Lambda表达式其实并不陌生,他的前生就是匿名函数,所以要谈Lambda表达式,就不得不谈匿名函数,要谈匿名函数,那又要不得不谈委托。
- 何为委托
- 匿名方法
- Lambda表达式
- 扩展方法
- 泛型委托
- A Simple Lambda Demo
- Lambda表达式树
何为委托
委托非常好理解,类似于C++里面的函数指针(指向了一个方法),并且委托约束了待指向方法的签名(由返回类型和参数组成)。
- using System;
- using System.Collections.Generic;
- using System.Linq;
- using System.Text;
- namespace 委托Test
- {
- delegate bool FilterDelegate(int i);
- class Program
- {
- static void Main(string[] args)
- {
- int[] array = { 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 6, 7, 8, 9 };
- List<int> newList = MyFilter(array,FilterOdd);
- foreach (int item in newList)
- {
- Console.WriteLine(item);
- }
- Console.ReadKey();
- }
- static List<int> MyFilter(int[] array, FilterDelegate filter)
- {
- List<int> list = new List<int>();
- for (int i = 0; i < array.Length; i++)
- {
- if (filter(i))
- {
- list.Add(i);
- }
- }
- return list;
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 偶数
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="i"></param>
- /// <returns></returns>
- static bool FilterEven(int i)
- {
- return i % 2 == 0;
- }
- /// <summary>
- /// 奇数
- /// </summary>
- /// <param name="i"></param>
- /// <returns></returns>
- static bool FilterOdd(int i)
- {
- return i % 2 == 1;
- }
- }
- }
对于上面这个Demo可以看出,我需要定义了两个方法(FilterOdd,FilterEven),让我的委托变量指向这两个方法。但有时候申明方法很麻烦,还要考虑方法名称不重复,所以对于一些我们只使用一次的方法,完全没有必要单独为其申明,使用匿名方法即可(C# 2.0为程序员提供了匿名方法),大大简化了操作
匿名方法
- //例如
- delegate void Del(int x);
- ....
- Del d = delegate(int k) { /* ... */ };
- using System;
- using System.Collections.Generic;
- using System.Linq;
- using System.Text;
- namespace 委托Test
- {
- delegate bool FilterDelegate(int i);
- class Program
- {
- static void Main(string[] args)
- {
- int[] array = { 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 6, 7, 8, 9 };
- //使用匿名方法来求偶数
- List<int> newList = MyFilter(array, delegate(int i) {
- return i % 2 == 0;
- });
-
- foreach (int item in newList)
- {
- Console.WriteLine(item);
- }
- Console.ReadKey();
- }
- static List<int> MyFilter(int[] array, FilterDelegate filter)
- {
- List<int> list = new List<int>();
- for (int i = 0; i < array.Length; i++)
- {
- if (filter(i))
- {
- list.Add(i);
- }
- }
- return list;
- }
- }
- }
- C# 2.0中加入的匿名方法,简化了我们编写事件处理函数的工作,使我们不再需要单独声明一个函数来与事件绑定,只需要使用delegate关键字在线编写事件处理代码。
- 而C# 3.0则更进一步,通过Lambda表达式,我们可以一种更为简洁方式编写事件处理代码,新的Lambda事件处理代码看上去就像一个计算表达式,它使用"=>"符号来连接事件参数和事件处理代码。我可以这样写:SomeEvent += 事件参数 => 事件处理代码;
所以上面代码稍稍修改后,用Lambda表达式来替换匿名方法:- using System;
- using System.Collections.Generic;
- using System.Linq;
- using System.Text;
- namespace 委托Test
- {
- delegate bool FilterDelegate(int i);
- class Program
- {
- static void Main(string[] args)
- {
- int[] array = { 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 6, 7, 8, 9 };
- //使用Lambda表达式来求偶数
- List<int> newList = MyFilter(array, i => i % 2==0);
-
- foreach (int item in newList)
- {
- Console.WriteLine(item);
- }
- Console.ReadKey();
- }
- static List<int> MyFilter(int[] array, FilterDelegate filter)
- {
- List<int> list = new List<int>();
- for (int i = 0; i < array.Length; i++)
- {
- if (filter(i))
- {
- list.Add(i);
- }
- }
- return list;
- }
- }
- }
注意:
- 使用Lambda表达式,"=>"之前为参数列表,如果有多个参数,则不能省略括号,比如:(s,e)=>....
- 如果方法有返回值,并且处理代码只有一行,可以简写成i=>i%2==0,等价于i=>{return i%2==0},反之对于有多行的处理代码,则不能简写,必须写完整,比如:(s,e)=>{...程序代码块...}
我们再来看看System.Linq名称空间下的扩展方法有什么特征:
第一个参数为扩展方法,我已经在前一篇文章《Linq快速入门——扩展方法》里提到了,我不做具体解释了,简单来说创建扩展方法就是这四步:
- 创建一个名为MyHelper的类,约定了此类中的方法均是扩展方法。注意这个类必须是静态类(Static)
- 扩展方法必须是Static静态方法
- 第一个参数为待扩展的类型,前面标注this
- 如果MyHelper在一个类库中,记得对其添加引用并using相关名称空间
对于第二个参数:System.Func predicate),我们再来深究下。
Fun and Action
- Fun:此委托封装一个具有一个参数并返回 TResult 参数指定的类型值的方法。所以在使用 Func 委托时,不必显式定义一个封装只有一个参数的方法并且其返回类型TResut的委托。
- Action:此委托封装一个方法,该方法只有一个参数并且不返回值。所以在使用 Action 委托时,不必显式定义一个封装只有一个参数的方法(并且不能返回值)的委托。
所以再对上面的Filter进行改进:- using System;
- using System.Collections.Generic;
- using System.Linq;
- using System.Text;
- namespace 委托Test
- {
- //delegate bool FilterDelegate(int i);
- class Program
- {
- static void Main(string[] args)
- {
- int[] array = { 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 6, 7, 8, 9 };
- //使用匿名方法来求偶数
- //List<int> newList = MyFilter(array, delegate(int i) {
- // return i % 2 == 0;
- //});
- //使用Lambda表达式求偶数
- List<int> newList = MyFilter(array, i => i % 2 == 0);
-
- foreach (int item in newList)
- {
- Console.WriteLine(item);
- }
- Console.ReadKey();
- }
- //Func<int,bool>: 封装了一个具有一个int参数并且返回类型为bool类型的方法
- static List<int> MyFilter(int[] array,Func<int,bool> filter)
- {
- List<int> list = new List<int>();
- for (int i = 0; i < array.Length; i++)
- {
- if (filter(i))
- {
- list.Add(i);
- }
- }
- return list;
- }
- }
- }
- 下面Demo首先申明 Func 变量,并为其分配了一个 lambda 表达式。
- 随后将封装此方法的委托(看下面实例)传递给Enumerable.Where、Enumerable.Order、 Enumerable.Select 方法,以将字符串数组中的字符串进行处理。
- ForEach 和 ForEach 方法都采用 Action 委托作为参数。 通过使用由委托封装的方法,可以对数组或列表中的每个元素执行操作
- using System;
- using System.Collections.Generic;
- using System.Linq;
- using System.Text;
- namespace LambdaDemo
- {
- class Program
- {
- static void Main(string[] args)
- {
-
- string[] names = {"Eyes","Voodoo","Tod","Chris","Christina","Maxisim" };
- Func<string, bool> filter = s => s.Length > 5;
- Func<string, string> order = s => s;
- Func<string, string> operating = s => s.ToUpper();
- IEnumerable<string> expr = names.Where(filter).OrderByDescending(order).Select(operating);
- expr.ToList<string>().ForEach(i => Console.WriteLine(i));
- Console.ReadKey();
- }
- }
- }
- 表达式树表示树状数据结构的代码,树状结构中的每个节点都是一个表达式,例如一个方法调用或类似 x < y 的二元运算。
- 并且你可以编译和运行由表达式树所表示的代码。这样的优势就是表达式树可以在运行的时候编译运行,而且可以对lambda表达式进行动态修改。
- 若要使用 API 创建表达式树,请使用 Expression 类。 此类包含创建特定类型的表达式树节点的静态工厂方法,例如,ParameterExpression(表示一个变量或参数),ConstantExpression(表示一个常量),MethodCallExpression(表示一个方法调用)。 ParameterExpression 、MethodCallExpression、ConstantExpression 以及其他表达式特定的类型也在 System.Linq.Expressions 命名空间中定义。 这些类型派生自抽象类型 Expression。
例如将表达式(Price-5)*Count*Rebate表示成一棵二叉树可以用以下方式表达:
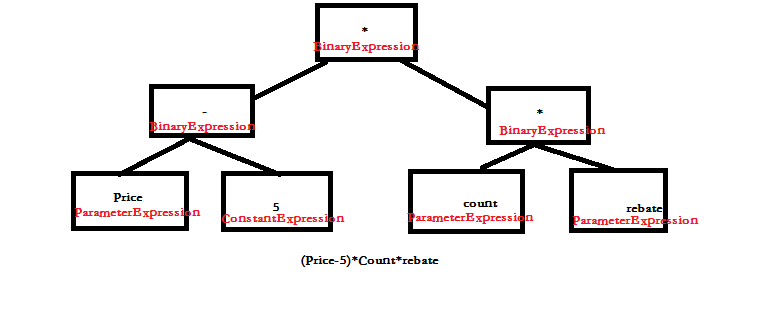
- using System;
- using System.Collections.Generic;
- using System.Linq;
- using System.Text;
- using System.Linq.Expressions;
- namespace Lambda表达式树
- {
- class Program
- {
- static void Main(string[] args)
- {
- //计算(Price-5)*Count*Rebate
- ParameterExpression paraPrice = Expression.Parameter(typeof(decimal),"price");
- ConstantExpression constant = Expression.Constant(5m,typeof(decimal));
- BinaryExpression result1 = Expression.Subtract(paraPrice, constant);
- ParameterExpression paraCount = Expression.Parameter(typeof(decimal),"count");
- ParameterExpression paraRebate = Expression.Parameter(typeof(decimal),"rebate");
- BinaryExpression result2 = Expression.Multiply(paraCount,paraRebate);
- BinaryExpression result3 = Expression.Multiply(result1,result2);
- Expression<Func<decimal, decimal, decimal, decimal>> totalPrice = Expression.Lambda<Func<decimal, decimal, decimal, decimal>>(result3,paraPrice,paraCount,paraRebate);
- Func<decimal, decimal, decimal, decimal> myFun = totalPrice.Compile();
- Console.WriteLine(myFun(125m,10m,0.5m));
- Console.ReadKey();
- }
-
- }
- }
Expression 类型提供 Compile 方法,该方法将表达式树表示的代码编译成一个可执行委托。
- using System;
- using System.Collections.Generic;
- using System.Linq;
- using System.Text;
- using System.Linq.Expressions;
- namespace ConsoleApplication2
- {
- class Program
- {
- static void Main(string[] args)
- {
-
- Expression<Func<int, int>> f1 = x => x + 1;
- //f1(1)//...错误,必须将表达式树表示的代码编译成一个可执行委托
- Func<int, int> f2 = f1.Compile();
- Console.WriteLine(f2(2));
- Console.ReadKey();
- }
- }
- }
未完,持续更新中
来源:程序园用户自行投稿发布,如果侵权,请联系站长删除
免责声明:如果侵犯了您的权益,请联系站长,我们会及时删除侵权内容,谢谢合作! |