1. Vue3简介
- 2020年9月18日,Vue.js发布版3.0版本,代号:One Piece(n
- 经历了:4800+次提交、40+个RFC、600+次PR、300+贡献者
- 官方发版地址:Release v3.0.0 One Piece · vuejs/core
- 截止2023年10月,最新的公开版本为:3.3.4
1.1. 【性能的提升】
- 打包大小减少41%。
- 初次渲染快55%, 更新渲染快133%。
- 内存减少54%。
1.2.【 源码的升级】
- 使用Proxy代替defineProperty实现响应式。
- 重写虚拟DOM的实现和Tree-Shaking。
1.3. 【拥抱TypeScript】
1.4. 【新的特性】
- Composition API(组合API):
- setup
- ref与reactive
- computed与watch
......
- 新的内置组件:
- Fragment
- Teleport
- Suspense
......
- 其他改变:
- 新的生命周期钩子
- data 选项应始终被声明为一个函数
- 移除keyCode支持作为 v-on 的修饰符
......
2. 创建Vue3工程
2.1. 【基于 vue-cli 创建】
点击查看官方文档
备注:目前vue-cli已处于维护模式,官方推荐基于 Vite 创建项目。
- ## 查看@vue/cli版本,确保@vue/cli版本在4.5.0以上
- vue --version
- ## 安装或者升级你的@vue/cli
- npm install -g @vue/cli
- ## 执行创建命令
- vue create vue_test
- ## 随后选择3.x
- ## Choose a version of Vue.js that you want to start the project with (Use arrow keys)
- ## > 3.x
- ## 2.x
- ## 启动
- cd vue_test
- npm run serve
vite 是新一代前端构建工具,官网地址:https://vitejs.cn,vite的优势如下:
- 轻量快速的热重载(HMR),能实现极速的服务启动。
- 对 TypeScript、JSX、CSS 等支持开箱即用。
- 真正的按需编译,不再等待整个应用编译完成。
- webpack构建 与 vite构建对比图如下:
<template>
< erson :list="persons"/> erson :list="persons"/>
</template>
- ## 1.创建命令
- npm create vue@latest
- ## 2.具体配置
- ## 配置项目名称
- √ Project name: vue3_test
- ## 是否添加TypeScript支持
- √ Add TypeScript? Yes
- ## 是否添加JSX支持
- √ Add JSX Support? No
- ## 是否添加路由环境
- √ Add Vue Router for Single Page Application development? No
- ## 是否添加pinia环境
- √ Add Pinia for state management? No
- ## 是否添加单元<Child @send-toy="toy = $event"/>
- <button @click="toy = $event">测试</button>
- √ Add Vitest for Unit Testing? No
- ## 是否添加端到端<Child @send-toy="toy = $event"/>
- <button @click="toy = $event">测试</button>方案
- √ Add an End-to-End Testing Solution? » No
- ## 是否添加ESLint语法检查
- √ Add ESLint for code quality? Yes
- ## 是否添加Prettiert代码格式化
- √ Add Prettier for code formatting? No
- <template>
-
- <h1>你好啊!</h1>
-
- </template>
总结:
<ul>Vite 项目中,index.html 是项目的入口文件,在项目最外层。
加载index.html后,Vite 解析 [/code]3. Vue3核心语法
3.1. 【OptionsAPI 与 CompositionAPI】
- Vue2的API设计是Options(配置)风格的。
- Vue3的API设计是Composition(组合)风格的。
Options API 的弊端
Options类型的 API,数据、方法、计算属性等,是分散在:data、methods、computed中的,若想新增或者修改一个需求,就需要分别修改:data、methods、computed,不便于维护和复用。
Composition API 的优势
可以用函数的方式,更加优雅的组织代码,让相关功能的代码更加有序的组织在一起。
说明:以上四张动图原创作者:大帅老猿
3.2. 【拉开序幕的 setup】
setup 概述
setup是Vue3中一个新的配置项,值是一个函数,它是 Composition API “表演的舞台”,组件中所用到的:数据、方法、计算属性、监视......等等,均配置在setup中。
特点如下:
- setup函数返回的对象中的内容,可直接在模板中使用。
- setup中访问this是undefined。
- setup函数会在beforeCreate之前调用,它是“领先”所有钩子执行的。
- <template>
-
- <h2>姓名:{{name}}</h2>
- <h2>年龄:{{age}}</h2>
- <button @click="changeName">修改名字</button>
- <button @click="changeAge">年龄+1</button>
- <button @click="showTel">点我查看联系方式</button>
-
- </template>
- 若返回一个对象:则对象中的:属性、方法等,在模板中均可以直接使用(重点关注)。
- 若返回一个函数:则可以自定义渲染内容,代码如下:
- setup(){
- return ()=> '你好啊!'
- }
- Vue2 的配置(data、methos......)中可以访问到 setup中的属性、方法。
- 但在setup中不能访问到Vue2的配置(data、methos......)。
- 如果与Vue2冲突,则setup优先。
setup 语法糖
setup函数有一个语法糖,这个语法糖,可以让我们把setup独立出去,代码如下:- <template>
-
- <h2>姓名:{{name}}</h2>
- <h2>年龄:{{age}}</h2>
- <button @click="changeName">修改名字</button>
- <button @click="changeAge">年龄+1</button>
- <button @click="showTel">点我查看联系方式</button>
-
- </template>
直接在steup的script标签写上
扩展:上述代码,还需要编写一个不写setup的script标签,去指定组件名字,比较麻烦,我们可以借助vite中的插件简化
- 第一步:npm i vite-plugin-vue-setup-extend -D
- 第二步:vite.config.ts
- import { defineConfig } from 'vite'
- import VueSetupExtend from 'vite-plugin-vue-setup-extend'
- export default defineConfig({
- plugins: [ VueSetupExtend() ]
- })
- 作用:定义一个响应式对象(基本类型不要用它,要用ref,否则报错)
- 语法:let 响应式对象= reactive(源对象)。
- 返回值:一个Proxy的实例对象,简称:响应式对象。
这个是将一个对象编程一个proxy创建的对象接受响应式(数组同理也是这个方法)
- 注意点:reactive定义的响应式数据是“深层次”的。
- <template>
-
- <h2>汽车信息:一台{{ car.brand }}汽车,价值{{ car.price }}万</h2>
- <h2>游戏列表:</h2>
- <ul>
- <li v-for="g in games" :key="g.id">{{ g.name }}</li>
- </ul>
- <h2><Child @send-toy="toy = $event"/>
- <button @click="toy = $event">测试</button>:{{obj.a.b.c.d}}</h2>
- <button @click="changeCarPrice">修改汽车价格</button>
- <button @click="changeFirstGame">修改第一游戏</button>
- <button @click="test"><Child @send-toy="toy = $event"/>
- <button @click="toy = $event">测试</button></button>
-
- </template>
- 其实ref接收的数据可以是:基本类型、对象类型。ref可以对对象响应式数据,但是注意改的时候要加value,特别是数组形式加在哪里
其原理还是把变量做了一个响应式变成了value形式,但是里面的对象还是做了一个proxy
- 若ref接收的是对象类型,内部其实也是调用了reactive函数。
- <template>
-
- <h2>汽车信息:一台{{ car.brand }}汽车,价值{{ car.price }}万</h2>
- <h2>游戏列表:</h2>
- <ul>
- <li v-for="g in games" :key="g.id">{{ g.name }}</li>
- </ul>
- <h2><Child @send-toy="toy = $event"/>
- <button @click="toy = $event">测试</button>:{{obj.a.b.c.d}}</h2>
- <button @click="changeCarPrice">修改汽车价格</button>
- <button @click="changeFirstGame">修改第一游戏</button>
- <button @click="test"><Child @send-toy="toy = $event"/>
- <button @click="toy = $event">测试</button></button>
-
- </template>
宏观角度看:
- ref用来定义:基本类型数据、对象类型数据;
- reactive用来定义:对象类型数据。
- ref创建的变量必须使用.value(可以使用volar插件自动添加.value)。
- reactive重新分配一个新对象,会失去响应式(可以使用Object.assign去整体替换)。
这样写也不行
可以这样
如果是用的ref响应对象,就可以直接改
- 若需要一个基本类型的响应式数据,必须使用ref。
- 若需要一个响应式对象,层级不深,ref、reactive都可以。
- 若需要一个响应式对象,且层级较深,推荐使用reactive。
3.7. 【toRefs 与 toRef】
如果像这样解构赋值,那么出来的name age都不是响应式数据
想让响应式数据转换出来也是响应式就押用到这个
- 作用:将一个响应式对象中的每一个属性,转换为ref对象。
注意:torefs之后会创建一个新的reactive响应式对象,但是值都是指向同一个值你修改一个两个都会变
- 备注:toRefs与toRef功能一致,但toRefs可以批量转换。
- 语法如下:
- <template>
-
- <h2>姓名:{{person.name}}</h2>
- <h2>年龄:{{person.age}}</h2>
- <h2>性别:{{person.gender}}</h2>
- <button @click="changeName">修改名字</button>
- <button @click="changeAge">修改年龄</button>
- <button @click="changeGender">修改性别</button>
-
- </template>
作用:根据已有数据计算出新数据(和Vue2中的computed作用一致)。
计算属性本身是监视它里面的值的变化从而引起自身的变化,所以要改他的时候,也不是直接改他本身,而是改他里面的值
- <template>
-
- 姓:<input type="text" v-model="firstName"> <br>
- 名:<input type="text" v-model="lastName"> <br>
- 全名:{{fullName}} <br>
- <button @click="changeFullName">全名改为:li-si</button>
-
- </template>
- 作用:监视数据的变化(和Vue2中的watch作用一致)
- 特点:Vue3中的watch只能监视以下四种数据:
- ref定义的数据。
- reactive定义的数据。
- 函数返回一个值(getter函数)。
- 一个包含上述内容的数组。
我们在Vue3中使用watch的时候,通常会遇到以下几种情况:
* 情况一
监视ref定义的【基本类型】数据:直接写数据名即可,监视的是其value值的改变。
stopwatch监视会返回一个值是一个箭头函数,调用这个函数可以取消掉监视- <template>
-
- <h1>情况一:监视【ref】定义的【基本类型】数据</h1>
- <h2>当前求和为:{{sum}}</h2>
- <button @click="changeSum">点我sum+1</button>
-
- </template>
监视ref定义的【对象类型】数据:直接写数据名,监视的是对象的【地址值】,若想监视对象内部的数据,要手动开启深度监视。
注意:
- 若修改的是ref定义的对象中的属性,newValue 和 oldValue 都是新值,因为它们是同一个对象。
- 若修改整个ref定义的对象,newValue 是新值, oldValue 是旧值,因为不是同一个对象了。
不开启深度,整个对象改变了,才会触发监视
- <template>
-
- <h1>情况二:监视【ref】定义的【对象类型】数据</h1>
- <h2>姓名:{{ person.name }}</h2>
- <h2>年龄:{{ person.age }}</h2>
- <button @click="changeName">修改名字</button>
- <button @click="changeAge">修改年龄</button>
- <button @click="changePerson">修改整个人</button>
-
- </template>
监视reactive定义的【对象类型】数据,且默认开启了深度监视。并且修改属性新老value还是一样的- <template>
-
- <h1>情况三:监视【reactive】定义的【对象类型】数据</h1>
- <h2>姓名:{{ person.name }}</h2>
- <h2>年龄:{{ person.age }}</h2>
- <button @click="changeName">修改名字</button>
- <button @click="changeAge">修改年龄</button>
- <button @click="changePerson">修改整个人</button>
- <hr>
- <h2><Child @send-toy="toy = $event"/>
- <button @click="toy = $event">测试</button>:{{obj.a.b.c}}</h2>
- <button @click="test">修改obj.a.b.c</button>
-
- </template>
监视ref或reactive定义的【对象类型】数据中的某个属性,注意点如下:
- 若该属性值不是【对象类型】,需要写成函数形式。
- 若该属性值是依然是【对象类型】,可直接写,也可写成函数,建议写成函数。
但是此时如果是这整个对象改变不会监视到
这样就是这个对象怎么变都监视得到,写成函数是为了整个对象变,deep是对象里面变化
结论:监视的要是对象里的属性,那么最好写函数式,注意点:若是对象监视的是地址值,需要关注对象内部,需要手动开启深度监视。- <template>
-
- <h1>情况四:监视【ref】或【reactive】定义的【对象类型】数据中的某个属性</h1>
- <h2>姓名:{{ person.name }}</h2>
- <h2>年龄:{{ person.age }}</h2>
- <h2>汽车:{{ person.car.c1 }}、{{ person.car.c2 }}</h2>
- <button @click="changeName">修改名字</button>
- <button @click="changeAge">修改年龄</button>
- <button @click="changeC1">修改第一台车</button>
- <button @click="changeC2">修改第二台车</button>
- <button @click="changeCar">修改整个车</button>
-
- </template>
监视上述的多个数据
写成数组形式就可以,value是这个数组
- <template>
-
- <h1>情况五:监视上述的多个数据</h1>
- <h2>姓名:{{ person.name }}</h2>
- <h2>年龄:{{ person.age }}</h2>
- <h2>汽车:{{ person.car.c1 }}、{{ person.car.c2 }}</h2>
- <button @click="changeName">修改名字</button>
- <button @click="changeAge">修改年龄</button>
- <button @click="changeC1">修改第一台车</button>
- <button @click="changeC2">修改第二台车</button>
- <button @click="changeCar">修改整个车</button>
-
- </template>
- 官网:立即运行一个函数,同时响应式地追踪其依赖,并在依赖更改时重新执行该函数。
- watch对比watchEffect
- 都能监听响应式数据的变化,不同的是监听数据变化的方式不同
- watch:要明确指出监视的数据
- watchEffect:不用明确指出监视的数据(函数中用到哪些属性,那就监视哪些属性)。
比如这个例子,都可以完成但是watcheffect上来就执行一次,而且会根据里面所写的自动监测要监视谁
- 示例代码:
- <template>
-
- <h1>需求:水温达到50℃,或水位达到20cm,则联系服务器</h1>
- <h2 id="demo">水温:{{temp}}</h2>
- <h2>水位:{{height}}</h2>
- <button @click="changePrice">水温+1</button>
- <button @click="changeSum">水位+10</button>
-
- </template>
3.11. 【标签的 ref 属性】
作用:用于注册模板引用。
- 用在普通DOM标签上,获取的是DOM节点。
- 用在组件标签上,获取的是组件实例对象。
用在普通DOM标签上:- <template>
-
- <h1 ref="title1">尚硅谷</h1>
- <h2 ref="title2">前端</h2>
- <h3 ref="title3">Vue</h3>
- <input type="text" ref="inpt"> <br><br>
- <button @click="showLog">点我打印内容</button>
-
- </template>
但是要获取组件上的数据需要子组件做出defineexpose导出操作- <template>
- <Person ref="ren"/>
- <button @click="test"><Child @send-toy="toy = $event"/>
- <button @click="toy = $event">测试</button></button>
- </template>
注意vue3引用组件直接导入即可
如果在子组件定义了一组数据,但是不小心名字打错了
后期就容易调用不到
我们就可以去定义一个接口来约束类型,一般是在src下面创建一个types文件夹,然后导出
要用的话就在组件导入,并且前面要加type表明导入的是一个类型,然后在要用的变量后规则如下
如果是一个数组数据想这样用就不行
除非是用泛型先规定它是一个数组,然后数组里面每一项需要符合这个规则
当然也可以去自定义类型,直接在ts里面声明
3.12. 【props】
- // 定义一个接口,限制每个Person对象的格式
- export interface PersonInter {
- id:string,
- name:string,
- age:number
- }
- // 定义一个自定义类型Persons
- export type Persons = Array<PersonInter>
注意用reactive响应式数据,此时接口应该用泛型来约束,而且数据是不能多不能少的
如果某个属性想可有可无
- <template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>
只接受会出问题,万一传过来是个数字也会遍历
注意接收+限制类型的写法,prop括号里面不写了,提出来规定一个泛型,里面为一个对象,谁要约束什么
限制必要性,一个?父组件就可传可不传了
如果不写自己还有默认值,导入,再用
用的时候注意,把原来写的全部包起来,第二个参数写默认值,并且键值对,属性值不能为一个数组形式,可以写为一个函数返回
- <template>
- <ul>
- <li v-for="item in list" :key="item.id">
- {{item.name}}--{{item.age}}
- </li>
- </ul>
- </template>
3.13. 【生命周期】
- 规律:
生命周期整体分为四个阶段,分别是:创建、挂载、更新、销毁,每个阶段都有两个钩子,一前一后。
- Vue2的生命周期
创建阶段:beforeCreate、created
挂载阶段:beforeMount、mounted
更新阶段:beforeUpdate、updated
销毁阶段:beforeDestroy、destroyed
v3的创建就是setup本身
- Vue3的生命周期
创建阶段:setup
挂载阶段:onBeforeMount、onMounted
更新阶段:onBeforeUpdate、onUpdated
卸载阶段:onBeforeUnmount、onUnmounted
- 常用的钩子:onMounted(挂载完毕)、onUpdated(更新完毕)、onBeforeUnmount(卸载之前)
- 示例代码:
- <template>
-
- <h2>当前求和为:{{ sum }}</h2>
- <button @click="changeSum">点我sum+1</button>
-
- </template>
3.14. 【自定义hook】
如果一个页面中全是数据和方法,看起很臃肿复杂,跟vue2又很像
注意:如果要往空数组push等作出操作需要规定数组的泛型

而hooks就类似于mixin,把所有代码模块化,src创建文件夹hooks,创建模块的ts文件,把该属于这个部分的代码都放进来

注意:这里面就跟刚才一样什么都能写包括生命钩子,但是会对外暴露一个函数,然后把所有数据方法返回
组件要用就直接导入,并且那边是函数,这边直接调用,通过解构赋值,获得return出来的数据和方法
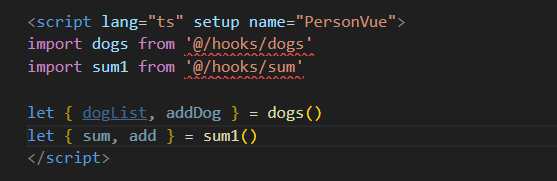
示例代码:
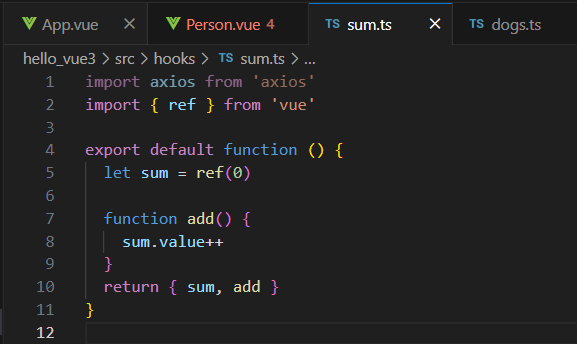
- useSum.ts中内容如下:
- import {ref,onMounted} from 'vue'export default function(){ let sum = ref(0) const increment = ()=>{ sum.value += 1 } const decrement = ()=>{ sum.value -= 1 } onMounted(()=>{ increment() }) //向外部暴露数据 return {sum,increment,decrement}}<template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>
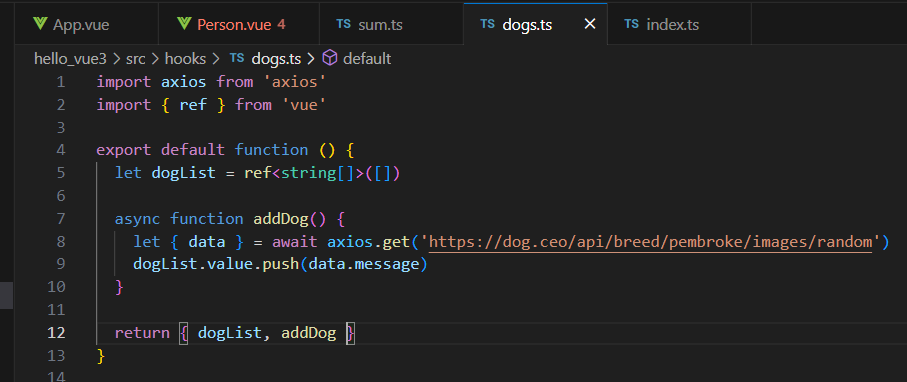
- useDog.ts中内容如下:
- import {reactive,onMounted} from 'vue'import axios,{AxiosError} from 'axios'export default function(){ let dogList = reactive([]) // 方法 async function getDog(){ try { // 发请求 let {data} = await axios.get('https://dog.ceo/api/breed/pembroke/images/random') // 维护数据 dogList.push(data.message) } catch (error) { // 处理错误 const err = error console.log(err.message) } } // 挂载钩子 onMounted(()=>{ getDog() })<template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template> //向外部暴露数据 return {dogList,getDog}}
- 组件中具体使用:
- <template>
- <h2>当前求和为:{{sum}}</h2>
- <button @click="increment">点我+1</button>
- <button @click="decrement">点我-1</button>
- <hr>
- <img v-for="(u,index) in dogList.urlList" :key="index" :src="(u as string)">
- 加载中......<br>
- <button @click="getDog">再来一只狗</button>
- </template>
4. 路由
4.1. 【对路由的理解】
4.2. 【基本切换效果】
- Vue3中要使用vue-router的最新版本,目前是4版本。
- 基本规则
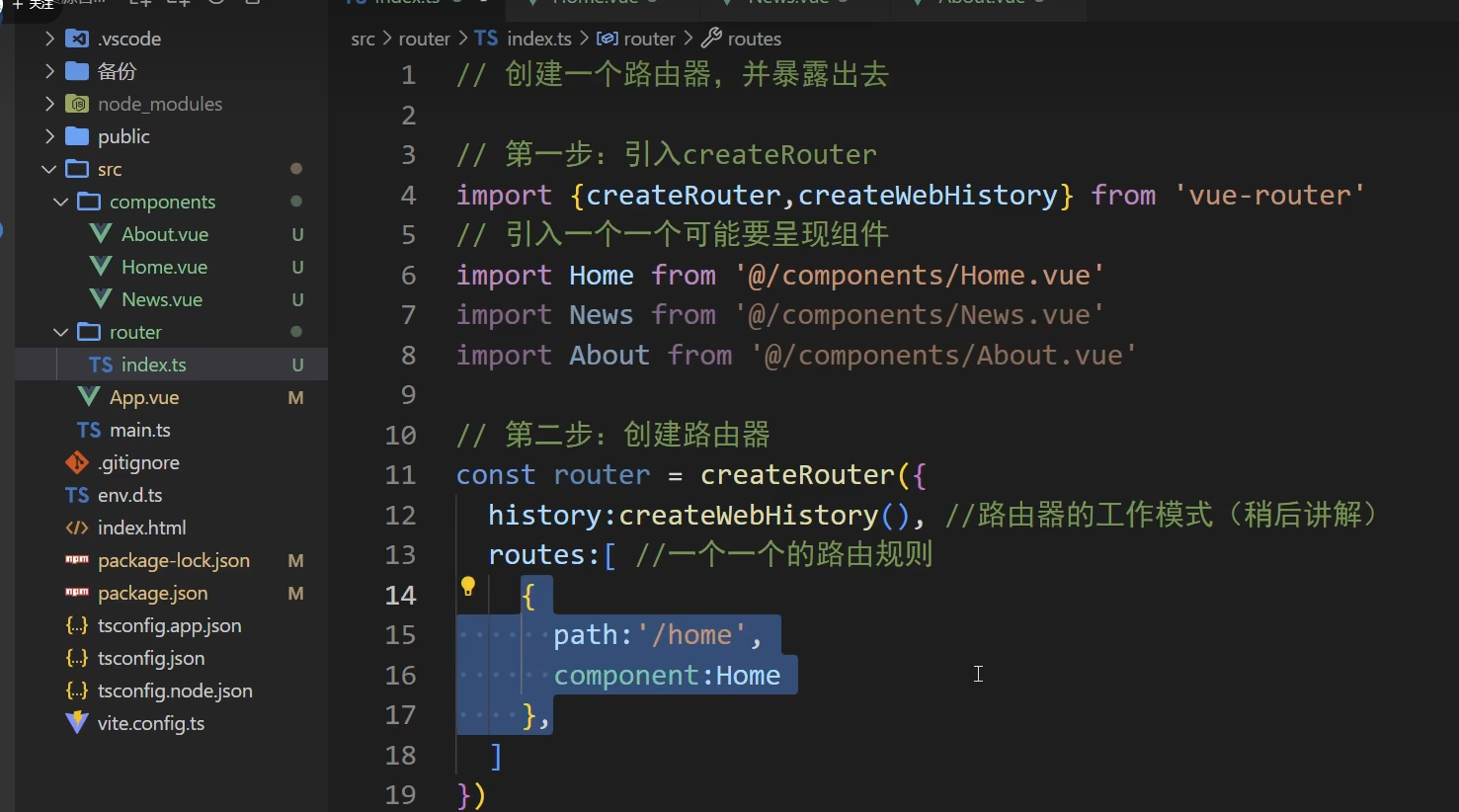
第一步,创建导航区,展示区
- 第二步创建store文件夹,导入两个api,第一个必须声明路由工作模式,第二个如何来创建路由createrouter
入口文件导入注册

- 路由配置文件代码如下:
- import {createRouter,createWebHistory} from 'vue-router'import Home from '@/pages/Home.vue'import <RouterLink replace .......>News</RouterLink> from '@/pages/<RouterLink replace .......>News</RouterLink>.vue'import About from '@/pages/About.vue'const router = createRouter({<template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>history:createWebHistory(),<template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>routes:[<template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>{<template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>path:'/home',<template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>component:Home<template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>},<template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>{<template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>path:'/about',<template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>component:About<template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>}<template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>]})export default router
- main.ts代码如下:
- import router from './router/index'
- app.use(router)
- app.mount('#app')
- App.vue代码如下 第三步
- <template>
-
- <h2 >Vue路由<Child @send-toy="toy = $event"/>
- <button @click="toy = $event">测试</button></h2>
-
-
- <RouterLink to="/home" active->首页</RouterLink>
- <RouterLink to="/news" active->新闻</RouterLink>
- <RouterLink to="/about" active->关于</RouterLink>
-
-
-
- <RouterView></RouterView>
-
-
- </template>
4.3. 【两个注意点】
- 路由组件通常存放在pages 或 views文件夹,一般组件通常存放在components文件夹。
- 通过点击导航,视觉效果上“消失” 了的路由组件,默认是被卸载掉的,需要的时候再去挂载。
4.4.【路由器工作模式】
- history模式
优点:URL更加美观,不带有#,更接近传统的网站URL。
缺点:后期项目上线,需要服务端配合处理路径问题,否则刷新会有404错误。- const router = createRouter({<template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>history:createWebHistory(), //history模式<template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>/******/})
- hash模式
优点:兼容性更好,因为不需要服务器端处理路径。
缺点:URL带有#不太美观,且在SEO优化方面相对较差。- const router = createRouter({<template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>history:createWebHashHistory(), //hash模式<template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>/******/})
4.5. 【to的两种写法】
- <router-link active- to="/home">主页</router-link>
- <router-link active- :to="{path:'/home'}">Home</router-link>
作用:可以简化路由跳转及传参(后面就讲)。
给路由规则命名:- routes:[
- {
- name:'zhuye',
- path:'/home',
- component:Home
- },
- {
- name:'xinwen',
- path:'/news',
- component:<RouterLink replace .......>News</RouterLink>,
- },
- {
- name:'guanyu',
- path:'/about',
- component:About
- }
- ]
- <router-link to="/news/detail">跳转</router-link>
- <router-link :to="{name:'guanyu'}">跳转</router-link>
- 编写<RouterLink replace .......>News</RouterLink>的子路由:Detail.vue
- 配置路由规则,使用children配置项:
- const router = createRouter({ history:createWebHistory(),<template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>routes:[<template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>{<template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>name:'zhuye',<template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>path:'/home',<template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>component:Home<template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>},<template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>{<template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>name:'xinwen',<template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>path:'/news',<template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>component:<RouterLink replace .......>News</RouterLink>,<template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>children:[<template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>{<template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>name:'xiang',<template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>path:'detail',<template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>component:Detail<template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>}<template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>]<template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>},<template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>{<template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>name:'guanyu',<template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>path:'/about',<template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>component:About<template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>}<template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>]})export default router
- 跳转路由(记得要加完整路径):
- <router-link to="/news/detail">xxxx</router-link>
- <router-link :to="{path:'/news/detail'}">xxxx</router-link>
- 记得去Home组件中预留一个
- <template>
-
- <nav >
- <RouterLink v-for="news in newsList" :key="news.id" :to="{path:'/news/detail'}">
- <template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template>{{news.name}}
- </RouterLink>
- </nav>
-
- <RouterView/>
-
-
- </template>
4.8. 【路由传参】
query参数
- 传递参数
- <template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>跳转<template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template> {{news.title}}
- 接收参数:
- import {useRoute} from 'vue-router'
- const route = useRoute()
- // 打印query参数
- console.log(route.query)
接收参数解构赋值版
但是这样有个问题,之前说过在响应式对象上面直接解构,会让他失去响应式,解决方法是一个torefs
params参数
要配置
- 传递参数
- {{news.title}}<template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template> {{news.title}}
- 接收参数:
- import {useRoute} from 'vue-router'
- const route = useRoute()
- // 打印params参数
- console.log(route.params)
备注1:传递params参数时,若使用to的对象写法,必须使用name配置项,不能用path。
备注2:传递params参数时,需要提前在规则中占位。
4.9. 【路由的props配置】
就算刚才用这个方法,但是还是复杂在标签上
作用:让路由组件更方便的收到参数(可以将路由参数作为props传给组件)
第一种,只需要在路由配置里面开启
第二种
- {<template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>name:'xiang',<template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>path:'detail/:id/:title/:content',<template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>component:Detail, // props的对象写法,作用:把对象中的每一组key-value作为props传给Detail组件 // props:{a:1,b:2,c:3}, // props的布尔值写法,作用:把收到了每一组params参数,作为props传给Detail组件 // props:true // props的函数写法,作用:把返回的对象中每一组key-value作为props传给Detail组件 props(route){ return route.query }}
- 作用:控制路由跳转时操作浏览器历史记录的模式。
- 浏览器的历史记录有两种写入方式:分别为push和replace:
- push是追加历史记录(默认值)。
- replace是替换当前记录。
- 开启replace模式:
- <RouterLink replace .......>News</RouterLink>
4.11. 【编程式导航】
路由组件的两个重要的属性:$route和$router变成了两个hooks- import {useRoute,useRouter} from 'vue-router'
- const route = useRoute()
- const router = useRouter()
- console.log(route.query)
- console.log(route.parmas)
- console.log(router.push)
- console.log(router.replace)
- 作用:将特定的路径,重新定向到已有路由。
- 具体编码:
- {
- path:'/',
- redirect:'/about'
- }
5. pinia
5.1【准备一个效果】
点击获取,就往数组增加一条土味情话
注意先从promise返回解构data,如果还想继续从data里面解构可以在后面来个:加对象,因为content是data对象里面的,甚至直接给content:给他来个别名
5.2【搭建 pinia 环境】
第一步:npm install pinia
第二步:操作src/main.ts- import { createApp } from 'vue'
- import App from './App.vue'
- /* 引入createPinia,用于创建pinia */
- import { createPinia } from 'pinia'
- /* 创建pinia */
- const pinia = createPinia()
- const app = createApp(App)
- /* 使用插件 */{}
- app.use(pinia)
- app.mount('#app')
5.3【存储+读取数据】
- 它有三个概念:state、getter、action,相当于组件中的: data、 computed 和 methods。
- 具体编码:src/store/count.ts
取名最好要跟hooks一样, 函数里面的名字最好跟文件名保持一致- // 引入defineStore用于创建store
- import {defineStore} from 'pinia'
- // 定义并暴露一个store
- export const useCountStore = defineStore('count',{
- // 动作
- actions:{},
- // 状态
- state(){
- return {
- sum:6
- }
- },
- // 计算
- getters:{}
- })
- 具体编码:src/store/talk.ts
- // 引入defineStore用于创建storeimport {defineStore} from 'pinia'// 定义并暴露一个storeexport const useTalkStore = defineStore('talk',{ // 动作 actions:{}, // 状态 state(){ return { talkList:[<template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template>{id:'yuysada01',content:'你今天有点怪,哪里怪?怪好看的!'}, <template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>{id:'yuysada02',content:'草莓、蓝莓、蔓越莓,你想我了没?'},<template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template>{id:'yuysada03',content:'心里给你留了一块地,我的死心塌地'} ] } }, // 计算 getters:{}})
- 组件中使用state中的数据
注意:单独用ref那么是.value,但是如果里面是ref定义,外面又用了一个reactive,那他就会给你拆包,也就是直接拿不用再value
得到对应store之后它是一个reactive对象,然后里面state定义的数据是放在ref里面的,那就拆包了
- <template>
- <h2>当前求和为:{{ sumStore.sum }}</h2>
- </template>
- <template>
- <ul>
- <li v-for="talk in talkStore.talkList" :key="talk.id">
- {{ talk.content }}
- </li>
- </ul>
- </template>
5.4.【修改数据】(三种方式)
- 第一种修改方式,直接修改
- 第二种修改方式:批量修改
要改的数据较多的时候- countStore.$patch({
- sum:999,
- school:'atguigu'
- })
- 第三种修改方式:借助action修改(action中可以编写一些业务逻辑)
- import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
- export const useCountStore = defineStore('count', {
- /*************/
- actions: {
- //加
- increment(value:number) {
- if (this.sum < 10) {
- <template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template>//操作countStore中的sum
- <template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template>this.sum += value
- }
- },
- //减
- decrement(value:number){
- if(this.sum > 1){
- <template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template>this.sum -= value
- }
- }
- },
- /*************/
- })
- 组件中调用action即可
- // 使用countStore
- const countStore = useCountStore()
- // 调用对应action
- countStore.incrementOdd(n.value)
5.5.【storeToRefs】
有个问题,现在模板上全部要加什么.sum都有个前缀,所以我想就是直接解构赋值拿到我要的数据,但是从响应式解构赋值又是老问题了
这样做可以得到响应式数据,但有点浪费,因为他不仅是将数据变成ref,把整个store包括里面的方法也变了
所以就可以用pinia上有个专门的方法来转他就是只变数据
- 借助storeToRefs将store中的数据转为ref对象,方便在模板中使用。
- 注意:pinia提供的storeToRefs只会将数据做转换,而Vue的toRefs会转换store中数据。
- <template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>[size=5]当前求和为:{{sum}}[/size]
- <template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>
- 概念:当state中的数据,需要经过处理后再使用时,可以使用getters配置。
- 追加getters配置。
- // 引入defineStore用于创建store
- import {defineStore} from 'pinia'
- // 定义并暴露一个store
- export const useCountStore = defineStore('count',{
- // 动作
- actions:{
- /************/
- },
- // 状态
- state(){
- return {
- sum:1,
- school:'atguigu'
- }
- },
- // 计算
- getters:{
- bigSum:(state):number => state.sum *10,
- upperSchool():string{
- return this. school.toUpperCase()
- }
- }
- })
- 组件中读取数据:
- const {increment,decrement} = countStore
- let {sum,school,bigSum,upperSchool} = storeToRefs(countStore)
5.7.【$subscribe】
通过 store 的 $subscribe() 方法侦听 state 及其变化- talkStore.$subscribe((mutate,state)=>{
- console.log('LoveTalk',mutate,state)
- localStorage.setItem('talk',JSON.stringify(talkList.value))
- })
- import {defineStore} from 'pinia'
- import axios from 'axios'
- import {nanoid} from 'nanoid'
- import {reactive} from 'vue'
- export const useTalkStore = defineStore('talk',()=>{
- // talkList就是state
- const talkList = reactive(
- JSON.parse(localStorage.getItem('talkList') as string) || []
- )
- // getATalk函数相当于action
- async function getATalk(){
- // 发请求,下面这行的写法是:连续解构赋值+重命名
- let {data:{content:title}} = await axios.get('https://api.uomg.com/api/rand.qinghua?format=json')
- // 把请求回来的字符串,包装成一个对象
- let obj = {id:nanoid(),title}
- // 放到数组中
- talkList.unshift(obj)
- }
- return {talkList,getATalk}
- })
Vue3组件通信和Vue2的区别:
- vuex换成了pinia。
- 把.sync优化到了v-model里面了。
- 把$listeners所有的东西,合并到$attrs中了。
- $children被砍掉了。
常见搭配形式:
6.1. 【props】
概述:props是使用频率最高的一种通信方式,常用与 :父 ↔ 子。
- 若 父传子:属性值是非函数。
- 若 子传父:属性值是函数。
父组件:- [size=4]父组件,[/size]
- <template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>[size=3]我的车:{{ car }}[/size]
- <template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>[size=3]儿子给的玩具:{{ toy }}[/size]
- <template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>
字传父一种是可以直接写在标签里面类似下面- [size=4]子组件[/size]
- <template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>[size=3]我的玩具:{{ toy }}[/size]
- <template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>[size=3]父给我的车:{{ car }}[/size]
- <template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>玩具给父亲
6.2. 【自定义事件】
event类型可以为event
- 原生事件:
- 事件名是特定的(click、mosueenter等等)
- 事件对象$event: 是包含事件相关信息的对象(pageX、pageY、target、keyCode)
- 自定义事件:
- 事件名是任意名称
- 事件对象$event: 是调用emit时所提供的数据,可以是任意类型!!!
- 示例:
- <Child @send-toy="toy = $event"/>
- <button @click="toy = $event">测试</button>
- //子组件中,触发事件:
- this.$emit('send-toy', 具体数据)
也可以正常走逻辑,这样来传
6.3. 【mitt】
概述:与消息订阅与发布(pubsub)功能类似,可以实现任意组件间通信。
安装mitt新建文件:src\utils\emitter.ts
都是写在这个ts文件里面,一共四个api,on是绑定,off解绑,emit触发,all全部事件可以.clear全部清空
- // 引入mitt
- import mitt from "mitt";
- // 创建emitter
- const emitter = mitt()
- /*
- // 绑定事件
- emitter.on('abc',(value)=>{
- console.log('abc事件被触发',value)
- })
- emitter.on('xyz',(value)=>{
- console.log('xyz事件被触发',value)
- })
- setInterval(() => {
- // 触发事件
- emitter.emit('abc',666)
- emitter.emit('xyz',777)
- }, 1000);
- setTimeout(() => {
- // 清理事件
- emitter.all.clear()
- }, 3000);
- */
- // 创建并暴露mitt
- export default emitter
接收数据的组件中:绑定事件、同时在销毁前解绑事件:- import emitter from "@/utils/emitter";
- import { onUnmounted } from "vue";
- // 绑定事件
- emitter.on('send-toy',(value)=>{
- console.log('send-toy事件被触发',value)
- })
- onUnmounted(()=>{
- // 解绑事件
- emitter.off('send-toy')
- })
- import emitter from "@/utils/emitter";
- function sendToy(){
- // 触发事件
- emitter.emit('send-toy',toy.value)
- }
6.4.【v-model】
- 概述:实现 父↔子 之间相互通信。
- 前序知识 —— v-model的本质
直接写$event.target.value会报错,e.target是一个对象,这个独享就可能为空,所以这里用了个断言告诉他是一个html输入的元素
- [/code]
- [*]组件标签上的v-model的本质::moldeValue + update:modelValue事件。
- 下面是本质,上面是程序员简写方式,如果v-model不写别名,默认名字传过去就是modelValue
- [code]
- <template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>
- 也可以更换value,例如改成abc
也可以改名字,注意:使用父组件这边可以直接使用简写方式,但是接受子组件这边,还是要跟着原理来,一个props绑定,一个触发自定义事件- [/code]AtguiguInput组件中:
- [code]<template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template>
- 如果value可以更换,那么就可以在组件标签上多次使用v-model
- [/code]
- [/list][size=5]6.5.【$attrs 】[/size]
- [list=1]
- [*]概述:([b]祖→孙[/b])。
- [*]具体说明:$attrs是一个对象,包含所有父组件传入的标签属性。
- [indent]注意:$attrs会自动排除props中声明的属性(可以认为声明过的 props 被子组件自己“消费”了)
- [align=center]
 [/align]
[/align] - [/indent][align=center]
 [/align]
[/align] - [/list]父组件:
- [code] [size=4]父组件[/size]
- <template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>
- <template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>[size=4]子组件[/size]
- <template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>
v-bind后面写对象,相当于一个一个绑定
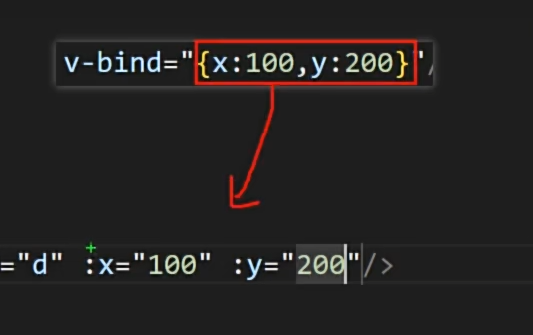
- <template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>[size=4]孙组件[/size]
- <template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>[size=3]a:{{ a }}[/size]
- <template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>[size=3]b:{{ b }}[/size]
- <template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>[size=3]c:{{ c }}[/size]
- <template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>[size=3]d:{{ d }}[/size]
- <template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>[size=3]x:{{ x }}[/size]
- <template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>[size=3]y:{{ y }}[/size]
- <template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template><template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>点我更新A<template>
- <Person :list="persons"/>
- </template>
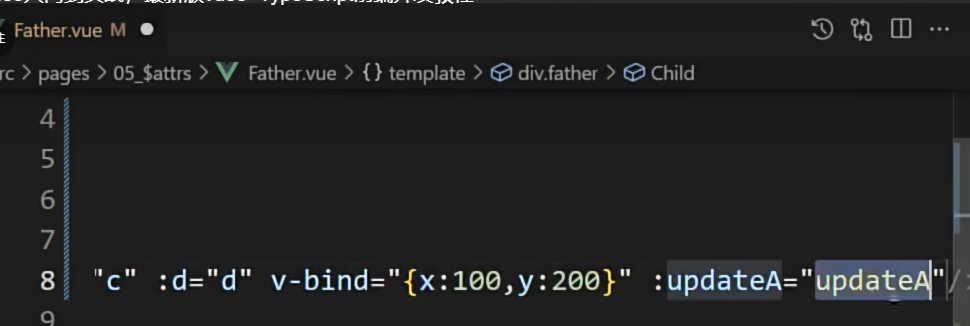

6.6. 【$refs、$parent】
- 概述:
父组件这边先给子组件绑定ref,然后给这个ref的名字调用ref函数,通过事件就可以拿到子组件传过来的
子组件
一个宏函数把数据曝光出来
`$refs就是一个api获取所有子组件
这里面放的就是一个个打了ref的子组件对象
父组件
- 原理如下:
属性说明$refs值为对象,包含所有被ref属性标识的DOM元素或组件实例。$parent值为对象,当前组件的父组件实例对象。
6.7. 【provide、inject】
- 概述:实现祖孙组件直接通信(attrs需要中间人)
- 具体使用:
- 在祖先组件中通过provide配置向后代组件提供数据
- 在后代组件中通过inject配置来声明接收数据
- 具体编码:
【第一步】父组件中,使用provide提供数据- <template>
-
- <h3>父组件</h3>
- <h4>资产:{{ money }}</h4>
- <h4>汽车:{{ car }}</h4>
- <button @click="money += 1">资产+1</button>
- <button @click="car.price += 1">汽车价格+1</button>
- <Child/>
-
- </template>
注意:子组件中不用编写任何东西,是不受到任何打扰的
提供数据时候,ref数据不用.value,前面名字,后面数据
【第二步】孙组件中使用inject配置项接受数据。- <template>
-
- <h3>我是孙组件</h3>
- <h4>资产:{{ money }}</h4>
- <h4>汽车:{{ car }}</h4>
- <button @click="updateMoney(6)">点我</button>
-
- </template>
注入数据,就用一个变量来接受就可以了,第二个参数是不写的话也可以由默认值
孙给爷传
爷组件
孙组件
6.8. 【pinia】
参考之前pinia部分的讲解
6.9. 【slot】
1. 默认插槽

- 父组件中:<template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template><template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template>
- [list]<template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template>
- [*]{{ g.name }}<template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template>
- [/list]<template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template>子组件中:<template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template><template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template><template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template> [size=4]{{ title }}[/size]
- <template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template><template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template><template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template><template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template><template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template>
2. 具名插槽
- 父组件中:<template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template><template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template><template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template>
- [list]<template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template>
- [*]{{ g.name }}<template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template>
- [/list]<template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template><template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template><template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template><template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template>更多<template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template><template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template> 子组件中:<template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template><template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template><template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template> [size=4]{{ title }}[/size]
- <template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template><template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template><template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template><template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template><template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template>
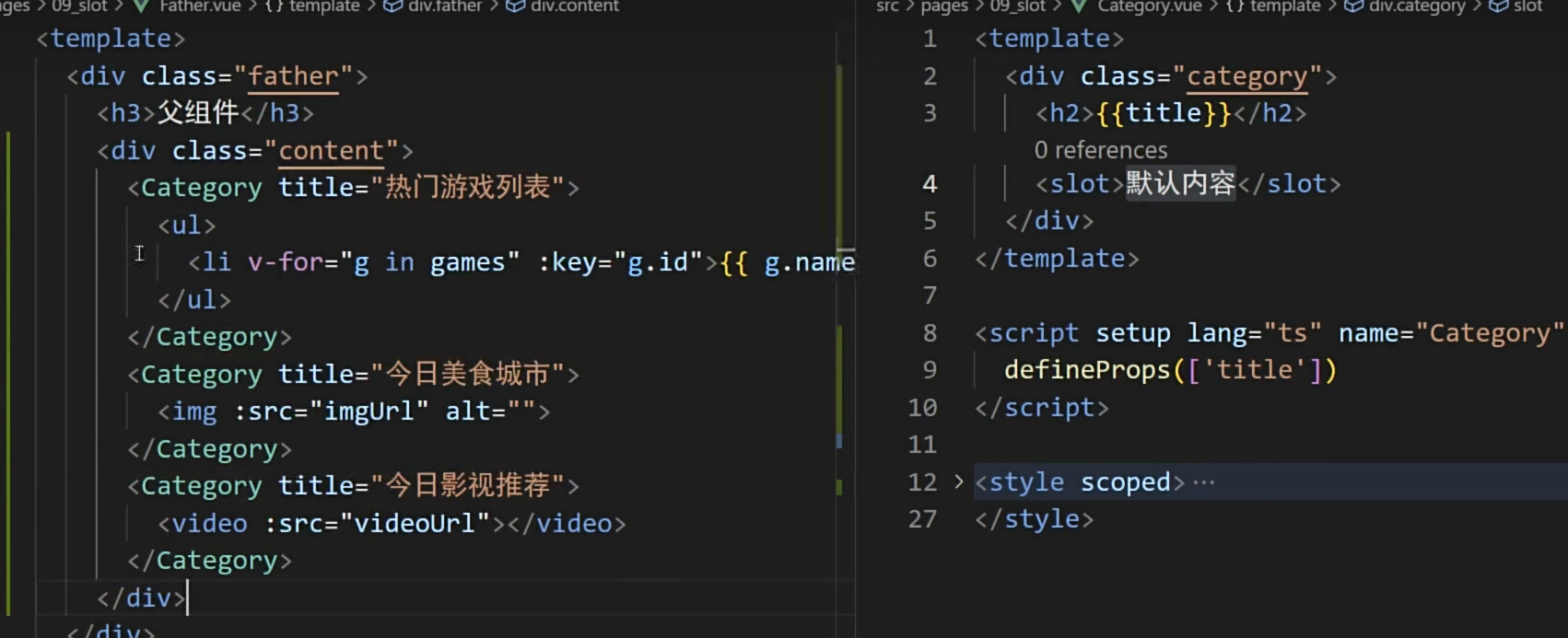
- 理解:数据在组件的自身,但根据数据生成的结构需要组件的使用者来决定。(新闻数据在<RouterLink replace .......>News</RouterLink>组件中,但使用数据所遍历出来的结构由App组件决定)
- 具体编码:
- 父组件中:
- [list]<template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template>
- [*]{{ g.name }}<template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template>
- [/list] 子组件中:<template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template><template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template><template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template>[size=5]今日游戏榜单[/size]
- <template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template><template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template><template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template>
作用于插槽也可以有名字

7. 其它 API
7.1.【shallowRef 与 shallowReactive 】
shallowRef
- 作用:创建一个响应式数据,但只对顶层属性进行响应式处理。
- 用法:
之前用ref绑定的数据随便改
如果都改为shallowref
之前单数据和整个对象还可以改,但是单独修改对象里面某个属性就不行了
此浅层就是只把第一层编程响应式,.value之后就不管了
用处就是如果有个对象很大,我不关心它里面某个值变没变化,就关心对象有没有整体被改就可以用这个
- 特点:只跟踪引用值的变化,不关心值内部的属性变化。
shallowReactive
- 作用:创建一个浅层响应式对象,只会使对象的最顶层属性变成响应式的,对象内部的嵌套属性则不会变成响应式的
- 用法:
此时修改都可以生效
如果用浅层次,那就是第二层改不了了
作用同上
- 特点:对象的顶层属性是响应式的,但嵌套对象的属性不是。
总结
通过使用 shallowRef() 和 shallowReactive() 来绕开深度响应。浅层式 API 创建的状态只在其顶层是响应式的,对所有深层的对象不会做任何处理,避免了对每一个内部属性做响应式所带来的性能成本,这使得属性的访问变得更快,可提升性能。
7.2.【readonly 与 shallowReadonly】
readonly
- 用法:
只能读不能改
也可以针对对象,里面的属性都不能改
- 特点:
- 对象的所有嵌套属性都将变为只读。
- 任何尝试修改这个对象的操作都会被阻止(在开发模式下,还会在控制台中发出警告)。
- 应用场景:
- 创建不可变的状态快照。
- 保护全局状态或配置不被修改。
shallowReadonly
- 作用:与 readonly 类似,但只作用于对象的顶层属性。
- 用法:
只对浅层次生效,也就是第二层可以改里面的属性可以改
上面不可改,下面可改
- 特点:
- 只将对象的顶层属性设置为只读,对象内部的嵌套属性仍然是可变的。
- 适用于只需保护对象顶层属性的场景。
7.3.【toRaw 与 markRaw】
toRaw
- 作用:用于获取一个响应式对象的原始对象, toRaw 返回的对象不再是响应式的,不会触发视图更新。
官网描述:这是一个可以用于临时读取而不引起代理访问/跟踪开销,或是写入而不触发更改的特殊方法。不建议保存对原始对象的持久引用,请谨慎使用。
何时使用? —— 在需要将响应式对象传递给非 Vue 的库或外部系统时,使用 toRaw 可以确保它们收到的是普通对象
使用场景,并不推荐,把一个响应对象变为不响应之后给到另一个对象,而是加入一个函数需要这个对象,要动到他,但是也不想引起改变
- 具体编码:
将一个响应式数据编程不再响应
markRaw
- 作用:标记一个对象,使其永远不会变成响应式的。
例如使用mockjs时,为了防止误把mockjs变为响应式对象,可以使用 markRaw 去标记mockjs
- 编码:
- /* markRaw */
- let citys = markRaw([
- {id:'asdda01',name:'北京'},
- {id:'asdda02',name:'上海'},
- {id:'asdda03',name:'天津'},
- {id:'asdda04',name:'重庆'}
- ])
- // 根据原始对象citys去创建响应式对象citys2 —— 创建失败,因为citys被markRaw标记了
- let citys2 = reactive(citys)
7.4.【customRef】
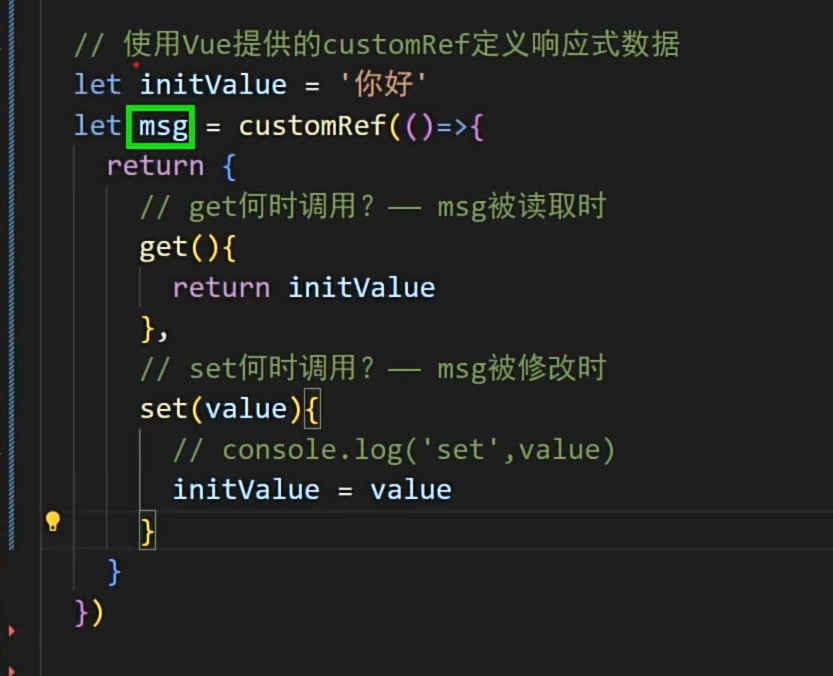
作用:创建一个自定义的ref,并对其依赖项跟踪和更新触发进行逻辑控制。
如果使用ref,那就是数据已更新,页面马上更新
如果我想实现数据更新,页面等一下在更新这个做不到

customref基本使用

需要一个初试值,但是模板用的还是ref的
但如果是这样写的,页面根本不会响应
真正写法,需要在其回调两个参数,在读取时调用前面那个函数,修改后调用后面那个函数

这两个函数很重要,面试容易问道
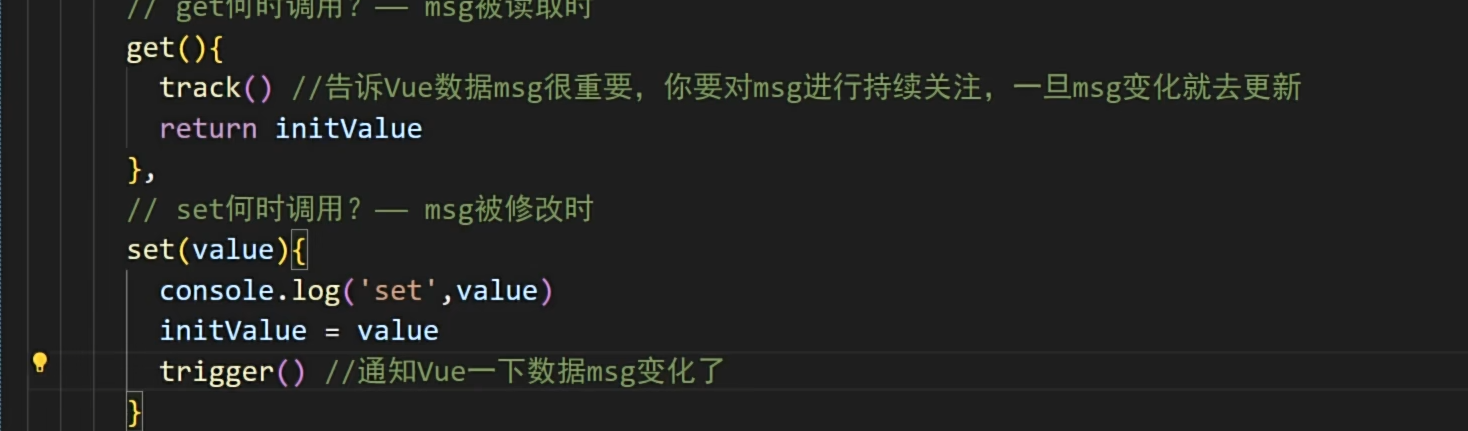
这样就可以实现刚才的效果了

自定义ref感觉就类似于defineproperty那个函数,就是对数据更新变化的时候可以去写一些自己的逻辑在里面
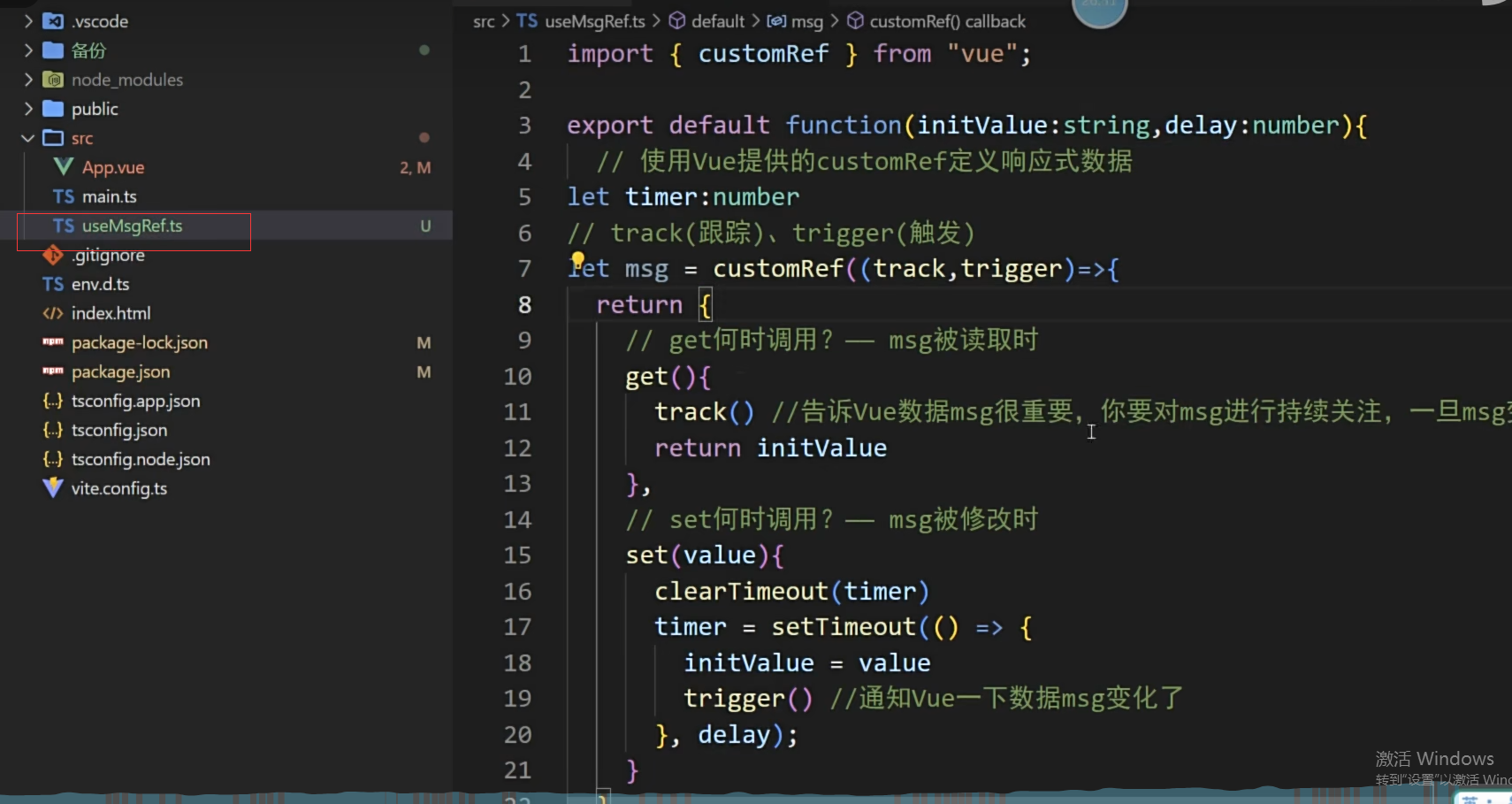
但是此时快速输入有bug,解决方式如下
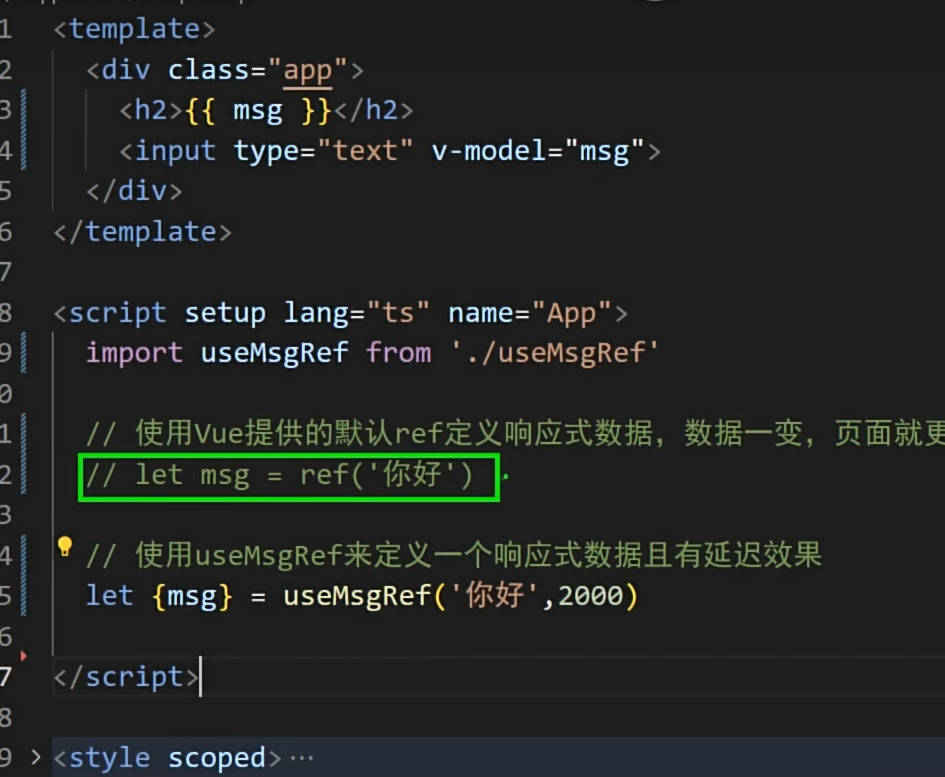
实现防抖效果(useSumRef.ts):- import {customRef } from "vue";export default function(initValue:string,delay:number){ let msg = customRef((track,trigger)=>{ let timer:number return { get(){<template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template>track() // 告诉Vue数据msg很重要,要对msg持续关注,一旦变化就更新<template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template>return initValue }, set(value){<template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template>clearTimeout(timer)<template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template>timer = setTimeout(() => {<template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template> initValue = value<template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template> trigger() //通知Vue数据msg变化了<template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template>}, delay); } } }) return {msg}}
8. Vue3新组件
8.1. 【Teleport】
- 什么是Teleport?—— Teleport 是一种能够将我们的组件html结构移动到指定位置的技术。
to里面可以为id class 标签等选择器- <template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template> [size=5]我是一个弹窗[/size]
- 我是弹窗中的一些内容
- 关闭弹窗
8.2. 【Suspense】
实验性功能
- 等待异步组件时渲染一些额外内容,让应用有更好的用户体验
比如现在子组件在发请求,如果半天出不来,那么先展示fallback插槽里面的内容,等异步回来之后在展示上面的内容
- 使用步骤:
- 异步引入组件
- 使用Suspense包裹组件,并配置好default 与 fallback
- import { defineAsyncComponent,Suspense } from "vue";
- const Child = defineAsyncComponent(()=>import('./Child.vue'))
- <template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template> [size=4]我是App组件[/size]
- <template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template><template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template><template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template><template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template><template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template><template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template><template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template> [size=4]加载中.......[/size]
- <template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template><template>
-
- <input
- type="text"
- :value="abc"
- @input="emit('update:abc',$event.target.value)"
- >
-
- </template>
所有组件都访问得到
但是会报错 vue官网关于这个属性global有解释

- app.mount
- app.unmount
- app.use
8.4.【其他】
- 过渡类名 v-enter 修改为 v-enter-from、过渡类名 v-leave 修改为 v-leave-from。
- keyCode 作为 v-on 修饰符的支持。
- v-model 指令在组件上的使用已经被重新设计,替换掉了 v-bind.sync。
- v-if 和 v-for 在同一个元素身上使用时的优先级发生了变化。(可以用在同一组件上)
- 移除了$on、$off 和 $once 实例方法。
- 移除了过滤器 filter。
- 移除了$children 实例 propert。
......
vue官网
基于vue2 vue3的改变 面试畅聊
本文由博客一文多发平台 OpenWrite 发布!
来源:程序园用户自行投稿发布,如果侵权,请联系站长删除
免责声明:如果侵犯了您的权益,请联系站长,我们会及时删除侵权内容,谢谢合作!
|