class TransactionManagerHolder {
- ...
- private TransactionManagerHolder() {
- }
-
- private static class SingletonHolder {
- private static TransactionManager INSTANCE = null;
- static {
- try {
- INSTANCE = EnhancedServiceLoader.load(TransactionManager.class);
- LOGGER.info("TransactionManager Singleton {}", INSTANCE);
- } catch (Throwable anyEx) {
- LOGGER.error("Failed to load TransactionManager Singleton! ", anyEx);
- }
- }
- }
-
- //Get transaction manager.
- public static TransactionManager get() {
- if (SingletonHolder.INSTANCE == null) {
- throw new ShouldNeverHappenException("TransactionManager is NOT ready!");
- }
- return SingletonHolder.INSTANCE;
- }
- ...
- }
- public class DefaultTransactionManager implements TransactionManager {
- ...
- @Override
- public GlobalStatus commit(String xid) throws TransactionException {
- GlobalCommitRequest globalCommit = new GlobalCommitRequest();
- globalCommit.setXid(xid);
- GlobalCommitResponse response = (GlobalCommitResponse) syncCall(globalCommit);
- return response.getGlobalStatus();
- }
-
- private AbstractTransactionResponse syncCall(AbstractTransactionRequest request) throws TransactionException {
- try {
- //TMNettyRemotingClient会和Seata Server基于Netty建立长连接
- return (AbstractTransactionResponse) TmNettyRemotingClient.getInstance().sendSyncRequest(request);
- } catch (TimeoutException toe) {
- throw new TmTransactionException(TransactionExceptionCode.IO, "RPC timeout", toe);
- }
- }
- ...
- }
ServerHandler的channelRead()方法会将收到的请求进行层层传递:首先交给DefaultCoordinator的onRequest()方法来进行处理,然后交给GlobalCommitRequest的handle()方法来进行处理,接着交给AbstractTCInboundHandler的handle()方法来进行处理,最后交给DefaultCoordinator的doGlobalCommit()方法来进行处理,也就是调用DefaultCore的commit()方法来提交全局事务。- public abstract class AbstractNettyRemotingServer extends AbstractNettyRemoting implements RemotingServer {
- ...
- @ChannelHandler.Sharable
- class ServerHandler extends ChannelDuplexHandler {
- @Override
- public void channelRead(final ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
- if (!(msg instanceof RpcMessage)) {
- return;
- }
- //接下来调用processMessage()方法对解码完毕的RpcMessage对象进行处理
- processMessage(ctx, (RpcMessage) msg);
- }
- ...
- }
- ...
- }
- public abstract class AbstractNettyRemoting implements Disposable {
- ...
- protected void processMessage(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RpcMessage rpcMessage) throws Exception {
- if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
- LOGGER.debug(String.format("%s msgId:%s, body:%s", this, rpcMessage.getId(), rpcMessage.getBody()));
- }
- Object body = rpcMessage.getBody();
- if (body instanceof MessageTypeAware) {
- MessageTypeAware messageTypeAware = (MessageTypeAware) body;
- //根据消息类型获取到一个Pair对象,该Pair对象是由请求处理组件和请求处理线程池组成的
- //processorTable里的内容,是NettyRemotingServer在初始化时,通过调用registerProcessor()方法put进去的
- //所以下面的代码实际上会由ServerOnRequestProcessor的process()方法进行处理
- final Pair<RemotingProcessor, ExecutorService> pair = this.processorTable.get((int) messageTypeAware.getTypeCode());
- if (pair != null) {
- if (pair.getSecond() != null) {
- try {
- pair.getSecond().execute(() -> {
- try {
- pair.getFirst().process(ctx, rpcMessage);
- } catch (Throwable th) {
- LOGGER.error(FrameworkErrorCode.NetDispatch.getErrCode(), th.getMessage(), th);
- } finally {
- MDC.clear();
- }
- });
- } catch (RejectedExecutionException e) {
- ...
- }
- } else {
- try {
- pair.getFirst().process(ctx, rpcMessage);
- } catch (Throwable th) {
- LOGGER.error(FrameworkErrorCode.NetDispatch.getErrCode(), th.getMessage(), th);
- }
- }
- } else {
- LOGGER.error("This message type [{}] has no processor.", messageTypeAware.getTypeCode());
- }
- } else {
- LOGGER.error("This rpcMessage body[{}] is not MessageTypeAware type.", body);
- }
- }
- ...
- }
- public class ServerOnRequestProcessor implements RemotingProcessor, Disposable {
- private final RemotingServer remotingServer;
- ...
- @Override
- public void process(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RpcMessage rpcMessage) throws Exception {
- if (ChannelManager.isRegistered(ctx.channel())) {
- onRequestMessage(ctx, rpcMessage);
- } else {
- try {
- if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
- LOGGER.info("closeChannelHandlerContext channel:" + ctx.channel());
- }
- ctx.disconnect();
- ctx.close();
- } catch (Exception exx) {
- LOGGER.error(exx.getMessage());
- }
- if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
- LOGGER.info(String.format("close a unhandled connection! [%s]", ctx.channel().toString()));
- }
- }
- }
-
- private void onRequestMessage(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RpcMessage rpcMessage) {
- Object message = rpcMessage.getBody();
- //RpcContext线程本地变量副本
- RpcContext rpcContext = ChannelManager.getContextFromIdentified(ctx.channel());
- if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
- LOGGER.debug("server received:{},clientIp:{},vgroup:{}", message, NetUtil.toIpAddress(ctx.channel().remoteAddress()), rpcContext.getTransactionServiceGroup());
- } else {
- try {
- BatchLogHandler.INSTANCE.getLogQueue().put(message + ",clientIp:" + NetUtil.toIpAddress(ctx.channel().remoteAddress()) + ",vgroup:" + rpcContext.getTransactionServiceGroup());
- } catch (InterruptedException e) {
- LOGGER.error("put message to logQueue error: {}", e.getMessage(), e);
- }
- }
- if (!(message instanceof AbstractMessage)) {
- return;
- }
- //the batch send request message
- if (message instanceof MergedWarpMessage) {
- ...
- } else {
- //the single send request message
- final AbstractMessage msg = (AbstractMessage) message;
- //最终调用到DefaultCoordinator的onRequest()方法来处理RpcMessage
- AbstractResultMessage result = transactionMessageHandler.onRequest(msg, rpcContext);
- //返回响应给客户端
- remotingServer.sendAsyncResponse(rpcMessage, ctx.channel(), result);
- }
- }
- ...
- }
- public class DefaultCoordinator extends AbstractTCInboundHandler implements TransactionMessageHandler, Disposable {
- ...
- @Override
- public AbstractResultMessage onRequest(AbstractMessage request, RpcContext context) {
- if (!(request instanceof AbstractTransactionRequestToTC)) {
- throw new IllegalArgumentException();
- }
- //传入的request其实就是客户端发送请求时的GlobalCommitRequest
- AbstractTransactionRequestToTC transactionRequest = (AbstractTransactionRequestToTC) request;
- transactionRequest.setTCInboundHandler(this);
- return transactionRequest.handle(context);
- }
- ...
- }
- public class GlobalCommitRequest extends AbstractGlobalEndRequest {
- @Override
- public short getTypeCode() {
- return MessageType.TYPE_GLOBAL_COMMIT;
- }
-
- @Override
- public AbstractTransactionResponse handle(RpcContext rpcContext) {
- return handler.handle(this, rpcContext);
- }
- }
- public abstract class AbstractTCInboundHandler extends AbstractExceptionHandler implements TCInboundHandler {
- ...
- @Override
- public GlobalCommitResponse handle(GlobalCommitRequest request, final RpcContext rpcContext) {
- GlobalCommitResponse response = new GlobalCommitResponse();
- response.setGlobalStatus(GlobalStatus.Committing);
- exceptionHandleTemplate(new AbstractCallback<GlobalCommitRequest, GlobalCommitResponse>() {
- @Override
- public void execute(GlobalCommitRequest request, GlobalCommitResponse response) throws TransactionException {
- try {
- doGlobalCommit(request, response, rpcContext);
- } catch (StoreException e) {
- throw new TransactionException(TransactionExceptionCode.FailedStore, String.format("global commit request failed. xid=%s, msg=%s", request.getXid(), e.getMessage()), e);
- }
- }
-
- @Override
- public void onTransactionException(GlobalCommitRequest request, GlobalCommitResponse response, TransactionException tex) {
- super.onTransactionException(request, response, tex);
- checkTransactionStatus(request, response);
- }
- @Override
- public void onException(GlobalCommitRequest request, GlobalCommitResponse response, Exception rex) {
- super.onException(request, response, rex);
- checkTransactionStatus(request, response);
- }
- }, request, response);
- return response;
- }
-
- protected abstract void doGlobalCommit(GlobalCommitRequest request, GlobalCommitResponse response, RpcContext rpcContext) throws TransactionException;
- ...
- }
- public class DefaultCoordinator extends AbstractTCInboundHandler implements TransactionMessageHandler, Disposable {
- private final DefaultCore core;
- ...
- @Override
- protected void doGlobalCommit(GlobalCommitRequest request, GlobalCommitResponse response, RpcContext rpcContext) throws TransactionException {
- MDC.put(RootContext.MDC_KEY_XID, request.getXid());
- //调用DefaultCore.commit()方法提交全局事务
- response.setGlobalStatus(core.commit(request.getXid()));
- }
- ...
- }
- public class DefaultCore implements Core {
- ...
- @Override
- public GlobalStatus commit(String xid) throws TransactionException {
- GlobalSession globalSession = SessionHolder.findGlobalSession(xid);
- if (globalSession == null) {
- return GlobalStatus.Finished;
- }
- globalSession.addSessionLifecycleListener(SessionHolder.getRootSessionManager());
- //just lock changeStatus
- boolean shouldCommit = SessionHolder.lockAndExecute(globalSession, () -> {
- if (globalSession.getStatus() == GlobalStatus.Begin) {
- //Highlight: Firstly, close the session, then no more branch can be registered.
- globalSession.closeAndClean();
- if (globalSession.canBeCommittedAsync()) {
- globalSession.asyncCommit();
- MetricsPublisher.postSessionDoneEvent(globalSession, GlobalStatus.Committed, false, false);
- return false;
- } else {
- globalSession.changeGlobalStatus(GlobalStatus.Committing);
- return true;
- }
- }
- return false;
- });
- if (shouldCommit) {
- boolean success = doGlobalCommit(globalSession, false);
- //If successful and all remaining branches can be committed asynchronously, do async commit.
- if (success && globalSession.hasBranch() && globalSession.canBeCommittedAsync()) {
- globalSession.asyncCommit();
- return GlobalStatus.Committed;
- } else {
- return globalSession.getStatus();
- }
- } else {
- return globalSession.getStatus() == GlobalStatus.AsyncCommitting ? GlobalStatus.Committed : globalSession.getStatus();
- }
- }
- @Override
- public boolean doGlobalCommit(GlobalSession globalSession, boolean retrying) throws TransactionException {
- boolean success = true;
- //start committing event
- MetricsPublisher.postSessionDoingEvent(globalSession, retrying);
- if (globalSession.isSaga()) {
- success = getCore(BranchType.SAGA).doGlobalCommit(globalSession, retrying);
- } else {
- //获取到全局事务的所有分支事务,并进行遍历提交
- Boolean result = SessionHelper.forEach(globalSession.getSortedBranches(), branchSession -> {
- //if not retrying, skip the canBeCommittedAsync branches
- if (!retrying && branchSession.canBeCommittedAsync()) {
- return CONTINUE;
- }
- BranchStatus currentStatus = branchSession.getStatus();
- if (currentStatus == BranchStatus.PhaseOne_Failed) {
- SessionHelper.removeBranch(globalSession, branchSession, !retrying);
- return CONTINUE;
- }
- try {
- //发送请求给Seata Client提交分支事务
- BranchStatus branchStatus = getCore(branchSession.getBranchType()).branchCommit(globalSession, branchSession);
- if (isXaerNotaTimeout(globalSession,branchStatus)) {
- LOGGER.info("Commit branch XAER_NOTA retry timeout, xid = {} branchId = {}", globalSession.getXid(), branchSession.getBranchId());
- branchStatus = BranchStatus.PhaseTwo_Committed;
- }
- switch (branchStatus) {
- case PhaseTwo_Committed:
- SessionHelper.removeBranch(globalSession, branchSession, !retrying);
- return CONTINUE;
- case PhaseTwo_CommitFailed_Unretryable:
- //not at branch
- SessionHelper.endCommitFailed(globalSession, retrying);
- LOGGER.error("Committing global transaction[{}] finally failed, caused by branch transaction[{}] commit failed.", globalSession.getXid(), branchSession.getBranchId());
- return false;
- default:
- if (!retrying) {
- globalSession.queueToRetryCommit();
- return false;
- }
- if (globalSession.canBeCommittedAsync()) {
- LOGGER.error("Committing branch transaction[{}], status:{} and will retry later", branchSession.getBranchId(), branchStatus);
- return CONTINUE;
- } else {
- LOGGER.error("Committing global transaction[{}] failed, caused by branch transaction[{}] commit failed, will retry later.", globalSession.getXid(), branchSession.getBranchId());
- return false;
- }
- }
- } catch (Exception ex) {
- StackTraceLogger.error(LOGGER, ex, "Committing branch transaction exception: {}", new String[] {branchSession.toString()});
- if (!retrying) {
- globalSession.queueToRetryCommit();
- throw new TransactionException(ex);
- }
- }
- return CONTINUE;
- });
- //Return if the result is not null
- if (result != null) {
- return result;
- }
- //If has branch and not all remaining branches can be committed asynchronously,
- //do print log and return false
- if (globalSession.hasBranch() && !globalSession.canBeCommittedAsync()) {
- LOGGER.info("Committing global transaction is NOT done, xid = {}.", globalSession.getXid());
- return false;
- }
- if (!retrying) {
- //contains not AT branch
- globalSession.setStatus(GlobalStatus.Committed);
- }
- }
- //if it succeeds and there is no branch, retrying=true is the asynchronous state when retrying. EndCommitted is
- //executed to improve concurrency performance, and the global transaction ends..
- if (success && globalSession.getBranchSessions().isEmpty()) {
- SessionHelper.endCommitted(globalSession, retrying);
- LOGGER.info("Committing global transaction is successfully done, xid = {}.", globalSession.getXid());
- }
- return success;
- }
- ...
- }
- public abstract class AbstractCore implements Core {
- protected RemotingServer remotingServer;
- ...
- @Override
- public BranchStatus branchCommit(GlobalSession globalSession, BranchSession branchSession) throws TransactionException {
- try {
- BranchCommitRequest request = new BranchCommitRequest();
- request.setXid(branchSession.getXid());
- request.setBranchId(branchSession.getBranchId());
- request.setResourceId(branchSession.getResourceId());
- request.setApplicationData(branchSession.getApplicationData());
- request.setBranchType(branchSession.getBranchType());
- return branchCommitSend(request, globalSession, branchSession);
- } catch (IOException | TimeoutException e) {
- throw new BranchTransactionException(FailedToSendBranchCommitRequest, String.format("Send branch commit failed, xid = %s branchId = %s", branchSession.getXid(), branchSession.getBranchId()), e);
- }
- }
-
- protected BranchStatus branchCommitSend(BranchCommitRequest request, GlobalSession globalSession, BranchSession branchSession) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
- BranchCommitResponse response = (BranchCommitResponse) remotingServer.sendSyncRequest(branchSession.getResourceId(), branchSession.getClientId(), request);
- return response.getBranchStatus();
- }
- ...
- }
- public abstract class AbstractNettyRemotingServer extends AbstractNettyRemoting implements RemotingServer {
- ...
- @Override
- public Object sendSyncRequest(Channel channel, Object msg) throws TimeoutException {
- if (channel == null) {
- throw new RuntimeException("client is not connected");
- }
- RpcMessage rpcMessage = buildRequestMessage(msg, ProtocolConstants.MSGTYPE_RESQUEST_SYNC);
- return super.sendSync(channel, rpcMessage, NettyServerConfig.getRpcRequestTimeout());
- }
- ...
- }
- public abstract class AbstractNettyRemoting implements Disposable {
- ...
- protected Object sendSync(Channel channel, RpcMessage rpcMessage, long timeoutMillis) throws TimeoutException {
- if (timeoutMillis <= 0) {
- throw new FrameworkException("timeout should more than 0ms");
- }
- if (channel == null) {
- LOGGER.warn("sendSync nothing, caused by null channel.");
- return null;
- }
- //把发送出去的请求封装到MessageFuture中,然后存放到futures这个Map里
- MessageFuture messageFuture = new MessageFuture();
- messageFuture.setRequestMessage(rpcMessage);
- messageFuture.setTimeout(timeoutMillis);
- futures.put(rpcMessage.getId(), messageFuture);
- channelWritableCheck(channel, rpcMessage.getBody());
- //获取远程地址
- String remoteAddr = ChannelUtil.getAddressFromChannel(channel);
- doBeforeRpcHooks(remoteAddr, rpcMessage);
- //异步化发送数据,同时对发送结果添加监听器
- //如果发送失败,则会对网络连接Channel进行销毁处理
- channel.writeAndFlush(rpcMessage).addListener((ChannelFutureListener) future -> {
- if (!future.isSuccess()) {
- MessageFuture messageFuture1 = futures.remove(rpcMessage.getId());
- if (messageFuture1 != null) {
- messageFuture1.setResultMessage(future.cause());
- }
- destroyChannel(future.channel());
- }
- });
- try {
- //然后通过请求响应组件MessageFuture同步等待Seata Server返回该请求的响应
- Object result = messageFuture.get(timeoutMillis, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
- doAfterRpcHooks(remoteAddr, rpcMessage, result);
- return result;
- } catch (Exception exx) {
- LOGGER.error("wait response error:{},ip:{},request:{}", exx.getMessage(), channel.remoteAddress(), rpcMessage.getBody());
- if (exx instanceof TimeoutException) {
- throw (TimeoutException) exx;
- } else {
- throw new RuntimeException(exx);
- }
- }
- }
- ...
- }
ClientHandler的channelRead()方法收到提交分支事务的请求后,会由RmBranchCommitProcessor的handleBranchCommit()方法进行处理。- -> AbstractRMHandler.onRequest()
- -> BranchCommitRequest.handle()
- -> AbstractRMHandler.handle()
- -> AbstractRMHandler.doBranchCommit()
- -> DataSourceManager.branchCommit()
- -> AsyncWorker.branchCommit()异步化提交分支事务
- public abstract class AbstractNettyRemotingClient extends AbstractNettyRemoting implements RemotingClient {
- ...
- @Sharable
- class ClientHandler extends ChannelDuplexHandler {
- @Override
- public void channelRead(final ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
- if (!(msg instanceof RpcMessage)) {
- return;
- }
- processMessage(ctx, (RpcMessage) msg);
- }
- ...
- }
- ...
- }
- public abstract class AbstractNettyRemoting implements Disposable {
- ...
- protected void processMessage(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RpcMessage rpcMessage) throws Exception {
- if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
- LOGGER.debug(String.format("%s msgId:%s, body:%s", this, rpcMessage.getId(), rpcMessage.getBody()));
- }
- Object body = rpcMessage.getBody();
- if (body instanceof MessageTypeAware) {
- MessageTypeAware messageTypeAware = (MessageTypeAware) body;
- //根据消息类型获取到一个Pair对象,该Pair对象是由请求处理组件和请求处理线程池组成的
- final Pair<RemotingProcessor, ExecutorService> pair = this.processorTable.get((int) messageTypeAware.getTypeCode());
- if (pair != null) {
- if (pair.getSecond() != null) {
- try {
- pair.getSecond().execute(() -> {
- try {
- pair.getFirst().process(ctx, rpcMessage);
- } catch (Throwable th) {
- LOGGER.error(FrameworkErrorCode.NetDispatch.getErrCode(), th.getMessage(), th);
- } finally {
- MDC.clear();
- }
- });
- } catch (RejectedExecutionException e) {
- ...
- }
- } else {
- try {
- pair.getFirst().process(ctx, rpcMessage);
- } catch (Throwable th) {
- LOGGER.error(FrameworkErrorCode.NetDispatch.getErrCode(), th.getMessage(), th);
- }
- }
- } else {
- LOGGER.error("This message type [{}] has no processor.", messageTypeAware.getTypeCode());
- }
- } else {
- LOGGER.error("This rpcMessage body[{}] is not MessageTypeAware type.", body);
- }
- }
- ...
- }
- public class RmBranchCommitProcessor implements RemotingProcessor {
- ...
- @Override
- public void process(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RpcMessage rpcMessage) throws Exception {
- String remoteAddress = NetUtil.toStringAddress(ctx.channel().remoteAddress());
- Object msg = rpcMessage.getBody();
- if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
- LOGGER.info("rm client handle branch commit process:" + msg);
- }
- handleBranchCommit(rpcMessage, remoteAddress, (BranchCommitRequest) msg);
- }
- private void handleBranchCommit(RpcMessage request, String serverAddress, BranchCommitRequest branchCommitRequest) {
- BranchCommitResponse resultMessage;
- resultMessage = (BranchCommitResponse) handler.onRequest(branchCommitRequest, null);
- if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
- LOGGER.debug("branch commit result:" + resultMessage);
- }
- try {
- this.remotingClient.sendAsyncResponse(serverAddress, request, resultMessage);
- } catch (Throwable throwable) {
- LOGGER.error("branch commit error: {}", throwable.getMessage(), throwable);
- }
- }
- ...
- }
- public abstract class AbstractRMHandler extends AbstractExceptionHandler implements RMInboundHandler, TransactionMessageHandler {
- ...
- @Override
- public AbstractResultMessage onRequest(AbstractMessage request, RpcContext context) {
- if (!(request instanceof AbstractTransactionRequestToRM)) {
- throw new IllegalArgumentException();
- }
- AbstractTransactionRequestToRM transactionRequest = (AbstractTransactionRequestToRM)request;
- transactionRequest.setRMInboundMessageHandler(this);
- return transactionRequest.handle(context);
- }
- ...
- }
- public class BranchCommitRequest extends AbstractBranchEndRequest {
- @Override
- public short getTypeCode() {
- return MessageType.TYPE_BRANCH_COMMIT;
- }
-
- @Override
- public AbstractTransactionResponse handle(RpcContext rpcContext) {
- return handler.handle(this);
- }
- }
- public abstract class AbstractRMHandler extends AbstractExceptionHandler implements RMInboundHandler, TransactionMessageHandler {
- @Override
- public BranchCommitResponse handle(BranchCommitRequest request) {
- BranchCommitResponse response = new BranchCommitResponse();
- exceptionHandleTemplate(new AbstractCallback<BranchCommitRequest, BranchCommitResponse>() {
- @Override
- public void execute(BranchCommitRequest request, BranchCommitResponse response) throws TransactionException {
- doBranchCommit(request, response);
- }
- }, request, response);
- return response;
- }
-
- protected void doBranchCommit(BranchCommitRequest request, BranchCommitResponse response) throws TransactionException {
- String xid = request.getXid();
- long branchId = request.getBranchId();
- String resourceId = request.getResourceId();
- String applicationData = request.getApplicationData();
- if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
- LOGGER.info("Branch committing: " + xid + " " + branchId + " " + resourceId + " " + applicationData);
- }
- BranchStatus status = getResourceManager().branchCommit(request.getBranchType(), xid, branchId, resourceId, applicationData);
- response.setXid(xid);
- response.setBranchId(branchId);
- response.setBranchStatus(status);
- if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
- LOGGER.info("Branch commit result: " + status);
- }
- }
- ...
- }
- //The type Data source manager. DataSourceManager是AT模式下的资源管理器
- public class DataSourceManager extends AbstractResourceManager {
- //异步化worker
- private final AsyncWorker asyncWorker = new AsyncWorker(this);
- ...
- @Override
- public BranchStatus branchCommit(BranchType branchType, String xid, long branchId, String resourceId, String applicationData) throws TransactionException {
- //通过asyncWorker,异步化提交分支事务
- return asyncWorker.branchCommit(xid, branchId, resourceId);
- }
- ...
- }
- public class AsyncWorker {
- ...
- public BranchStatus branchCommit(String xid, long branchId, String resourceId) {
- Phase2Context context = new Phase2Context(xid, branchId, resourceId);
- addToCommitQueue(context);
- return BranchStatus.PhaseTwo_Committed;
- }
-
- private void addToCommitQueue(Phase2Context context) {
- if (commitQueue.offer(context)) {
- return;
- }
- CompletableFuture.runAsync(this::doBranchCommitSafely, scheduledExecutor).thenRun(() -> addToCommitQueue(context));
- }
-
- void doBranchCommitSafely() {
- try {
- doBranchCommit();
- } catch (Throwable e) {
- LOGGER.error("Exception occur when doing branch commit", e);
- }
- }
-
- private void doBranchCommit() {
- if (commitQueue.isEmpty()) {
- return;
- }
- //transfer all context currently received to this list
- List<Phase2Context> allContexts = new LinkedList<>();
- commitQueue.drainTo(allContexts);
- //group context by their resourceId
- Map<String, List<Phase2Context>> groupedContexts = groupedByResourceId(allContexts);
- groupedContexts.forEach(this::dealWithGroupedContexts);
- }
-
- private void dealWithGroupedContexts(String resourceId, List<Phase2Context> contexts) {
- DataSourceProxy dataSourceProxy = dataSourceManager.get(resourceId);
- if (dataSourceProxy == null) {
- LOGGER.warn("failed to find resource for {} and requeue", resourceId);
- addAllToCommitQueue(contexts);
- return;
- }
- Connection conn = null;
- try {
- conn = dataSourceProxy.getPlainConnection();
- UndoLogManager undoLogManager = UndoLogManagerFactory.getUndoLogManager(dataSourceProxy.getDbType());
- //split contexts into several lists, with each list contain no more element than limit size
- List<List<Phase2Context>> splitByLimit = Lists.partition(contexts, UNDOLOG_DELETE_LIMIT_SIZE);
- //全局事务的提交,就是让各个分支事务把本地的undo logs删除掉即可
- for (List<Phase2Context> partition : splitByLimit) {
- deleteUndoLog(conn, undoLogManager, partition);
- }
- } catch (SQLException sqlExx) {
- addAllToCommitQueue(contexts);
- LOGGER.error("failed to get connection for async committing on {} and requeue", resourceId, sqlExx);
- } finally {
- IOUtil.close(conn);
- }
- }
- ...
- }
18.全局事务回滚的过程源码
全局事务的回滚流程和提交流程几乎一样:
一.Seata Client发起全局事务回滚请求
二.Server向Client发送分支事务回滚请求
三.Seata Client处理分支事务回滚的请求
来源:程序园用户自行投稿发布,如果侵权,请联系站长删除
免责声明:如果侵犯了您的权益,请联系站长,我们会及时删除侵权内容,谢谢合作! |